Related Research Articles

An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal. It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is defined as a circuit that has a power gain greater than one.
In electrical engineering, a ground plane is an electrically conductive surface, usually connected to electrical ground. It is also used to provide a low-impedance path for electrical current. They also serve as a stabilizing factor for the signal, ensuring that antennas have a consistent baseline from which to transmit and receive information. Ground planes are typically made of copper or aluminum, and they are often located on the bottom of printed circuit boards (PCBs).

In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a two-port circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output port by adding energy converted from some power supply to the signal. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal amplitude or power at the output port to the amplitude or power at the input port. It is often expressed using the logarithmic decibel (dB) units. A gain greater than one, that is, amplification, is the defining property of an active device or circuit, while a passive circuit will have a gain of less than one.

In radio engineering, an antenna or aerial is an electronic device that converts an alternating electric current into radio waves (transmitting), or radio waves into an electric current (receiving). It is the interface between radio waves propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver. In transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic waves. In reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of a radio wave in order to produce an electric current at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be amplified. Antennas are essential components of all radio equipment.

In electronics, negative resistance (NR) is a property of some electrical circuits and devices in which an increase in voltage across the device's terminals results in a decrease in electric current through it.
A low-noise amplifier (LNA) is an electronic component that amplifies a very low-power signal without significantly degrading its signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Any electronic amplifier will increase the power of both the signal and the noise present at its input, but the amplifier will also introduce some additional noise. LNAs are designed to minimize that additional noise, by choosing special components, operating points, and circuit topologies. Minimizing additional noise must balance with other design goals such as power gain and impedance matching.

In electrical engineering, impedance matching is the practice of designing or adjusting the input impedance or output impedance of an electrical device for a desired value. Often, the desired value is selected to maximize power transfer or minimize signal reflection. For example, impedance matching typically is used to improve power transfer from a radio transmitter via the interconnecting transmission line to the antenna. Signals on a transmission line will be transmitted without reflections if the transmission line is terminated with a matching impedance.
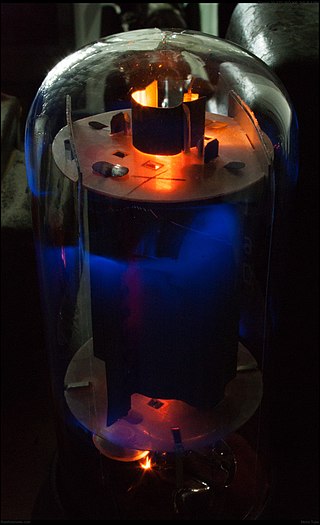
A valve amplifier or tube amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that uses vacuum tubes to increase the amplitude or power of a signal. Low to medium power valve amplifiers for frequencies below the microwaves were largely replaced by solid state amplifiers in the 1960s and 1970s. Valve amplifiers can be used for applications such as guitar amplifiers, satellite transponders such as DirecTV and GPS, high quality stereo amplifiers, military applications and very high power radio and UHF television transmitters.
The Hartley oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit in which the oscillation frequency is determined by a tuned circuit consisting of capacitors and inductors, that is, an LC oscillator. The circuit was invented in 1915 by American engineer Ralph Hartley. The distinguishing feature of the Hartley oscillator is that the tuned circuit consists of a single capacitor in parallel with two inductors in series, and the feedback signal needed for oscillation is taken from the center connection of the two inductors.

A regenerative circuit is an amplifier circuit that employs positive feedback. Some of the output of the amplifying device is applied back to its input to add to the input signal, increasing the amplification. One example is the Schmitt trigger, but the most common use of the term is in RF amplifiers, and especially regenerative receivers, to greatly increase the gain of a single amplifier stage.

In radio communications, a radio receiver, also known as a receiver, a wireless, or simply a radio, is an electronic device that receives radio waves and converts the information carried by them to a usable form. It is used with an antenna. The antenna intercepts radio waves and converts them to tiny alternating currents which are applied to the receiver, and the receiver extracts the desired information. The receiver uses electronic filters to separate the desired radio frequency signal from all the other signals picked up by the antenna, an electronic amplifier to increase the power of the signal for further processing, and finally recovers the desired information through demodulation.
An antenna tuner, a matchbox, transmatch, antenna tuning unit (ATU), antenna coupler, or feedline coupler is a device connected between a radio transmitter or receiver and its antenna to improve power transfer between them by matching the impedance of the radio to the antenna's feedline. Antenna tuners are particularly important for use with transmitters. Transmitters feed power into a resistive load, very often 50 ohms, for which the transmitter is optimally designed for power output, efficiency, and low distortion. If the load seen by the transmitter departs from this design value due to improper tuning of the antenna/feedline combination the power output will change, distortion may occur and the transmitter may overheat.
A Colpitts oscillator, invented in 1918 by Canadian-American engineer Edwin H. Colpitts using vacuum tubes, is one of a number of designs for LC oscillators, electronic oscillators that use a combination of inductors (L) and capacitors (C) to produce an oscillation at a certain frequency. The distinguishing feature of the Colpitts oscillator is that the feedback for the active device is taken from a voltage divider made of two capacitors in series across the inductor.

Electronic filters are a type of signal processing filter in the form of electrical circuits. This article covers those filters consisting of lumped electronic components, as opposed to distributed-element filters. That is, using components and interconnections that, in analysis, can be considered to exist at a single point. These components can be in discrete packages or part of an integrated circuit.

An electronic component is any basic discrete electronic device or physical entity part of an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not to be confused with electrical elements, which are conceptual abstractions representing idealized electronic components and elements. A datasheet for an electronic component is a technical document that provides detailed information about the component's specifications, characteristics, and performance. Discrete circuits are made of individual electronic components that only perform one function each as packaged, which are known as discrete components, although strictly the term discrete component refers to such a component with semiconductor material such as individual transistors.
A radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves with frequencies between about 30 Hz and 300 GHz. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves. Transmitters are necessary parts of all systems that use radio: radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, wireless networks, radar, two way radios like walkie talkies, radio navigation systems like GPS, remote entry systems, among numerous other uses.
In electronics, motorboating is a type of low frequency parasitic oscillation that sometimes occurs in audio and radio equipment and often manifests itself as a sound similar to an idling motorboat engine, a "put-put-put", in audio output from speakers or earphones. It is a problem encountered particularly in radio transceivers and older vacuum tube audio systems, guitar amplifiers, PA systems and is caused by some type of unwanted feedback in the circuit. The amplifying devices in audio and radio equipment are vulnerable to a variety of feedback problems, which can cause distinctive noise in the output. The term motorboating is applied to oscillations whose frequency is below the range of hearing, from 1 to 10 hertz, so the individual oscillations are heard as pulses. Sometimes the oscillations can even be seen visually as the woofer cones in speakers slowly moving in and out.
A radio transmitter or receiver is connected to an antenna which emits or receives the radio waves. The antenna feed system or antenna feed is the cable or conductor, and other associated equipment, which connects the transmitter or receiver with the antenna and makes the two devices compatible. In a radio transmitter, the transmitter generates an alternating current of radio frequency, and the feed system feeds the current to the antenna, which converts the power in the current to radio waves. In a radio receiver, the incoming radio waves excite tiny alternating currents in the antenna, and the feed system delivers this current to the receiver, which processes the signal.
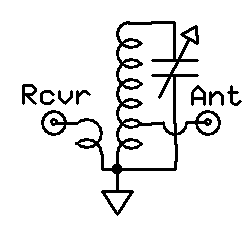
A preselector is a name for an electronic device that connects between a radio antenna and a radio receiver. The preselector is a band-pass filter that blocks troublesome out-of-tune frequencies from passing through from the antenna into the radio receiver that otherwise would be directly connected to the antenna.

Distributed-element circuits are electrical circuits composed of lengths of transmission lines or other distributed components. These circuits perform the same functions as conventional circuits composed of passive components, such as capacitors, inductors, and transformers. They are used mostly at microwave frequencies, where conventional components are difficult to implement.
References
Ulrich L. Rohde: Active Antennas, RF Design, May/June 1981
Ulrich L. Rohde, Magdalena Salazar Palma, Tapan K. Sarkar: Electrically short antennas, , Feb 11, 2016
- ↑ Poole, Ian D. "Antenna Systems." Newnes Guide to Radio and Communications Technology. Amsterdam; London: Newnes, 2003. Print.