Related Research Articles
20 Aquarii, abbreviated 20 Aqr, is a star in the constellation Aquarius. 20 Aquarii is the Flamsteed designation. It is a dim star with an apparent visual magnitude of 6.38. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 15.34 mas, it is located 213 light years away but is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −23 km/s. The star is predicted to come to within 110 light-years in around 1.9 million years.
Xi Aurigae, Latinized from ξ Aurigae, is the Bayer designation for a single, white-hued star in the northern constellation of Auriga. This star was once considered part of the constellation of Camelopardalis and held the Flamsteed designation 32 Camelopardalis. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +5.0. The measured annual parallax shift of this star is 13.37 ± 0.17 mas, which corresponds to a physical distance of 244 light-years with a 3 light-year margin of error. At that distance, the visual magnitude of the star is diminished by an extinction of 0.108 due to interstellar dust.

28 Cancri is a star system in the zodiac constellation of Cancer. It is a variable star with the designation CX Cancri, and is close to the lower limit of visibility with the naked eye, having a mean apparent visual magnitude of 6.05. The annual parallax shift seen from Earth's orbit is 8.5 mas, which provides a distance estimate of about 384 light years. It is moving away from the Sun with a radial velocity of around +9 km/s.
42 Camelopardalis is a single star in the constellation Camelopardalis, located roughly 770 light years away from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, blue-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.14. The visual magnitude of the star is diminished by an extinction of 0.22 due to interstellar dust. It is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of 3 km/s. 42 Camelopardalis has a peculiar velocity of 24.4+1.9
−2.1 km/s and may be a runaway star.
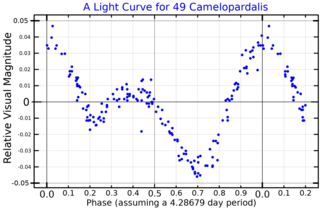
49 Camelopardalis is a variable star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Camelopardalis, located 313 light years from the Sun based on parallax measurements. It has the variable star designation BC Camelopardalis; 49 Camelopardalis is the Flamsteed designation. This star is a challenge to view with the naked eye, having a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 6.50. It is moving away from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +6.5 km/s.
HD 178233 is a single star in the northern constellation of Lyra. It is bright enough to be dimly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.53, making it a sixth magnitude star. The distance to HD 178233 is 134 light years based on parallax measurements, but it is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of approximately −24 km/s.
HD 6114 is a visual binary star system in the northern constellation of Andromeda. With a combined apparent magnitude of 6.46, the star can only be seen with the naked eye by keen-eyed observers even on the best of nights. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 10.4 mas as seen from Earth's orbit, the system is located approximately 108 parsecs (350 ly) distant.
4 Camelopardalis is a probable multiple star in the northern constellation of Camelopardalis, located 177 light years away from the Sun, based upon parallax. With a combined apparent visual magnitude of 5.29, it is visible to the naked eye as a faint, white-hued star. The pair have a relatively high proper motion, traversing the celestial sphere at an angular rate of 0.158″ per year. The system's proper motion makes it a candidate for membership in the IC 2391 supercluster. They are moving away from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of 22.5 km/s.
HR 3082 is a double star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Camelopardalis. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.39. The system is moving closer to the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of +2.7 km/s. It is currently at a distance of around 341 light years, based upon an annual parallax shift of 9.57 mas.
35 Vulpeculae is a single, white-hued star in the northern constellation of Vulpecula. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.39. An annual parallax shift of 16.9162±0.0681 mas provides a distance estimate of about 193 light years. It is moving closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −8 km/s.
14 Camelopardalis is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Camelopardalis, located 272 light years away from the Sun as determined by parallax measurements. With an apparent visual magnitude of 6.49, it is a challenge to view with the naked eye even in excellent viewing conditions. The heliocentric radial velocity value is poorly constrained, but it appears to be moving closer to the Earth at the rate of around −4 km/s.
HD 201507, also designated HR 8095, is a white-hued star located in the equatorial constellation Equuleus. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.43, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility. Parallax measurements place the object at a distance of 214 light years and it is currently drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −43 km/s.

θ Pavonis, Latinized as Theta Pavonis, is a single star in the southern constellation of Pavo. It is just visible to the naked eye as a dim, white-hued star, having an apparent visual magnitude of 5.71. This star is located 213 light years from the Sun based on parallax.

HD 90132 is a solitary white hued star located in the southern constellation Antlia. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.33, making it one of the brighter members of this generally faint constellation. The star is relatively close at a distance of 135 light years but is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 17 km/s.

HD 26764, also known as HR 1314 or rarely 14 H. Camelopardalis, is a solitary white hued star located in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.19, making it faintly to the naked eye if viewed under good conditions. Gaia DR3 parallax measurements place the object at a distance of 266 light years and is drifting closer with a poorly constrained heliocentric radial velocity of 3 km/s. At its current distance, HD 26764's brightness is diminished by 0.26 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.
37 Camelopardalis is a solitary star in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.36, allowing it to be seen with the naked eye under ideal conditions. Located about 444 light years away, the star is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 30.86 km/s.
HD 75171, also known as HR 3495, is a solitary, white hued star located in the southern constellation of Volans. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.02, making it faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. The object is relatively close at a distance of 191 light years but is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 10.7 km/s. Eggen (1995) lists it as a probable member of the Hyades Supercluster.

HD 36187, also known as HR 1835, is a solitary, bluish-white hued star located in the southern constellation Columba, the dove. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.55, making it faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft, it is estimated to be 282 light years away from the Solar System. However, it is receding rapidly with a heliocentric radial velocity of 50 km/s. At its current distance, HD 36187's brightness is diminished by 0.21 magnitude due to interstellar dust.

HD 27322, also known as HR 1342, is a binary star located in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis. The visible component is faintly visible to the naked eye as a white-hued point of light with an apparent magnitude of 5.92. The object is located relatively close at a distance of 313 light-years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements, and it is drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of approximately −13 km/s. At its current distance, HD 27322's brightness is diminished by 0.24 magnitudes due to interstellar extinction and it has an absolute magnitude of +0.98.
HD 84607 is a solitary star located in the equatorial constellation Sextans. It is faintly visible to the naked eye as a yellowish-white hued point of light with an apparent magnitude of 5.64. The object is located relatively close at a distance of 250 light-years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements, but it is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 7.8 km/s. At its current distance, HD 84607's brightness is diminished by an interstellar extinction of 0.18 magnitudes and it has an absolute magnitude +1.12.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics . 616. A1. arXiv: 1804.09365 . Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G . doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201833051 . Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters, 38 (5): 331, arXiv: 1108.4971 , Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, S2CID 119257644.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Zorec, J.; et al. (2012), "Rotational velocities of A-type stars. IV. Evolution of rotational velocities", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 537: A120, arXiv: 1201.2052 , Bibcode:2012A&A...537A.120Z, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201117691, S2CID 55586789.
- 1 2 Cowley, A.; et al. (1969), "A study of the bright A stars. I. A catalogue of spectral classifications", Astronomical Journal, 74: 375, Bibcode:1969AJ.....74..375C, doi:10.1086/110819.
- 1 2 3 David, Trevor J.; Hillenbrand, Lynne A. (2015), "The Ages of Early-Type Stars: Strömgren Photometric Methods Calibrated, Validated, Tested, and Applied to Hosts and Prospective Hosts of Directly Imaged Exoplanets", The Astrophysical Journal, 804 (2): 146, arXiv: 1501.03154 , Bibcode:2015ApJ...804..146D, doi:10.1088/0004-637X/804/2/146, S2CID 33401607.
- ↑ Netopil, Martin (August 2017), "Metallicity calibrations for dwarf stars and giants in the Geneva photometric system", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 469 (3): 3042–3055, arXiv: 1705.00883 , Bibcode:2017MNRAS.469.3042N, doi: 10.1093/mnras/stx1077 , S2CID 119034918.
- ↑ "HD 38091". SIMBAD . Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved 2018-07-10.
- ↑ De Rosa, R. J.; Patience, J.; Wilson, P. A.; Schneider, A.; Wiktorowicz, S. J.; Vigan, A.; Marois, C.; Song, I.; MacIntosh, B.; Graham, J. R.; Doyon, R.; Bessell, M. S.; Thomas, S.; Lai, O. (2014), "The VAST Survey - III. The multiplicity of A-type stars within 75 pc", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 437 (2): 1216, arXiv: 1311.7141 , Bibcode:2014MNRAS.437.1216D, doi: 10.1093/mnras/stt1932 , S2CID 88503488.
- ↑ Samus, N. N.; et al. (2017), "General Catalogue of Variable Stars", Astronomy Reports, 5.1, 61 (1): 80–88, Bibcode:2017ARep...61...80S, doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085, S2CID 125853869.