
Henry Middleton was a planter, public official from South Carolina. A member of the colonial legislature, during the American Revolution he attended the First Continental Congress and served as that body's president for four days in 1774 after the passage of the Continental Association, which he signed. He left the Second Continental Congress before it declared independence. Back in South Carolina, he served as president of the provincial congress and senator in the newly created state government. After his capture by the British in 1780, he accepted defeat and returned to the status of a British subject until the end of the war.

The War of 1812, called the American War of 1812 in Britain, was fought by the United States and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its own indigenous allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It began when the United States declared war on Britain on 18 June 1812. Although peace terms were agreed upon in the December 1814 Treaty of Ghent, the war did not officially end until the peace treaty was ratified by the United States Congress on 17 February 1815.

The Treaty of Ghent was the peace treaty that ended the War of 1812 between the United States and the United Kingdom. It took effect in February 1815. Both sides signed it on December 24, 1814, in the city of Ghent, United Netherlands. The treaty restored relations between the two parties to status quo ante bellum by restoring the pre-war borders of June 1812. Both sides were eager to end the war. It ended when the treaty arrived in Washington and was immediately ratified unanimously by the United States Senate and exchanged with British officials the next day.

The 13th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1813, to March 4, 1815, during the fifth and sixth years of James Madison's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1810 United States census. Both chambers had a Democratic-Republican majority. The first two sessions were held at the Capitol building while the third, convened after the Burning of Washington, took place in the First Patent Building.

George Izard was a senior officer of the United States Army who served as the second governor of Arkansas Territory from 1825 to 1828. He was elected as a member to the American Philosophical Society in 1807.

William Harris Crawford was an American politician and judge during the early 19th century. He served as US Secretary of War and US Secretary of the Treasury before he ran for US president in the 1824 election.

Charles Manigault Morris was an officer in the United States Navy and later in the Confederate States Navy. Morris was a descendant of several of the most prominent Northern and Southern families in colonial America.
HMS Anaconda was an 18-gun brig-sloop of the Royal Navy during the War of 1812. She was cruising as an American privateer until sailors from HMS Sceptre captured her in 1813. She served briefly in the Royal Navy during the later stages of the War of 1812, especially at the Battle of New Orleans, before being sold in Jamaica in 1815.
Fort Bowyer was a short-lived earthen and stockade fortification that the United States Army erected in 1813 on Mobile Point, near the mouth of Mobile Bay in what is now Baldwin County, Alabama, but then was part of the Mississippi Territory. The British twice attacked the fort during the War of 1812.
Events from the year 1783 in the United States. The American Revolution officially ended with the Treaty of Paris.
Events from the year 1804 in the United States.
Events from the year 1807 in the United States.
Events from the year 1810 in the United States.
Events from the year 1811 in the United States.
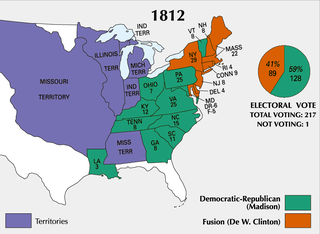
The following is a partial list of events from the year 1812 in the United States. After years of increasing tensions, the United States declares war on the British Empire, starting the War of 1812.
Events from the year 1813 in the United States.
Events from the year 1814 in the United States.
Events from the year 1816 in the United States.
Events from the year 1817 in the United States.
Henry Carroll was a Colonial lawyer and who served as secretary to Henry Clay, Congressman and a member of the Treaty of Ghent Peace Commission.








