| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 2011 List of years in Georgia (country) | ||||
Events in the year 2011 in Georgia .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 2011 List of years in Georgia (country) | ||||
Events in the year 2011 in Georgia .
In music: Georgia in the Eurovision Song Contest 2011.
Football (soccer) competitions: Umaglesi Liga, Georgian Cup.

Georgia is a country located in Eastern Europe and West Asia. It is part of the Caucasus region, bounded by the Black Sea to the west, Russia to the north and northeast, Turkey to the southwest, Armenia to the south, and by Azerbaijan to the southeast. The country covers an area of 69,700 square kilometres (26,900 sq mi), and has a population of 3.7 million people. Tbilisi is its capital and largest city, home to roughly a third of the Georgian population.

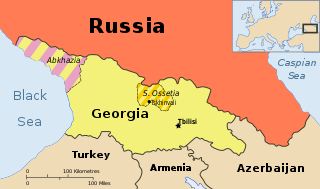
South Ossetia, officially the Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania, is a partially recognised landlocked state in the South Caucasus. It has an officially stated population of just over 56,500 people (2022), who live in an area of 3,900 square kilometres (1,500 sq mi), with 33,000 living in the capital city, Tskhinvali.

Mikheil Saakashvili is a Georgian and Ukrainian politician and jurist. He was the third president of Georgia for two consecutive terms from 25 January 2004 to 17 November 2013. From May 2015 until November 2016, Saakashvili was the governor of Ukraine's Odesa Oblast. He is the founder and former chairman of the United National Movement party. Saakashvili heads the executive committee of Ukraine's National Reform Council since 7 May 2020. He is currently serving a prison sentence in Georgia on charges of abuse of power and organization of an assault occasioning grievous bodily harm against an opposition lawmaker Valery Gelashvili.

United National Movement is a liberal and pro-western political party in Georgia founded by Mikheil Saakashvili which rose to power following the Rose Revolution. Since the 2012 parliamentary election, it is the main opposition party.

Eduard Dzhabeyevich Kokoyty is an Ossetian politician who served as President of the partially recognized state of South Ossetia from 2001 to 2011.

Irakli Okruashvili is a Georgian politician who had served on various important posts in the Government of Georgia under President Mikheil Saakashvili, including being the Minister of Defense from December 2004 until being dismissed in November 2006.

Zurab Nogaideli is a Georgian businessman and a politician who served as the Prime Minister of Georgia from February 2005 until he resigned, citing health problems, on 16 November 2007. In December 2008, Nogaideli withdrew into opposition, setting up the Movement for a Fair Georgia party.

The Georgian–Ossetian conflict is an ethno-political conflict over Georgia's former autonomous region of South Ossetia, which evolved in 1989 and developed into a war. Despite a declared ceasefire and numerous peace efforts, the conflict remained unresolved. In August 2008, military tensions and clashes between Georgia and South Ossetian separatists erupted into the Russo-Georgian War. Since then, South Ossetia has been under Russian occupation.

Georgia has a monarchic tradition that traces its origins to the Hellenistic period. The medieval Kingdom of Georgia ruled by the Bagrationi dynasty has left behind a legacy that lasts in Georgia even in modern times. The qualities and symbols associated with the Bagrationi monarchy have been crucial in the making of the Georgian nation and the subsequent construction of national history. Their rule ended with the annexation of Georgian lands by the Russian Empire early in the 19th century, although several branches of the dynasty survive to this day. The monarchic restoration was considered by various royalist groups throughout the 20th century. Although Georgia's politics has been taking place in the framework of a semi-presidential republic since the nation regained its independence from the Soviet Union in 1991, the debate on monarchy, particularly its constitutional form, has never actually ceased. The issue came up most recently amid a political crisis in late 2007.
An international diplomatic crisis between Georgia and Russia began in 2008, when Russia announced that it would no longer participate in the Commonwealth of Independent States economic sanctions imposed on Abkhazia in 1996 and established direct relations with the separatist authorities in Abkhazia and South Ossetia. The crisis was linked to the push for Georgia to receive a NATO Membership Action Plan and, indirectly, the unilateral declaration of independence by Kosovo.

The 2008 Russo-Georgian War was a war between Russia, alongside the Russian-backed self-proclaimed republics of South Ossetia and Abkhazia, and Georgia. The war took place in August following a diplomatic crisis between Russia and Georgia, both formerly constituent republics of the Soviet Union. The fighting took place in the strategically important South Caucasus region. It is regarded as the first European war of the 21st century.
The Russo-Georgian War broke out in August 2008 and involved Georgia, Russian Federation, South Ossetia and Abkhazia.

This article describes the background of the Russo-Georgian War.

Abkhazia and South Ossetia are disputed territories in the Caucasus. Most countries recognise them as part of Georgia, while Russia, Venezuela, Nicaragua, Nauru, and Syria regard them as independent. Russia's initial recognition of the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia occurred in the aftermath of the Russo-Georgian War in 2008. The government of Georgia considers the republics to be Russian-occupied territories.

The Armed Forces of South Ossetia is the military of the partially recognised state of South Ossetia. It includes an Army and an Air Corps.

Both sides of the 2008 war between Russia and Georgia blamed each other for starting the war.

Giorgi Bagrationi (Georgian: გიორგი ბაგრატიონი;, is a Georgian prince of the Bagrationi dynasty, which reigned until the early 19th century in Georgia and its successive realms.
In 2013, Georgia finalized its first-ever peaceful change of power and transition to a parliamentary republic. The Georgian Dream-dominated government, which came to power after defeating, in October 2012, the United National Movement led by the outgoing President Mikheil Saakashvili, promised more democratic reforms. The Georgian Dream candidate Giorgi Margvelashvili won the presidential election in October 2013 and the new constitution significantly reducing the authority of the president in favor of those of the prime minister and government came into effect. In November, the leader of the Georgian Dream, Prime Minister Bidzina Ivanishvili announced his withdrawal from politics as promised earlier, and the Parliament of Georgia approved his nominee, Irakli Garibashvili, as the country's new head of government.
The events in 2010 in Georgia.