| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
| 1805 in the United States |
| 1805 in U.S. states |
|---|
| States |
| Washington, D.C. |
| List of years in the United States |
Events from the year 1805 in the United States.
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
| 1805 in the United States |
| 1805 in U.S. states |
|---|
| States |
| Washington, D.C. |
| List of years in the United States |
Events from the year 1805 in the United States.



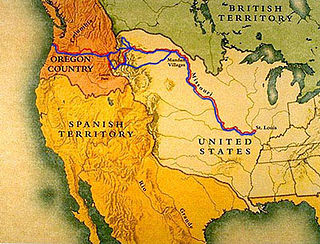
The Lewis and Clark Expedition, also known as the Corps of Discovery Expedition, was the United States expedition to cross the newly acquired western portion of the country after the Louisiana Purchase. The Corps of Discovery was a select group of U.S. Army and civilian volunteers under the command of Captain Meriwether Lewis and his close friend Second Lieutenant William Clark. Clark and 30 members set out from Camp Dubois, Illinois, on May 14, 1804, met Lewis and ten other members of the group in St. Charles, Missouri, then went up the Missouri River. The expedition crossed the Continental Divide of the Americas near the Lemhi Pass, eventually coming to the Columbia River, and the Pacific Ocean in 1805. The return voyage began on March 23, 1806, at Fort Clatsop, Oregon, and ended on September 23 of the same year.

The Territory of Louisiana or Louisiana Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 4, 1805, until June 4, 1812, when it was renamed the Missouri Territory. The territory was formed out of the District of Louisiana, which consisted of the portion of the Louisiana Purchase north of the 33rd parallel.

Meriwether Lewis was an American explorer, soldier, politician, and public administrator, best known for his role as the leader of the Lewis and Clark Expedition, also known as the Corps of Discovery, with William Clark. Their mission was to explore the territory of the Louisiana Purchase, establish trade with, and sovereignty over the natives near the Missouri River, and claim the Pacific Northwest and Oregon Country for the United States before European nations. They also collected scientific data, and information on indigenous nations. President Thomas Jefferson appointed him Governor of Upper Louisiana in 1806. He died of gunshot wounds in what was either a murder or suicide, in 1809.

William Clark was an American explorer, soldier, Indian agent, and territorial governor. A native of Virginia, he grew up in pre-statehood Kentucky before later settling in what became the state of Missouri.

Toussaint Charbonneau was a Canadian-born explorer, fur trapper and merchant who is best known for his role in the Lewis and Clark Expedition as the husband of Sacagawea.

The Corps of Discovery was a specially established unit of the United States Army which formed the nucleus of the Lewis and Clark Expedition that took place between May 1804 and September 1806. The Corps was led jointly by Captain Meriwether Lewis and Capitan William Clark. Commissioned by President Thomas Jefferson, the Corps' objectives were scientific and commercial – to study the area's plants, animal life, and geography, and to learn how the Louisiana Purchase could be exploited economically. Aside from its military composition, the Corps' additional personnel included scouts, boatmen, and civilians.

Jean Baptiste Charbonneau was a Native American-French Canadian explorer, guide, fur trapper, trader, military scout during the Mexican–American War, alcalde (mayor) of Mission San Luis Rey de Francia and a gold digger and hotel operator in Northern California. His mother was Sacagawea, a Shoshone Native who worked as a guide and interpreter for the Lewis and Clark Expedition. Charbonneau spoke French and English and learned German and Spanish during his six years in Europe from 1823 to 1829. He spoke Shoshone and other western Native American languages, which he picked up during his years of trapping and guiding.

This is the timeline of the Lewis and Clark Expedition through the American West, 1803–1806.

Fort Mandan was the name of the encampment which the Lewis and Clark Expedition built for wintering over in 1804–1805. The encampment was located on the Missouri River approximately twelve miles (19 km) from the site of present-day Washburn, North Dakota, which developed later. The precise location is not known for certain. It is believed now to be under the water of the river. A replica of the fort has been constructed near the original site.

The Great Falls of the Missouri River are a series of waterfalls on the upper Missouri River in north-central Montana in the United States. From upstream to downstream, the five falls along a 10-mile (16 km) segment of the river are:
Cameahwait was the brother of Sacagawea, and a Shoshone chief. He was the head of the first group of inhabitants of modern-day Idaho who were encountered by Europeans.

Sacagawea was a Lemhi Shoshone woman who, in her teens, helped the Lewis and Clark Expedition in achieving their chartered mission objectives by exploring the Louisiana Territory. Sacagawea traveled with the expedition thousands of miles from North Dakota to the Pacific Ocean, helping to establish cultural contacts with Native American people and contributing to the expedition's knowledge of natural history in different regions.
The first Fort Lisa (1810-1812), also known as the Fort Manuel Lisa Trading Post, Fort Manuel or Fort Mandan, was started by the notable fur trader Manuel Lisa of the Missouri Fur Company in 1809. This fort was likely where Sacagawea died; she had been the guide for the Lewis and Clark Expedition. Fort Lisa superseded Fort Raymond as the uppermost post of the Missouri Fur Company on the Missouri River. In 1812 Lisa built a replacement fort downriver near present-day North Omaha, Nebraska, which he also named Fort Lisa.

The Far Horizons is a 1955 American Western film directed by Rudolph Maté, starring Fred MacMurray, Charlton Heston, Donna Reed and Barbara Hale. It is about the early 19th century Lewis and Clark Expedition, which was sent by President Thomas Jefferson to survey the territory that the United States has just acquired in the Louisiana Purchase from France. They are able to overcome the dangers they encounter along the way with the help of a Shoshone woman named Sacagawea. This is currently the only major American motion picture on the Lewis and Clark Expedition. Many details are fictional, and the minor scene where the group reaches the Pacific Ocean reflects the low budget of the film. The film was re-released in 1962 by Citation Films Inc. as Untamed West in a double feature with Jungle Attack.
Events from the year 1804 in the United States.
Events from the year 1806 in the United States.
This is a bibliography of literature dealing with the Lewis and Clark Expedition.

The Lewis and Clark Exposition Gold dollar is a commemorative coin that was struck in 1904 and 1905 as part of the United States government's participation in the Lewis and Clark Centennial Exposition, held in the latter year in Portland, Oregon. Designed by United States Bureau of the Mint Chief Engraver Charles E. Barber, the coin did not sell well and less than a tenth of the authorized mintage of 250,000 was issued.
Otter Woman was a Shoshone woman who was the wife of Smoked Lodge. Otter Woman was likely kidnapped by the Hidatsa and purchased by Toussaint Charbonneau, who is best known as the husband of Sacagawea. At the time of Sacagawea's abduction and sale to Charbonneau, Otter Woman was already living with Charbonneau as his wife. Charbonneau and Sacagawea were to gain fame as part of the Lewis and Clark Expedition, supported by the Corps of Discovery.

Sakakawea is a monumental sized bronze sculpture created by Leonard Crunelle. It was dedicated on October 13, 1914 and stands on the grounds of the North Dakota State Capitol in Bismarck, North Dakota. A recasting was done in 2004 to place in the United States Capitol.