
Nevis is a small island in the Caribbean Sea that forms part of the inner arc of the Leeward Islands chain of the West Indies. Nevis and the neighbouring island of Saint Kitts constitute one country: the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis. Nevis is located near the northern end of the Lesser Antilles archipelago, about 350 kilometres (220 mi) east-southeast of Puerto Rico and 80 kilometres (50 mi) west of Antigua. Its area is 93 square kilometres (36 sq mi) and the capital is Charlestown.

Saint Kitts and Nevis, officially the Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis, is an island country and microstate consisting of the two islands of Saint Kitts and Nevis, both located in the West Indies, in the Leeward Islands chain of the Lesser Antilles. With 261 square kilometers of territory, and roughly 50,000 inhabitants, it is the smallest sovereign state in the Western Hemisphere, in both area and population, as well as the world's smallest sovereign federation. The country is a Commonwealth realm, with Charles III as King and head of state. It is the only sovereign federation in the Caribbean.
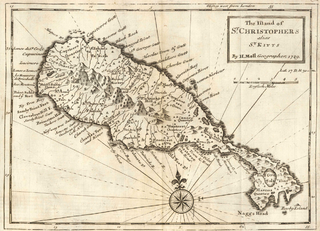
Saint Kitts and Nevis have one of the longest written histories in the Caribbean, both islands being among Spain's and England's first colonies in the archipelago. Despite being only two miles apart and quite diminutive in size, Saint Kitts and Nevis were widely recognized as being separate entities with distinct identities until they were forcibly united in the late 19th century.
The history of Anguilla runs from the beginning of human habitation, probably via settlement from South America, through its colonization by the English in the early modern period, to the present day. Following a series of rebellions and a short-lived period as an independent republic during the 1960s, Anguilla has been a separate British overseas territory since 1980.

Robert Llewellyn Bradshaw was the first Premier of Saint Kitts and Nevis, and previously served as Chief Minister, legislator, and labour activist.

Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla was a British colony in the West Indies from 1882 to 1983, consisting of the islands of Anguilla, Nevis, and Saint Christopher. From 1882 to 1951, and again from 1980, the colony was known simply as Saint Christopher and Nevis. Saint Christopher and Nevis gained independence in 1983 as the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis, while Anguilla would remain a British overseas territory.

The National Assembly and the King of Saint Christopher and Nevis jointly make up the legislature of Saint Kitts and Nevis.
West Indies Associated States was the collective name for a number of islands in the Eastern Caribbean whose status changed from being British colonies to states in free association with the United Kingdom in 1967. These states were Antigua, Dominica, Grenada, Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla, Saint Lucia, and Saint Vincent.

Simeon Daniel was the first Premier of Nevis.

The Republic of Anguilla was a short-lived, unrecognised independent state on the island of Anguilla. It lasted from 11 July 1967 until 19 March 1969, when British control was re-established.

General elections were held in Saint Kitts-Nevis-Anguilla on 6 October 1952, the country's first elections held with universal suffrage. The Workers' League won seven of the eight elected seats.

General elections were held in Saint Kitts-Nevis-Anguilla on 16 November 1961. The result was a victory for the Saint Kitts-Nevis-Anguilla Labour Party, which won seven of the ten elected seats.

The Constitution of Saint Kitts and Nevis was adopted on 23 June 1983 and took effect when the country became independent on 19 September 1983. It consists of 11 chapters and various schedules, which establish the rights, responsibilities and definition of the citizens of the federation. It also provides the form and structure of government, and enumerates the powers of the different branches of government. Its treatment of the island of Nevis is rather unusual among federated nations.

General elections were held in Saint Kitts-Nevis-Anguilla on 16 September 1940. The Workers' League won all the elected seats.

General elections were held in Saint Kitts-Nevis-Anguilla on 20 September 1943. The Workers' League won all the elected seats, defeating an alliance of merchants and planters nominated by the Agricultural and Commercial Society.

General elections were held in Saint Kitts-Nevis-Anguilla on 30 July 1946. The Workers' League won all the elected seats, with no party running against them.

General elections were planned to be held in Anguilla on 25 October 1967 following the Anguillian Revolution in May. However, only five candidates stood for the five seats, with all elected unopposed.

General elections were held in Anguilla on 30 July 1968.

The primary law governing Saint Kitts and Nevis nationality regulations is the Saint Christopher and Nevis Citizenship Act, which came into force on 28 February 1984.

Snap general elections were held in Saint Kitts and Nevis on 5 August 2022, following the decision of incumbent prime minister Timothy Harris to dissolve the parliament on 11 May. Snap elections are constitutionally required within ninety days following the dissolution of parliament.










