Methuselah was a biblical patriarch and a figure in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. He had the longest lifespan of all those given in the Bible, having died at the age of 969. According to the Book of Genesis, Methuselah was the son of Enoch, the father of Lamech, and the grandfather of Noah. Elsewhere in the Bible, Methuselah is mentioned in genealogies in 1 Chronicles and the Gospel of Luke.

The term bristlecone pine covers three species of pine tree. All three species are long-lived and highly resilient to harsh weather and bad soils. One of the three species, Pinus longaeva, is among the longest-lived life forms on Earth. The oldest of this species is more than 4,800 years old, making it the oldest known individual of any species. Many scientists are curious as to why this tree is able to live so long. In one study, they discovered that Pinus longaeva has higher levels of telomerase activity, which further slows or prevents the attrition rate of telomeres. This potentially contributes to the extended life of the bristlecone pine.
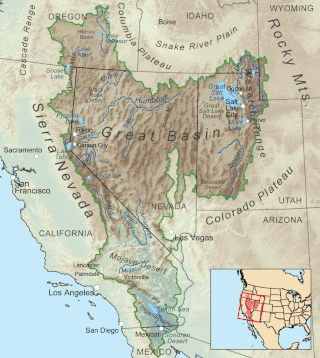
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets to the ocean, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California. It is noted for both its arid climate and the basin and range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin in Death Valley to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than 100 miles (160 km) away at the summit of Mount Whitney. The region spans several physiographic divisions, biomes, ecoregions, and deserts.

The White Mountains of California and Nevada are a triangular fault-block mountain range facing the Sierra Nevada across the upper Owens Valley. They extend for approximately 60 mi (97 km) as a greatly elevated plateau about 20 mi (32 km) wide on the south, narrowing to a point at the north, with elevations generally increasing south to north. The range's broad southern end is near the community of Big Pine, where Westgard Pass and Deep Springs Valley separate it from the Inyo Mountains. The narrow northern end is at Montgomery Pass, where U.S. Route 6 crosses. The Fish Lake Valley lies east of the range; the southeast part of the mountains are separated from the Silver Peak Range by block faulting across the Furnace Creek Fault Zone, forming a feeder valley to Fish Lake Valley. The range lies within the eastern section of the Inyo National Forest.

Pinus longaeva is a long-living species of bristlecone pine tree found in the higher mountains of California, Nevada, and Utah. Methuselah is a bristlecone pine that is 4,855 years old and has been credited as the oldest known living non-clonal organism on Earth. To protect it, the exact location of this tree is kept secret. In 1987, the bristlecone pine was designated one of Nevada's state trees.

Pinus aristata, the Rocky Mountain bristlecone pine, is a long-living species of bristlecone pine tree native to the United States. It appears in the Rocky Mountains in Colorado and northern New Mexico, with isolated populations in the San Francisco Peaks in Arizona and the Kaibab National Forest north of the Grand Canyon. It is usually found at very high altitudes, from 7,000–13,000 feet (2,100–4,000 m), in cold, dry subalpine climate conditions, often at the tree line, although it also forms extensive closed-canopy stands at somewhat lower elevations.

Inyo National Forest is a United States National Forest covering parts of the eastern Sierra Nevada of California and the White Mountains of California and Nevada. The forest hosts several superlatives, including Mount Whitney, the highest point in the contiguous United States; Boundary Peak, the highest point in Nevada; and the Ancient Bristlecone Pine Forest, which protects the oldest living trees in the world. The forest, encompassing much of the Owens Valley, was established by Theodore Roosevelt as a way of sectioning off land to accommodate the Los Angeles Aqueduct project in 1907, making the Inyo National Forest one of the least wooded forests in the U.S. National Forest system.

Telescope Peak is the highest point within Death Valley National Park, in the U.S. state of California. It is also the highest point of the Panamint Range, and lies in Inyo County. From atop this desert mountain one can see for over one hundred miles in many directions, including west to Mount Whitney, and east to Charleston Peak. The mountain was named for the great distance visible from the summit.

Prometheus was the oldest known non-clonal organism, a Great Basin bristlecone pine tree growing near the tree line on Wheeler Peak in eastern Nevada, United States. The tree, which was at least 4,862 years old and possibly more than 5,000, was cut down in 1964 by a graduate student and United States Forest Service personnel for research purposes. Those involved did not know of its world-record age before the cutting, and the circumstances and decision-making process remain controversial.

The Snake Range is a mountain range in White Pine County, Nevada, United States. The south-central portion of the range is included within Great Basin National Park, with most of the remainder included within the Humboldt-Toiyabe National Forest. The range reaches a maximum elevation of 13,065 feet (3,982 m) at the summit of Wheeler Peak, the tallest independent mountain within Nevada and the second highest point within the state. The range also contains four of the five highest mountain peaks in Nevada, including all peaks greater than 12,000 feet (3,658 m) except for Boundary Peak.

Methuselah is a 4,855-year-old Great Basin bristlecone pine tree growing high in the White Mountains of Inyo County in eastern California. It is recognized as the non-clonal tree with the greatest confirmed age in the world. The tree's name refers to the biblical patriarch Methuselah, who is said to have reached 969 years of age before his death, thus becoming synonymous with longevity or old age in many European languages including English.

The Currant Mountain Wilderness is a 47,357-acre (19,165 ha) wilderness area centered on Currant Mountain in the White Pine Range of Nye County and White Pine County, in the eastern section of the state of Nevada in the western United States.
Donald Rusk Currey was an American professor of geography. While known in academia for his extensive research and exploration of relics of the ancient Lake Bonneville in the eastern Great Basin, he was best known to the public for his controversial felling of Prometheus, the oldest living non-clonal organism known at the time, while a graduate student in 1964.

The Madrean Region is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom in North America, as delineated by Armen Takhtajan and Robert F. Thorne. It occupies arid or semiarid areas in the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico and is bordered by the Rocky Mountain Floristic Region and North American Atlantic Region of the Holarctic Kingdom in the north and in the east, Caribbean Region of the Neotropical Kingdom in the south.
The White Pine Range Wilderness is a 40,013-acre (16,193 ha) wilderness area in southwestern White Pine County, in the U.S. state of Nevada.

Negligible senescence is a term coined by biogerontologist Caleb Finch to denote organisms that do not exhibit evidence of biological aging (senescence), such as measurable reductions in their reproductive capability, measurable functional decline, or rising death rates with age. There are many species where scientists have seen no increase in mortality after maturity. This may mean that the lifespan of the organism is so long that researchers' subjects have not yet lived up to the time when a measure of the species' longevity can be made. Turtles, for example, were once thought to lack senescence, but more extensive observations have found evidence of decreasing fitness with age.
Great Basin may refer to:

The Great Basin montane forests is an ecoregion of the Temperate coniferous forests biome, as designated by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF).

The Methuselah Tree is a giant sequoia located in Mountain Home State Forest, a sequoia grove located in Sequoia National Forest in the Sierra Nevada in eastern California. It is the 28th largest giant sequoia in the world, and could be considered the 27th largest depending on how badly Ishi Giant atrophied during the Rough Fire in 2015.