 |
|---|
Parliamentary elections were held in Somalia on 30 March 1964. The result was a victory for the Somali Youth League (SYL), which won 69 of the 123 seats. [1] [2]
 |
|---|
Parliamentary elections were held in Somalia on 30 March 1964. The result was a victory for the Somali Youth League (SYL), which won 69 of the 123 seats. [1] [2]
The elections were the first to be held since the merger of British Somaliland and Italian Somaliland created Somalia in 1960. After the union, the two territories' parliaments had merged, retaining the same number of seats as in the 1960 elections in British Somaliland and the 1959 elections in Italian Somaliland.
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Somali Youth League | 472,296 | 51.67 | 69 | −14 | |
| Somali National Congress | 186,208 | 20.37 | 22 | New | |
| Somali Democratic Union | 95,707 | 10.47 | 15 | New | |
| Somali Independent Constitutional Party | 80,173 | 8.77 | 9 | +4 | |
| United Somali Party | 7,552 | 0.83 | 1 | −11 | |
| Liberal Party of Somali Youth | 6,766 | 0.74 | 1 | New | |
| Somali National League | 4,354 | 0.48 | 1 | −19 | |
| Somali African National Union | 3,930 | 0.43 | 1 | New | |
| 13 other parties | 57,083 | 6.24 | 4 | New | |
| Total | 914,069 | 100.00 | 123 | 0 | |
| Source: Nohlen et al. | |||||
Djibouti is a country in the Horn of Africa bordered by Somalia to the southeast, Eritrea and the Red Sea to the north and northwest, Ethiopia to the west and south, and the Gulf of Aden to the east.
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia and formerly known as the Somali Democratic Republic, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. The country was an important centre for commerce with the rest of the ancient world, and according to most scholars, it is among the most probable locations of the fabled ancient Land of Punt. During the Middle Ages, several powerful Somali states and port towns dominated the regional trade, the Mogadishu Sultanate and Ajuran Sultanate both centered around the port town Mogadishu, but also the port towns of Barawe and Merca.

Somaliland, officially the Republic of Somaliland, is an unrecognised sovereign state in the Horn of Africa, recognised internationally as de jure part of Somalia. It is located in the southern coast of the Gulf of Aden and bordered by Djibouti to the northwest, Ethiopia to the south and west, and Somalia to the east. Its claimed territory has an area of 176,120 square kilometres (68,000 sq mi), with approximately 5.7 million residents as of 2021. The capital and largest city is Hargeisa. The government of Somaliland regards itself as the successor state to British Somaliland, which, as the briefly independent State of Somaliland, united from 1960 to 1991 with the Trust Territory of Somaliland to form the Somali Republic.

British Somaliland, officially the Somaliland Protectorate, was a crown colony and protectorate of the United Kingdom in modern Somaliland. During its existence, the territory was bordered by Italian Somalia, French Somali Coast and Abyssinia. From 1940 to 1941, it was occupied by the Italians and was part of Italian East Africa.

The flag of Somalia, also known as the Somali flag, was adopted on October 12, 1954, and was designed by Mohammed Awale Liban. The flag was initially used within the Trust Territory of Somaliland before being adopted by the short-lived State of Somaliland and the Somali Republic. It is an ethnic flag for the Somali people; the flag's five-pointed star represents the five regions in which Somalis reside.

Italian Somaliland was a protectorate and later colony of the Kingdom of Italy in present-day Somalia. Ruled in the 19th century by the Somali Sultanates of Hobyo and Majeerteen in the north, and in the south by political entities such as the Hiraab Imamate and Geledi Sultanate.

Las Anod is the administrative capital of the Sool region of Somaliland.
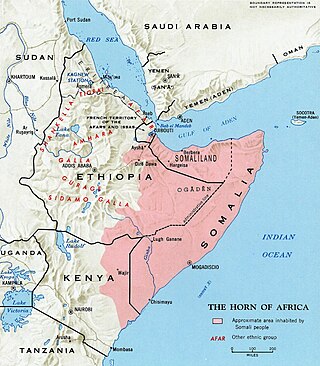
Greater Somalia is a concept to unite all ethnic Somalis comprising the regions in or near the Horn of Africa in which ethnic Somalis live and have historically inhabited. The territory historically encompassed British Jubaland Province, British Somaliland, Italian Somaliland, parts of French Somaliland, the Somali Region in Ethiopia, the Northern Frontier District in Kenya, and the intra-46th meridian east territories. At the present, it encompasses Somalia proper, Jubaland, southern and eastern Djibouti, the Somali Region and Dire Dawa in Ethiopia, and the Garissa, Wajir and Mandera Counties in Kenya.

Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke, also known as Abdirashid Shermarke, was Prime Minister of Somali Republic from 12 July 1960, to 14 June 1964, and President of Somali Republic from 6 July 1967, until his assassination on October 15, 1969. He was the father of Somali Prime Minister Omar Sharmarke.

The Somali Republic was the name given to the newly independent state of Somalia, following the unification of the Trust Territory of Somaliland and the State of Somaliland. A government was formed by Abdullahi Issa Mohamud and Muhammad Haji Ibrahim Egal and other members of the trusteeship and protectorate administrations, with Haji Bashir Ismail Yusuf as President of the Somali National Assembly and Aden Abdullah Osman Daar as President of the Somali Republic. On 22 July 1960, Daar appointed Abdirashid Ali Shermarke as Prime Minister. On 20 July 1961 and through a popular referendum, Somalia ratified a new constitution, which was first drafted in 1960. The new constitution was rejected by Somaliland.

The history of Somaliland, a country in the eastern Horn of Africa bordered by the Gulf of Aden, and the East African land mass, begins with human habitation tens of thousands of years ago. It includes the civilizations of Punt, the Ottomans, and colonial influences from Europe and the Middle East.
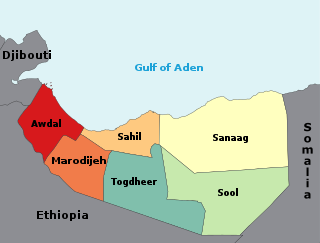
The regions of Somaliland is divided into six administrative regions, Awdal, Sahil, Maroodi-Jeeh, Togdheer, Sanaag and Sool. These are in turn subdivided into twenty-two districts. Regions of Somaliland are the primary geographical divisions through which Somaliland is administered. A distinction is made between districts of grades A, B, C and D, with the classification being based on population, area, economy and production.

The State of Somaliland was a short-lived independent country in the territory of present-day unilaterally declared Republic of Somaliland. It existed on the territory of former British Somaliland for five days between 26 June 1960 and 1 July 1960, when it merged with the formerly Italian administered Trust Territory of Somaliland to form the Somali Republic.

The Somali Youth League, initially known as the Somali Youth Club (SYC), was the first political party in Somalia.

The Trust Territory of Somaliland, officially the "Trust Territory of Somaliland under Italian administration", was a United Nations Trust Territory situated in present-day Somalia. Its capital was Mogadishu and was administered by Italy from 1950 to 1960, following the dissolution of the former British Military Administration. It gained independence in 1960.

The following is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Somalia. From the late 1800s to 1960, northwestern present-day Somalia was administered as British Somaliland, while the northeastern, central and southern part of the country were concurrently administered as Italian Somaliland. In 1960, the two territories were unified as the Somali Republic.

Parliamentary elections were held in British Somaliland on 17 February 1960. The result was a victory for the Somali National League (SNL), which won 20 of the 33 seats in the Legislative Council.

Somali nationality law is regulated by the Constitution of Somalia, as amended; the Somali Citizenship Law, and its revisions; and various international agreements to which the country is a signatory. These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a national of Somalia. The legal means to acquire nationality, formal legal membership in a nation, differ from the domestic relationship of rights and obligations between a national and the nation, known as citizenship. Nationality describes the relationship of an individual to the nation under international law, whereas citizenship is the domestic relationship of an individual and the state. Somali nationality is typically obtained under the principle of jus soli, i.e. by birth in Somalia, or jus sanguinis, born to parents with Somali nationality. It can be granted to persons with an affiliation to the country, or to a permanent resident who has lived in the country for a given period of time through grant (naturalization).

Somaliland a self-declared independent country in the Horn of Africa in which inhabitants were initially governed by various kinship networks. Upon contact with Europeans, treaties were signed in the area to secure rights to trade in the territory in exchange for protection of clans from rivals. Britain formally extended a protectorate over British Somaliland in 1898. Inhabitants of Somaliland were British Protected Persons from that date until they gained their independence in 1960 and joined in the union of their state with Italian Somaliland to form the Somali Republic. Inhabitants derive their nationality from Somali law. The legal means to acquire nationality, formal legal membership in a sovereign nation, differ from the domestic relationship of rights and obligations between a citizen within its nation, known as citizenship. Nationality describes the relationship of an individual to the nation under international law, whereas citizenship is the domestic relationship of an individual within the state. As the African Union, United Nations, and no independent nation has recognized its national sovereignty, Somaliland's inhabitants are Somali nationals, but since declaring its independence in 1991, it has de facto authority to control internal affairs and citizenship within its territory.

The Government of Somaliland (JSL) is the central government of Somaliland. The Government of Somaliland consists of legislative, executive, and judicial branches, each of which functions independently from the others. The Government runs under the framework established by the Constitution of Somaliland, adopted in 2001. It is a unitary state. The seat of the government is located in Hargeisa, the capital of Somaliland.