MagSafe is a series of proprietary magnetically attached power connectors developed by Apple Inc. for Mac laptops. MagSafe was introduced on 10 January 2006, in conjunction with the MacBook Pro, the first Intel-based Mac laptop, at the Macworld Expo. A MagSafe connector is held in place magnetically so that if it is tugged, it will be pulled out of the port without damaging the connector or the port, and without pulling the computer off its surface. A thinner and wider version, called MagSafe 2, was introduced in 2012. It was discontinued across Apple's product lines between 2016 and 2019 and replaced with USB-C. MagSafe returned to Mac laptops with the introduction of updated MacBook Pro models with MagSafe 3 in 2021.

A dock connector is an electrical connector used to attach a mobile device simultaneously to multiple external resources. The dock connector will typically carry a variety of signals and power, through a single connector, to simplify the process of docking the device. A dock connector may be embedded in a mechanical fixture used to support or align the mobile device or may be at the end of a cable.

Universal charger or common charger refers to various projects to standardize the connectors of power supplies, particularly for battery-powered devices.

Apple Inc. has produced and sold headphones since 2001, available for standalone purchase and bundled with iPhone and iPod products. Apple's current product line consists of EarPods, AirPods and AirPods Pro, and AirPods Max.

The Magic Mouse is a multi-touch wireless mouse sold by Apple Inc. and manufactured by Foxconn. The first-generation Magic Mouse was released on October 20, 2009, and introduced multi-touch functionality to a computer mouse. Taking after the iPhone, iPod Touch, and multi-touch MacBook trackpads, the Magic Mouse allows the use of multi-touch gestures and inertia scrolling across the surface of the mouse, designed for use with macOS.

The iPad is a brand of iOS and iPadOS-based tablet computers that are developed by Apple, first introduced on January 27, 2010. The iPad range consists of the original iPad lineup and the flagship products iPad Mini, iPad Air, and iPad Pro.

The iPad is a tablet computer produced and marketed by Apple Inc. Compared to its predecessor, the third-generation iPad, the fourth-generation iPad maintained the Retina Display but featured new and upgraded components such as the Apple A6X chip and the Lightning connector, which was introduced on September 12, 2012. It shipped with iOS 6, which provides a platform for audio-visual media, including electronic books, periodicals, films, music, computer games, presentations and web content. Like the third-generation iPad it replaced, it was supported by five major iOS releases, in this case iOS 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10.

Apple Inc.'s MFi Program, referring to "Made for iPhone/iPod/iPad", is a licensing program for developers of hardware and software peripherals that work with Apple's iPod, iPad and iPhone. The name is a shortened version of the long-form Made for iPod, the original program that ultimately became MFi.

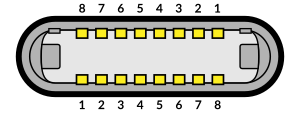
USB-C, or USB Type-C, is a 24-pin connector that supersedes previous USB connectors and can carry audio, video and other data, e.g., to drive multiple displays or to store a backup to an external drive. It can also provide and receive power, such as powering a laptop or a mobile phone. It is applied not only by USB technology, but also by other protocols, including Thunderbolt, PCIe, HDMI, DisplayPort, and others. It is extensible to support future standards.

The fifth generation iPod Touch was unveiled at Apple's media event alongside the iPhone 5 on September 12, 2012, and was released on October 11, 2012. A mobile device designed and marketed by Apple Inc. with a touchscreen-based user interface, it succeeded the 4th-generation iPod Touch. It is compatible with up to iOS 9.3.5, which was released on August 25, 2016.

The iPad Pro is a series of tablet computers, positioned as a premium model of Apple's iPad tablet computer. It runs iPadOS, a tablet-optimized version of the iOS operating system.
Apple Pencil is a line of wireless stylus pen accessories designed and developed by Apple Inc. for use with supported iPad tablets.
The initial versions of the USB standard specified connectors that were easy to use and that would have acceptable life spans; revisions of the standard added smaller connectors useful for compact portable devices. Higher-speed development of the USB standard gave rise to another family of connectors to permit additional data paths. All versions of USB specify cable properties; version 3.x cables include additional data paths. The USB standard included power supply to peripheral devices; modern versions of the standard extend the power delivery limits for battery charging and devices requiring up to 240 watts. USB has been selected as the standard charging format for many mobile phones, reducing the proliferation of proprietary chargers.

AirPods Pro are wireless Bluetooth in-ear headphones designed by Apple, initially introduced on October 30, 2019. They are Apple's mid-range wireless headphones, available alongside the base-level AirPods and the highest-end AirPods Max.

The iPhone 12 and iPhone 12 Mini are smartphones designed, developed, and marketed by Apple Inc. They are the fourteenth-generation iPhones, succeeding the iPhone 11. They were unveiled at a virtually held Apple Special Event at Apple Park in Cupertino, California, on October 13, 2020, alongside the "premium flagship" iPhone 12 Pro and iPhone 12 Pro Max and HomePod Mini. Pre-orders for the iPhone 12 started on October 16, 2020, and the phone was released in most countries on October 23, 2020, alongside the iPhone 12 Pro and fourth-generation iPad Air. Pre-orders for the iPhone 12 Mini began on November 6, 2020, and the phone was released on November 13, 2020, alongside the iPhone 12 Pro Max.
The iPhone 12 Pro and iPhone 12 Pro Max are smartphones designed, developed, and marketed by Apple Inc. They are the flagship smartphones in the fourteenth generation of the iPhone, succeeding the iPhone 11 Pro and iPhone 11 Pro Max, respectively. They were unveiled alongside the iPhone 12 and iPhone 12 Mini at an Apple Special Event at Apple Park in Cupertino, California on October 13, 2020, with the iPhone 12 Pro being released on October 23, 2020, and the iPhone 12 Pro Max on November 13, 2020. They were discontinued on September 14, 2021, along with the iPhone XR, following the announcement of the iPhone 13 and iPhone 13 Pro.

MagSafe is a proprietary, magnetically attached wireless power transfer and accessory-attachment standard developed by Apple Inc. for its iPhone and AirPods product lines. It was announced on 13 October 2020, in conjunction with the iPhone 12 and 12 Pro series. It provides up to 15 W of power and is compatible with the open Qi standard for up to 7.5 W of power. The connector also enables connecting non-charger accessories such as card holders and cases with communication through an integrated NFC loop. The charger uses a circle of rare-earth magnets.
The iPhone's hardware is designed by Apple Inc. Apple directly sub-contracts hardware production to external OEM companies, maintaining a high degree of control over the end product.

The sixth-generation iPad Mini is a tablet computer in the iPad Mini line, designed, developed and marketed by Apple Inc. It was announced on September 14, 2021, and released on September 24, 2021, alongside the ninth-generation iPad, iPhone 13 and iPhone 13 Pro. Its predecessor, the fifth-generation iPad Mini, was discontinued on the same day. It is available in four colors: Space Gray, Starlight, Pink, and Purple.
The iPad , unofficially known as the iPad 10, is a tablet computer developed and marketed by Apple Inc. as the successor to the ninth-generation iPad. It was announced on October 18, 2022, and was released on October 26, 2022.