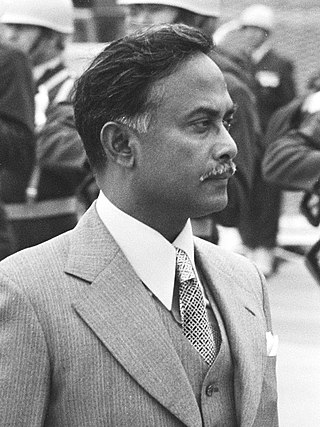Politics of Bangladesh takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the Prime Minister of Bangladesh is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and parliament. The Constitution of Bangladesh was written in 1972 and has undergone seventeen amendments.
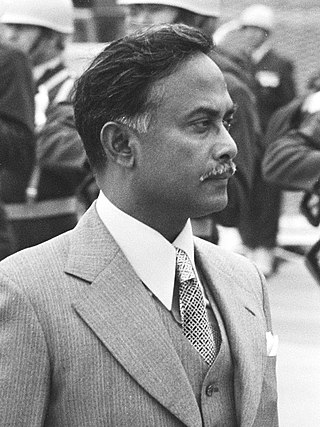
Ziaur Rahman was a Bangladeshi military officer and politician who served as the President of Bangladesh from 1977 until his assassination. He was the founder of the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) and served as its chairman until his assassination. He previously served as the second chief of army staff from 1975 to 1978 with a minor break.

The Bangladesh Nationalist Party is a major political party in Bangladesh. Founded on 1 September 1978 by the late Bangladeshi president Ziaur Rahman, with a view of uniting people with a nationalist ideology, BNP later came out as one of the two most dominant parties in Bangladesh, along with its archrival Awami League. Initially being a big tent centrist party, it moved towards more right-wing politics later.

The Bangladesh Awami League, often simply called the Awami League or AL, is one of the major political parties in Bangladesh. The oldest existing political party in the country, Awami League successfully lead Bangladesh to the independence. One of the two most dominant parties in the country, along with its archrival Bangladesh Nationalist Party, it has been the ruling party since 2009, and has since been described as authoritarian.

Hussain Muhammad Ershad was a Bangladeshi military officer and politician who served as the president of Bangladesh from 1983 to 1990, heading a military dictatorship.

Bangladesh elects on national level a legislature with one house or chamber. The unicameral Jatiyo Sangshad, meaning national parliament, has 350 members of which 300 members are directly elected through a national election for a five-year term in single-seat constituencies while 50 memberships are reserved for the women who are selected by the ruling party or coalition. The Prime Minister is the head of the government. The president who is the head of the state is elected by the National Parliament. The president of Bangladesh is a ceremonial post and does not exercise any control over the running of the state.

The Jatiya Party is a centre-right, conservative, nationalist political party in Bangladesh and is currently the main opposition in the Jatiya Sangsad, against the Awami League. The current chairman of the party is Begum Rowshan Ershad. On 3 January 2019, the party announced its decision to join the Bangladesh Awami League-led Grand Alliance after having been in opposition for the previous parliamentary term. However, the party backtracked the next day and announced that it intended to remain part of the opposition. Currently, it holds Rangpur out of Bangladesh's 12 city corporations.
The Bangladesh Krishak Sramik Awami League (BaKSAL) (Bengali: বাংলাদেশ কৃষক শ্রমিক আওয়ামী লীগ, English: Bangladesh Worker-Peasant's People's League; বাকশাল) was a political front and dictatorship comprising the Bangladesh Awami League, the Communist Party of Bangladesh, the National Awami Party (Muzaffar) and Bangladesh Jatiya League.

Ziaur Rahman, the sixth president of Bangladesh, was assassinated by a faction of officers of Bangladesh Army, on 30 May 1981, in the south-eastern port city of Chittagong. Rahman went to Chittagong to arbitrate in a clash between the local leaders of his political party, the Bangladesh Nationalist Party. On the night of 30 May, a group of officers commandeered the Chittagong Circuit House, a government residence where Rahman was staying, shooting him and several others.
The Jatiyatabadi Ganatantrik Dal was a 1977-78 coalition of the political supporters of the then-President of Bangladesh Ziaur Rahman. The convenor of the party was Vice President Justice Abdus Sattar. It was the predecessor of the modern Bangladesh Nationalist Party that was formed on 1 September 1978.

The Jatiya Samajtantrik Dal is a political party in Bangladesh. The party was founded by Serajul Alam Khan. The party was very dominant during 1972–1975 Bangladesh insurgency.

General elections were held in Bangladesh on 7 May 1986. A total of 1,527 candidates contested the election. The result was a victory for the Jatiya Party, which won 153 of the 300 directly elected seats. Voter turnout was 61%. Bangladesh Nationalist Party, the winner of the previous elections, boycotted the election.

The history of Bangladesh (1971–present) refers to the period after the independence of Bangladesh from Pakistan.
Hajee Mohammad Danesh was a Bangladeshi politician and communist activist born in the British India.

Presidential elections were held in Bangladesh on 15 November 1981. The result was a victory for the incumbent acting President Abdus Sattar of the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP), who received 65.5% of the vote, beating his principal challenger Kamal Hossain of the Awami League. Voter turnout was 56.5%.

The 1990 Mass Uprising, popularly known as '90's Anti-Authoritarian Movement, was a democratic movement that took place on 4 December and led to the fall of General Hussain Muhammad Ershad in Bangladesh. The uprising was the result of a series of popular protests that started from 10 October 1990 to topple General Ershad who came to power in 1982 by imposing martial law and replaced a democratically elected President through a bloodless coup.
1972–1975 Bangladesh insurgency refers to the period after the independence of Bangladesh when left-wing Communist insurgents, particularly the Gonobahini fought against the government of the Prime Minister Sheikh Mujibur Rahman.
Sheikh Shawkat Hossain Nilu was a Bangladeshi politician and chairman of the National People's Party.