| |||||
| Centuries: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decades: | |||||
| See also: | Other events of 2011 Years in North Korea Timeline of Korean history 2011 in South Korea | ||||
Events in the year 2011 in North Korea .
| |||||
| Centuries: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decades: | |||||
| See also: | Other events of 2011 Years in North Korea Timeline of Korean history 2011 in South Korea | ||||
Events in the year 2011 in North Korea .

Kim Jong Il was a North Korean politician who was the second supreme leader of North Korea. He led North Korea from the death of his father Kim Il Sung in 1994 until his own death in 2011, when he was succeeded by his son, Kim Jong Un. Afterwards, Kim Jong Il was declared Eternal General Secretary of the WPK.

Kim Jong Un is a North Korean politician who has been supreme leader of North Korea since 2011 and the leader of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK) since 2012. He is the third son of Kim Jong Il, who was North Korea's second supreme leader from 1994 until his death in 2011, and Ko Yong Hui. He is a grandson of Kim Il Sung, who was the founder and first supreme leader of North Korea from its establishment in 1948 until his death in 1994.
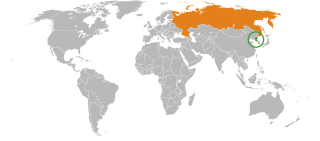
North Korea–Russia relations are the bilateral relations between Russia and North Korea. The Soviet Union was the first to recognize North Korea on October 12, 1948, shortly after the proclamation, as the sole legitimate authority in all of Korea. The Soviet Union supported North Korea during the Korean War. North Korea was founded as part of the Communist bloc, and received major Soviet military and political support. The comprehensive personality cult around North Korea's ruling family was heavily influenced by Stalinism. China and the Soviet Union competed for influence in North Korea during the Sino-Soviet split in the 1960s, as North Korea tried to maintain good relations with both countries.

Jang Song-thaek was a North Korean politician. He was married to Kim Kyong-hui, the only daughter of North Korean premier Kim Il Sung and his first wife Kim Jong-suk, and only sister of North Korean general secretary Kim Jong Il. He was therefore the uncle of the current leader of North Korea, Kim Jong Un.

Inter-Korean summits are meetings between the leaders of North and South Korea. To date, there have been five such meetings so far, three of them being in Pyongyang, with another two in Panmunjom. The importance of these summits lies in the lack of formal communication between North and South Korea, which makes discussing political and economic issues difficult. The summits' agendas have included topics such as the ending of the 1950-53 war, the massive deployment of troops at the DMZ, the development of nuclear weapons by North Korea, and human rights issues.

The title of supreme leader of North Korea generally means the de facto paramount leader of the Workers' Party of Korea, the state and the Korean People's Army. Most of the North Korea's leaders, who are called Supreme Leader, were not called this until after their death, going by other names like "Great Leader" and "Dear Leader" during their lifetimes. The leaders of North Korea also go by many other names and titles, see List of Kim Il Sung's titles, List of Kim Jong Il's titles and List of Kim Jong Un's titles.
Kim Kyong-hui is the aunt of current North Korean leader, Kim Jong Un. She is the daughter of the founding North Korean leader Kim Il Sung and the sister of the late leader Kim Jong Il. She currently serves as Secretary for Organization of the Workers' Party of Korea. An important member of Kim Jong Il's inner circle of trusted friends and advisors, she was director of the WPK Light Industry Department from 1988 to 2012. She was married to Jang Song-thaek, who was executed in December 2013 in Pyongyang, after being charged with treason and corruption.
Kim Jong-gak is a Korean People's Army (KPA) official. He was a member of the Politburo of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK). He served as Minister of Defence briefly in 2012, and Director of the General Political Bureau of the KPA in 2018.

The death of Kim Jong Il was reported by North Korean state television news on 19 December 2011. The presenter Ri Chun-hee announced that he had died on 17 December at 8:30 am of a massive heart attack while travelling by train to an area outside Pyongyang. Reportedly, he had received medical treatment for cardiac and cerebrovascular diseases, and during the trip, Kim was said to have had an "advanced acute myocardial infarction, complicated with a serious heart shock". However, it was reported in December 2012 by South Korean media that the heart attack had instead occurred in a fit of rage over construction faults in a crucial power plant project at Huichon in Chagang Province.

Kim Il Sung died of a sudden heart attack on the early morning of 8 July 1994 at age 82. North Korea's government did not report the death for more than 34 hours after it occurred. An official mourning period was declared from 8–17 July, during which the national flag was flown at half mast throughout the country, and all forms of amusement and dancing were prohibited.

Choe Ryong-hae is a North Korean politician and military officer who currently serves as Chairman of the Standing Committee of the Supreme People's Assembly and First Vice President of the State Affairs Commission, holding both positions since April 2019. Due to holding the first office, he was considered the head of state of North Korea before the country's constitution was amended to transfer this position to the President of the State Affairs Commission, Kim Jong Un. He is also a member of the Presidium of the Politburo and Vice Chairman of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK). He also served as Supreme Leader Kim Jong Un's military second-in-command, currently being third top-ranking official in North Korea after Kim Jong Un and premier Kim Tok-hun.

Hyon Song-wol is a North Korean singer, band leader, and politician. She is the leader of the Moranbong Band and of the Samjiyon Orchestra. She was formerly a featured vocalist for the Pochonbo Electronic Ensemble in the early 2000s, a pop group which found fame in North Korea in the late 1980s and 1990s. She has been a member in the Central Committee of the Workers' Party of Korea since 2017.
Hyon Yong-chol was a North Korean general and Workers' Party of Korea (WPK) politician. He served as Minister of Defence from 2014 to 2015. In 2015, he was reportedly removed from his post.

Kim Yo Jong is a North Korean politician and diplomat. She is the Deputy Department Director of the Publicity and Information Department of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK). Since September 2021, she has been a member of State Affairs Commission of North Korea, the only woman on the panel.
General Choe Pu-il is a North Korean politician who served as head of North Korea's Ministry of People's Security.

The Kim family, also known as the Kim dynasty or the Mount Paektu bloodline in the ideological discourse of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK), is a three-generation lineage of North Korean leadership, descending from the country's founder and first leader, Kim Il Sung. The patriarch came to rule the north in 1948, after the end of Japanese rule split the region in 1945. He began the Korean War in 1950, in a failed attempt to reunify the Korean Peninsula. In the 1980s, Kim Il Sung developed a cult of personality closely tied to the North Korean state philosophy of Juche. Following his death in 1994, Kim Il Sung's role as supreme leader was passed on to his son Kim Jong Il, and then to his grandson Kim Jong Un. All three men have served as leaders of the WPK and have exercised absolute control over North Korea since the state's establishment in 1948.
The following lists events that happened in 2012 in North Korea.
2018 in North Korea was marked by attempts by the government to develop its international relationships, particularly in regards to South Korea. In February, North Korean athletes marched alongside their South Korean counterparts under the Korean Unification Flag at the 2018 Seoul Olympic Games. North Korea's Kim Jong-Un met with South Korea's Moon Jae-in three times during the year. Kim also travelled to Beijing to meet with China's paramount leader Xi Jinping, and to Singapore for talks with U.S. President Donald Trump.
Choe Ik-gyu, also known under the pseudonym Choe Sang-gun, is a North Korean film director, propagandist, and politician.

The Propaganda and Agitation Department, officially translated as the Publicity and Information Department, is a department of the Central Committee of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK) tasked with coordinating the creation and dissemination of propaganda in North Korea. It is the highest propaganda organization in the country.