| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1911 History of China • Timeline • Years | ||||
The following lists events that happened during 1911 in China .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1911 History of China • Timeline • Years | ||||
The following lists events that happened during 1911 in China .

Yuan Shikai was a Chinese general and statesman who served as the second provisional president of the Republic of China, head of the Beiyang government from 1912 to 1916 and Emperor of China from 1915 to 1916. A major political figure during the late Qing dynasty, he spearheaded a number of major modernisation programs and reforms and played a decisive role in securing the abdication of the Xuantong Emperor in 1912, which marked the collapse of the Qing monarchy and the end of imperial rule in China.
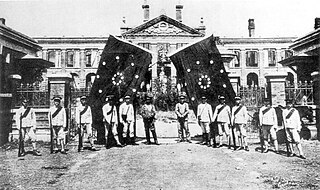
The Wuchang Uprising was an armed rebellion against the ruling Qing dynasty that took place in Wuchang, Hubei, China on 10 October 1911, beginning the Xinhai Revolution that successfully overthrew China's last imperial dynasty. It was led by elements of the New Army, influenced by revolutionary ideas from Tongmenghui. The uprising and the eventual revolution directly led to the downfall of the Qing dynasty with almost three centuries of imperial rule, and the establishment of the Republic of China (ROC), which commemorates the anniversary of the uprising's starting date of 10 October as the National Day of the Republic of China.

Empress Dowager Cixi, was a Manchu noblewoman of the Yehe Nara clan who effectively controlled the Chinese government in the late Qing dynasty as empress dowager and regent for almost 50 years, from 1861 until her death in 1908. Selected as a concubine of the Xianfeng Emperor in her adolescence, she gave birth to a son, Zaichun, in 1856. After the Xianfeng Emperor's death in 1861, his five-year-old son became the Tongzhi Emperor, and Cixi assumed the role of co-empress dowager alongside Xianfeng's widow, Empress Dowager Ci'an. Cixi ousted a group of regents appointed by the late emperor and assumed the regency along with Ci'an. Cixi then consolidated control over the dynasty when she installed her nephew as the Guangxu Emperor at the death of the Tongzhi Emperor in 1875. Ci'an continued as co-regent until her death in 1881.

The Guangxu Emperor, also known by his temple name Emperor Dezong of Qing, personal name Zaitian, was the tenth emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the ninth Qing emperor to rule over China proper. His reign was largely dominated by his maternal aunt Empress Dowager Cixi. He initiated the radical Hundred Days' Reform but was abruptly stopped when the Empress Dowager launched a coup in 1898, after which he was held under virtual house arrest until his death.

The Tongzhi Emperor, also known by his temple name Emperor Muzong of Qing, personal name Zaichun, was the ninth emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the eighth Qing emperor to rule over China proper. His reign, which effectively lasted through his adolescence, was largely overshadowed by the rule of Empress Dowager Cixi. Although he had little influence over state affairs, the events of his reign gave rise to what historians call the "Tongzhi Restoration", an unsuccessful modernization program.

The Xianfeng Emperor, also known by his temple name Emperor Wenzong of Qing, personal name Yizhu, was the eighth emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the seventh Qing emperor to rule over China proper. During his reign, the Qing dynasty experienced several wars and rebellions including the Taiping Rebellion, the Nian Rebellion, and the Second Opium War. He was the last Chinese emperor to exercise sole power.

The 1911 Revolution, also known as the Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China. The revolution was the culmination of a decade of agitation, revolts, and uprisings. Its success marked the collapse of the Chinese monarchy, the end of over two millennia of imperial rule in China and over 200 years of the Qing dynasty, and the beginning of China's early republican era.

Zaifeng, also known as Tsai Feng, Prince of Ch'ün, formally known by his title Prince Chun, was a Manchu prince and regent of the late Qing dynasty. He was a son of Yixuan, the seventh son of the Daoguang Emperor, and the father of Puyi, the Last Emperor. He served as prince regent from 1908 to 1911 during the reign of his son until the Qing dynasty was overthrown by the Xinhai Revolution in 1911.

Yikuang, formally known as Prince Qing, was a Manchu noble and politician of the Qing dynasty. He served as the first Prime Minister of the Imperial Cabinet, an office created in May 1911 to replace the Grand Council.
Yehe Nara Jingfen, of the Manchu Bordered Yellow Banner Yehe Nara clan, was the wife and empress consort of Zaitian, the Guangxu Emperor. She was empress consort of Qing from 1889 until her husband's death in 1908, after which she was honoured as Empress Dowager Longyu. She was posthumously honoured with the title Empress Xiaodingjing.

Cen Chunxuan, courtesy name Yunjie, was a Zhuang Chinese politician who lived in the late Qing dynasty and Republic of China.
Imperial Noble Consort Xianzhe, of the Manchu Bordered Blue Banner Hešeri clan, was a consort of the Tongzhi Emperor.

Late Qing reforms, commonly known as New Policies of the late Qing dynasty, or New Deal of the late Qing dynasty, simply referred to as New Policies, were a series of cultural, economic, educational, military, diplomatic, and political reforms implemented in the last decade of the Qing dynasty to keep the dynasty in power after the invasions of the great powers of the Eight Nation Alliance in league with the ten provinces of the Southeast Mutual Protection during the Boxer Rebellion.

The Soviet intervention in Mongolia was when Soviet troops fought in 1921 at the request of the communist government of the Mongolian People's Party against the anti-communist government of White Russian general Baron Ungern and occupied the entirety of Mongolia. Later there was the establishment of the Mongolian People's Republic, and the formation of modern ideas of Mongolian nationalism, which fully pulled Mongolia out of the influence of the Beiyang government of China and under the influence of Soviet Russia.

The Prime Minister of the Imperial Cabinet was a position created on 8 May 1911 during the late Qing dynasty, as part of the imperial government's unsuccessful attempts at creating a constitutional monarchy in China.
The following lists events that happened during 1909 in China.
Events in the year 1913 in China.

The Royalist Party, officially the Society for Monarchical Constitutionalism, was a monarchist political party and militant organization active in China during the early Republican Era. Supported by the Empire of Japan, its members sought to restore the Chinese monarchy under the Qing dynasty by launching insurgencies and advocating the secession of Manchuria and Inner Mongolia from the rest of China. Although it largely lacked a firm structure and consisted of loosely tied factions, the Royalist Party played a major role in Chinese politics during the 1910s.
The Imperial Edict of the Abdication of the Qing Emperor was an official decree issued by the Empress Dowager Longyu on behalf of the six-year-old Xuantong Emperor, the last emperor of the Qing dynasty of China, on 12 February 1912, as a response to the Xinhai Revolution. The revolution led to the self-declared independence of 13 southern Chinese provinces and the subsequent peace negotiation between the rest of Qing China and the collective of the southern provinces.

The Articles of Favourable Treatment of the Great Qing Emperor after His Abdication, also known simply as the Articles of Favourable Treatment, was an agreement drawn up by the Qing dynasty government and the Provisional Government of the Republic of China on the relevant protection measures after the abdication of the Qing imperial family and the Xinhai Revolution. The document is dated 26 December, 1914.