
A nickel metal hydride battery is a type of rechargeable battery. The chemical reaction at the positive electrode is similar to that of the nickel–cadmium cell (NiCd), with both using nickel oxide hydroxide (NiOOH). However, the negative electrodes use a hydrogen-absorbing alloy instead of cadmium. NiMH batteries can have two to three times the capacity of NiCd batteries of the same size, with significantly higher energy density, although much less than lithium-ion batteries.

Sanyo Electric Co., Ltd., stylized as SANYO, was a Japanese electronics company and formerly a member of the Fortune Global 500 whose headquarters was located in Moriguchi, Osaka prefecture, Japan. Sanyo had over 230 subsidiaries and affiliates, and was founded by Toshio Iue in 1947.

Duracell Inc. is an American manufacturer of alkaline batteries, specialty cells, rechargeables and smart power systems; it is a wholly owned subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway. The company has its origins in the 1920s, through the work of Samuel Ruben and Philip Mallory, and the formation of the P. R. Mallory Company.
A primary battery or primary cell is a battery that is designed to be used once and discarded, and not recharged with electricity and reused like a secondary cell. In general, the electrochemical reaction occurring in the cell is not reversible, rendering the cell unrechargeable. As a primary cell is used, chemical reactions in the battery use up the chemicals that generate the power; when they are gone, the battery stops producing electricity. In contrast, in a secondary cell, the reaction can be reversed by running a current into the cell with a battery charger to recharge it, regenerating the chemical reactants. Primary cells are made in a range of standard sizes to power small household appliances such as flashlights and portable radios.

The AA battery is a standard size single cell cylindrical dry battery. The IEC 60086 system calls the size R6, and ANSI C18 calls it 15. It is named UM-3 by JIS of Japan. Historically, it is known as D14, U12 – later U7, or HP7 in official documentation in the United Kingdom, or a pen cell.

AlphaSmart, Inc. was an education technology company founded by Apple Computer engineers Joe Barrus and Ketan Kothari, and Kothari's brother, Manish, in the early 90's. At the time of their initial release in 1993, the first AlphaSmart models were marketed as smart keyboards designed to promote writing in the classroom as an alternative to expensive computer labs. The units' durability, long battery life, and limited functionality made them ideal for K-12 classrooms. Later models expanded functionality to spell-checking, running applications, and accessing wireless printers.

Apple Inc. has designed and developed many external keyboard models for use with families of Apple computers, such as the Apple II, Mac, and iPad. The Magic Keyboard and Magic Keyboard with Numeric Keypad designed to be used via either Bluetooth and USB connectivity, and have integrated rechargeable batteries; The Smart Keyboard and Magic Keyboard accessories for iPads are designed to be directly attached to and powered by a host iPad. All current Apple keyboards utilize low-profile key designs, and common modifier keys.

A battery charger, recharger, or simply charger, is a device that stores energy in a battery by running an electric current through it. The charging protocol depends on the size and type of the battery being charged. Some battery types have high tolerance for overcharging and can be recharged by connection to a constant voltage source or a constant current source, depending on battery type. Simple chargers of this type must be manually disconnected at the end of the charge cycle. Other battery types use a timer to cut off when charging should be complete. Other battery types cannot withstand over-charging, becoming damaged, over heating or even exploding. The charger may have temperature or voltage sensing circuits and a microprocessor controller to safely adjust the charging current and voltage, determine the state of charge, and cut off at the end of charge. Chargers may elevate the output voltage proportionally with current to compensate for impedance in the wires.

A rechargeable alkaline battery, also known as alkaline rechargeable or rechargeable alkaline manganese (RAM), is a type of alkaline battery that is capable of recharging for repeated use. The formats include AAA, AA, C, D, and snap-on 9-volt batteries. Rechargeable alkaline batteries are manufactured fully charged and have the ability to hold their charge for years, longer than NiCd and NiMH batteries, which self-discharge. Rechargeable alkaline batteries can have a high recharging efficiency and have less environmental impact than disposable cells.

A CR-V3 battery is a type of disposable high-capacity 3-Volt battery used in various electronic appliances, including some digital cameras. It has the shape and size of two side-by-side AA batteries. This allows CR-V3 batteries to function in many devices originally designed for only AA batteries. An RCR-V3 battery is a rechargeable 3.7 V lithium-ion battery.
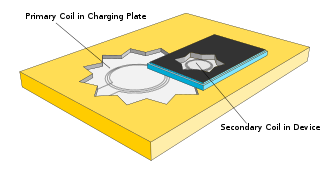
Inductive charging is a type of wireless power transfer. It uses electromagnetic induction to provide electricity to portable devices. Inductive charging is also used in vehicles, power tools, electric toothbrushes, and medical devices. The portable equipment can be placed near a charging station or inductive pad without needing to be precisely aligned or make electrical contact with a dock or plug.

Eneloop is a brand of 1.2-volt low self-discharge nickel–metal hydride (NiMH) rechargeable batteries and accessories developed by Sanyo and introduced in 2005. Panasonic acquired a majority stake in Sanyo in 2009, and Eneloop batteries were thereafter branded, but not manufactured, by Panasonic.

A battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices. When a battery is supplying power, its positive terminal is the cathode and its negative terminal is the anode. The terminal marked negative is the source of electrons that will flow through an external electric circuit to the positive terminal. When a battery is connected to an external electric load, a redox reaction converts high-energy reactants to lower-energy products, and the free-energy difference is delivered to the external circuit as electrical energy. Historically the term "battery" specifically referred to a device composed of multiple cells; however, the usage has evolved to include devices composed of a single cell.

The Magic Mouse is a multi-touch wireless mouse that is manufactured by Foxconn and sold by Apple Inc.. The first-generation Magic Mouse was released on October 20, 2009, and introduced multi-touch functionality to a computer mouse. Taking after the iPhone, iPod Touch, and multi-touch MacBook trackpads, the Magic Mouse allows the use of multi-touch gestures and inertia scrolling across the surface of the mouse, designed for use with macOS.
Since the release of the Nintendo Wii, many aesthetic, ergonomic and functional accessories have been developed by third parties for the console’s controller, the Wii Remote.
This is a list of commercially-available battery types summarizing some of their characteristics for ready comparison.

The Magic Keyboard is a family of wireless computer keyboards manufactured by Foxconn under contract for Apple Inc. The keyboards are bundled with the iMac and Mac Pro, and also sold as standalone accessories. They replaced the Apple Wireless Keyboard product line. Each Magic Keyboard model combination has a compact or full-size key layout for a specific region, a function key or Touch ID sensor next to F12, and color scheme variant.
The initial versions of the USB standard specified connectors that were easy to use and that would have acceptable life spans; revisions of the standard added smaller connectors useful for compact portable devices. Higher-speed development of the USB standard gave rise to another family of connectors to permit additional data paths. All versions of USB specify cable properties; version 3.x cables include additional data paths. The USB standard included power supply to peripheral devices; modern versions of the standard extend the power delivery limits for battery charging and devices requiring up to 100 watts. USB has been selected as the standard charging format for many mobile phones, reducing the proliferation of proprietary chargers.












