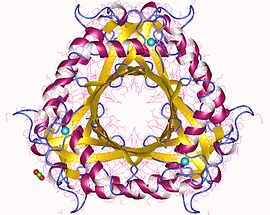
GTP cyclohydrolase I (GTPCH) (EC 3.5.4.16) is a member of the GTP cyclohydrolase family of enzymes. GTPCH is part of the folate and biopterin biosynthesis pathways. It is responsible for the hydrolysis of guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to form 7,8-dihydroneopterin triphosphate (7,8-DHNP-3'-TP, 7,8-NH2-3'-TP).
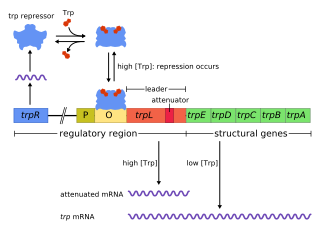
The trp operon is a group of genes that are transcribed together, encoding the enzymes that produce the amino acid tryptophan in bacteria. The trp operon was first characterized in Escherichia coli, and it has since been discovered in many other bacteria. The operon is regulated so that, when tryptophan is present in the environment, the genes for tryptophan synthesis are repressed.
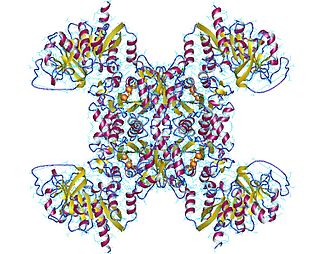
CTP synthase is an enzyme involved in pyrimidine biosynthesis that interconverts UTP and CTP.

Biopterins are pterin derivatives which function as endogenous enzyme cofactors in many species of animals and in some bacteria and fungi. The prototypical compound of the class is biopterin, as shown in the infobox. Biopterins act as cofactors for aromatic amino acid hydroxylases (AAAH), which are involved in synthesizing a number of neurotransmitters including dopamine, norepinephrine, epinepherine, and serotonin, along with several trace amines. Nitric oxide synthesis also uses biopterin derivatives as cofactors. In humans, tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) is the endogenous cofactor for AAAH enzymes.

The transsulfuration pathway is a metabolic pathway involving the interconversion of cysteine and homocysteine through the intermediate cystathionine. Two transsulfurylation pathways are known: the forward and the reverse.
In enzymology, a 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin 2'-reductase (EC 1.1.1.220) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Isochorismate synthase ( EC 5.4.4.2) is an isomerase enzyme that catalyzes the first step in the biosynthesis of vitamin K2 (menaquinone) in Escherichia coli.

In enzymology, a phosphoribosylanthranilate isomerase (PRAI) is an enzyme that catalyzes the third step of the synthesis of the amino acid tryptophan.

In enzymology, a dihydrofolate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

o-Succinylbenzoate—CoA ligase, encoded from the menE gene in Escherichia coli, catalyzes the fifth reaction in the synthesis of menaquinone. This pathway is called 1, 4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoate biosynthesis I. Vitamin K is a quinone that serves as an electron transporter during anaerobic respiration. This process of anaerobic respiration allows the bacteria to generate the energy required to survive.
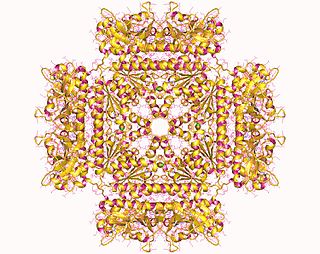
In molecular biology, the protein domain SAICAR synthase is an enzyme which catalyses a reaction to create SAICAR. In enzymology, this enzyme is also known as phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthase. It is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase catalyzes the following chemical reaction:

In enzymology, a 2-amino-4-hydroxy-6-hydroxymethyldihydropteridine diphosphokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In molecular biology, the Cofactor transferase family is a family of protein domains that includes biotin protein ligases, lipoate-protein ligases A, octanoyl-(acyl carrier protein):protein N-octanoyltransferases, and lipoyl-protein:protein N-lipoyltransferases. The metabolism of the cofactors Biotin and lipoic acid share this family. They also share the target modification domain, and the sulfur insertion enzyme.
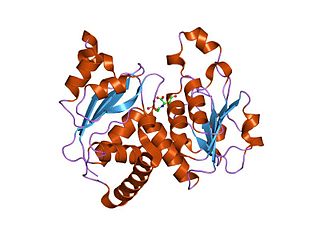
In molecular biology, the ATCase/OTCase family is a protein family which contains two related enzymes: aspartate carbamoyltransferase EC 2.1.3.2 and ornithine carbamoyltransferase EC 2.1.3.3. It has been shown that these enzymes are evolutionary related. The predicted secondary structure of both enzymes is similar and there are some regions of sequence similarities. One of these regions includes three residues which have been shown, by crystallographic studies to be implicated in binding the phosphoryl group of carbamoyl phosphate and may also play a role in trimerisation of the molecules. The N-terminal domain is the carbamoyl phosphate binding domain. The C-terminal domain is an aspartate/ornithine-binding domain.

In enzymology, SEPHCHC synthase (EC EC 2.2.1.9), encoded by menD gene in E. coli, is an enzyme that catalyzes the second step of menaquinone (vitamin K2) biosynthesis. The two substrates of this enzyme are 2-oxoglutarate and isochorismate. The products of this enzyme are 5-enolpyruvoyl-6-hydroxy-2-succinyl-cyclohex-3-ene-1-carboxylate and CO2. It belongs to the transferase family.
S-Adenosylmethionine:tRNA ribosyltransferase-isomerase is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:7-aminomethyl-7-deazaguanosine ribosyltransferase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Thiazole synthase (EC 2.8.1.10, thiG (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate:thiol sulfurtransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
7-Carboxy-7-deazaguanine synthase (EC 4.3.99.3, 7-carboxy-7-carbaguanine synthase, queE (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 6-carboxy-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropterin ammonia-lyase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
7-cyano-7-deazaguanine synthase (EC 6.3.4.20, preQ0 synthase, 7-cyano-7-carbaguanine synthase, queC (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 7-carboxy-7-carbaguanine:ammonia ligase (ADP-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction