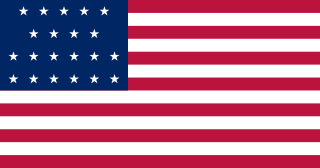
The Territory of Alabama was an organized incorporated territory of the United States. The Alabama Territory was carved from the Mississippi Territory on August 15, 1817 and lasted until December 14, 1819, when it was admitted to the Union as the twenty-second state.

The Legislative Assembly of Alberta is the deliberative assembly of the province of Alberta, Canada. It sits in the Alberta Legislature Building in Edmonton. Since 2012 the Legislative Assembly has had 87 members, elected first past the post from single-member electoral districts. Bills passed by the Legislative Assembly are given royal assent by the lieutenant governor of Alberta, as the viceregal representative of the King of Canada. The Legislative Assembly and the Lieutenant Governor together make up the unicameral Alberta Legislature.
The 1816–17 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 30, 1816 and August 14, 1817. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 15th United States Congress convened on December 1, 1817. The size of the House increased to 184 after Indiana and Mississippi achieved statehood.

Legislative elections were held in France on 25 May and 1 June 1997 to elect the 11th National Assembly of the French Fifth Republic. It was the consequence of President Jacques Chirac's decision to call the legislative election one year before the deadline.

Legislative elections were held in France on 5 and 12 June 1988, to elect the ninth National Assembly of the Fifth Republic, one month after the re-election of François Mitterrand as President of France.
The 9th Parliament of Lower Canada was in session from January 15, 1817, to February 9, 1820. Elections to the Legislative Assembly in Lower Canada had been held in March 1816. All sessions were held at Quebec City.

Parliamentary elections were held in the Republic of the Congo on 24 June 2007, with a second round initially planned for 22 July 2007, but then postponed to 5 August 2007. According to the National Commission of the Organization of the Elections (CONEL), 1,807 candidates stood in the first round for 137 seats in the National Assembly. The ruling Congolese Labour Party and parties and independent candidates allied with it won 125 seats, while two opposition parties won a combined 12 seats.
Events from the year 1885 in France.
Events from the year 1869 in France.
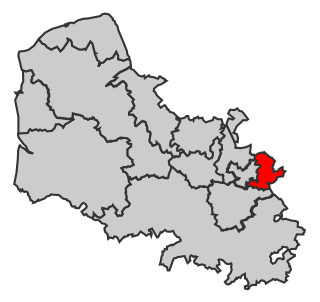
The 11th constituency of the Pas-de-Calais is a French legislative constituency in the Pas-de-Calais département. It elects one député to the National Assembly. It has been represented by Marine Le Pen since 2017.

The 1816–17 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1816 and 1817, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.

The 1st constituency of French Polynesia is a French legislative constituency in French Polynesia.

Partial legislative elections were held in France on 11 September 1819, during the Second Restoration, to choose delegates to the French Chamber of Deputies. It was the third of three elections under a new law that called for legislative elections to be held annually in one-fifth of the nation's departments.

The 6th constituency of the Bas-Rhin is a French legislative constituency in the Bas-Rhin département.

The 9th constituency of the Bas-Rhin is a French legislative constituency in the Bas-Rhin département.

The 10th constituency of Val-de-Marne is a French legislative constituency in the Val-de-Marne département.

Legislative elections were held in France on 11 and 18 June 2017 to elect the 577 members of the 15th National Assembly of the Fifth Republic. They followed the two-round presidential election won by Emmanuel Macron. The centrist party he founded in 2016, La République En Marche! (LREM), led an alliance with the centrist Democratic Movement (MoDem); together, the two parties won 350 of the 577 seats—a substantial majority—in the National Assembly, including an outright majority of 308 seats for LREM. The Socialist Party (PS) was reduced to 30 seats and the Republicans (LR) reduced to 112 seats, and both parties' allies also suffered from a marked drop in support; these were the lowest-ever scores for the centre-left and centre-right in the legislative elections. The movement founded by Jean-Luc Mélenchon, la France Insoumise (FI), secured 17 seats, enough for a group in the National Assembly. Among other major parties, the French Communist Party (PCF) secured ten and the National Front (FN) obtained eight seats. Both rounds of the legislative election were marked by record low turnout.

Legislative elections were held in France on 12 and 19 June 2022 to elect the 577 members of the 16th National Assembly of the Fifth Republic. The elections took place following the 2022 French presidential election, which was held in April 2022. They have been described as the most indecisive legislative elections since the establishment of the five-year presidential term in 2000 and subsequent change of the electoral calendar in 2002. The governing Ensemble coalition remained the largest bloc in the National Assembly but substantially lost its ruling majority, resulting in the formation of France's first minority government since 1993; for the first time since 1997, the incumbent president of France did not have an absolute majority in Parliament. As no alliance won a majority, it resulted in a hung parliament for the first time since 1988.
The Liberals was a short lived French liberal political party which was active in several elections before being absorbed into the Doctrinaires, a fellow constitutional monarchy party. Several members of the Liberals eventually went on to serve in the Movement Party and even later in the Orléanist parties. The precedent set by the party would help form modern French classical liberalism, something used in the modern centre-right Republicans party.














