
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great vessels and support the shoulder girdle to form the core part of the axial skeleton.

The left and right brachiocephalic veins are major veins in the upper chest, formed by the union of the ipsilateral internal jugular vein and subclavian vein behind the sternoclavicular joint. The left brachiocephalic vein is more than twice the length of the right brachiocephalic vein.

The intercostal muscles comprise many different groups of muscles that run between the ribs, and help form and move the chest wall. The intercostal muscles are mainly involved in the mechanical aspect of breathing by helping expand and shrink the size of the chest cavity.

In human anatomy, the internal thoracic artery (ITA), also known as the internal mammary artery, is an artery that supplies the anterior chest wall and the breasts. It is a paired artery, with one running along each side of the sternum, to continue after its bifurcation as the superior epigastric and musculophrenic arteries.

The internal intercostal muscles are a group of skeletal muscles located between the ribs. They are eleven in number on either side. They commence anteriorly at the sternum, in the intercostal spaces between the cartilages of the true ribs, and at the anterior extremities of the cartilages of the false ribs, and extend backward as far as the angles of the ribs, hence they are continued to the vertebral column by thin aponeuroses, the posterior intercostal membranes. They pull the sternum and ribs upward and inward.

The intercostal space (ICS) is the anatomic space between two ribs. Since there are 12 ribs on each side, there are 11 intercostal spaces, each numbered for the rib superior to it.
The subcostal arteries, so named because they lie below the last ribs, constitute the lowest pair of branches derived from the thoracic aorta, and are in series with the intercostal arteries.

The intercostal arteries are a group of arteries passing within an intercostal space. There are 9 anterior and 11 posterior intercostal arteries on each side of the body. The anterior intercostal arteries are branches of the internal thoracic artery and its terminal branch - the musculophrenic artery. The posterior intercostal arteries are branches of the supreme intercostal artery and thoracic aorta.
The subcostal vein is a vein in the human body that runs along the bottom of the twelfth rib. It has the same essential qualities as the posterior intercostal veins, except that it cannot be considered intercostal because it is not between two ribs.

The lumbar veins are four pairs of veins running along the inside of the posterior abdominal wall, and drain venous blood from parts of the abdominal wall. Each lumbar vein accompanies a single lumbar artery. The lower two pairs of lumbar veins all drain directly into the inferior vena cava, whereas the fate of the upper two pairs is more variable.

The external vertebral venous plexuses consist of anterior and posterior plexuses which anastomose freely with each other. They are most prominent in the cervical region where they form anastomoses with the vertebral, occipital, and deep cervical veins.
Intercostal vessels may refer to:
The esophageal veins drain blood from the esophagus to the azygos vein, in the thorax, and to the inferior thyroid vein in the neck. It also drains, although with less significance, to the hemiazygos vein, posterior intercostal vein and bronchial veins.

The intercostal veins are a group of veins which drain the area between the ribs ("costae"), called the intercostal space.
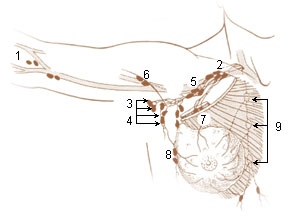
The parasternal lymph nodes are placed at the anterior ends of the intercostal spaces, by the side of the internal thoracic artery.

Anterior spinal veins are veins that receive blood from the anterior spinal cord.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The posterior cardinal veins or postcardinal veins join with the corresponding right and left cardinal veins to form the left common cardinal veins, which empty in the sinus venosus. In the development of a human embryo, most of the posterior cardinal veins regress, and what remains of them forms the renal segment of the inferior vena cava and the common iliac veins. Later in the development stages, the posterior cardinal veins are replaced by the subcardinal and supracardinal veins. The subcardinal veins form part of the inferior vena cava, the renal veins and the gonadal veins. The supracardinal veins form part of the inferior vena cava, the intercostal veins, the hemiazygos vein and the azygos vein.

The pulmonary pleurae are the two flattened sacs ensheathing each lung, locally appearing as two opposing layers of serous membrane separating the lungs from the mediastinum and the inside surfaces of the surrounding chest walls.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.













