 |
|---|
Government
|
Judiciary
|
Exiled government
|
Related topics |
The Arakanese Muslim Association was a political party in Burma. The party was led by Sultan Mahmud, who served as Minister of Health during the U Nu period. [1]
 |
|---|
The Arakanese Muslim Association was a political party in Burma. The party was led by Sultan Mahmud, who served as Minister of Health during the U Nu period. [1]
Affiliated with the Anti-Fascist People's Freedom League, the party won three seats in the Chamber of Deputies in the 1951–52 elections. [2]

Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar, also known as Burma, is a country in Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia, and had a population of about 54 million in 2017. It is bordered by Bangladesh and India to its northwest, China to its northeast, Laos and Thailand to its east and southeast, and the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal to its south and southwest. The country's capital city is Naypyidaw, and its largest city is Yangon.

The National League for Democracy is a deregistered liberal democratic political party in Myanmar (Burma). It became the country's ruling party after a landslide victory in the 2015 general election but was overthrown in a military coup d'état in early 2021 following another landslide election victory in 2020.
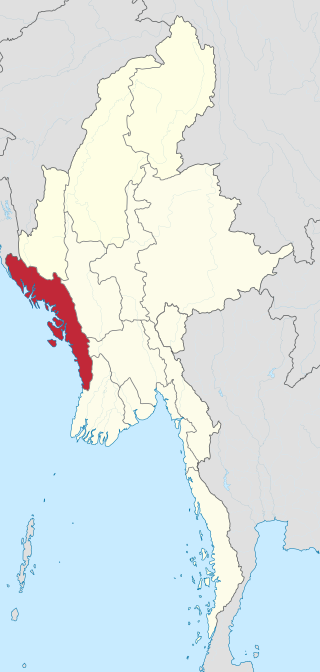
Rakhine State is a state in Myanmar (Burma). Situated on the western coast, it is bordered by Chin State to the north, Magway Region, Bago Region and Ayeyarwady Region to the east, the Bay of Bengal to the west and the Chittagong Division of Bangladesh to the northwest. It is located approximately between latitudes 17°30' north and 21°30' north and longitudes 92°10' east and 94°50' east. The Arakan Mountains or Rakhine Yoma separated Rakhine State from central Burma from North to South. Off the coast of Rakhine State there are some fairly large islands such as Ramree, Cheduba and Myingun. Rakhine State has an area of 36,762 square kilometres (14,194 sq mi) and its capital is Sittwe.

The Anti-Fascist People's Freedom League (AFPFL) was the dominant political alliance in Burma from 1945 to 1958. It consisted of political parties and mass and class organizations.

The Rohingya people are a stateless Indo-Aryan ethnic group who predominantly follow Islam and reside in Rakhine State, Myanmar. Before the Rohingya genocide in 2017, when over 740,000 fled to Bangladesh, an estimated 1.4 million Rohingya lived in Myanmar. Described by journalists and news outlets as one of the most persecuted minorities in the world, the Rohingya are denied citizenship under the 1982 Myanmar nationality law. There are also restrictions on their freedom of movement, access to state education and civil service jobs. The legal conditions faced by the Rohingya in Myanmar have been compared to apartheid by some academics, analysts and political figures, including Nobel laureate Bishop Desmond Tutu, a South African anti-apartheid activist. The most recent mass displacement of Rohingya in 2017 led the International Criminal Court to investigate crimes against humanity, and the International Court of Justice to investigate genocide.

Burmese Indians are a group of people of Indian origin who live in Myanmar (Burma). The term 'Burmese Indian' refers to a broad range of people from South Asia, most notably from present-day countries such as India, Bangladesh and also Pakistan. While Indians have lived in Burma for many centuries, most of the ancestors of the current Burmese Indian community emigrated to Burma from the start of British rule in the mid-19th century to the separation of British Burma from British India in 1937. During colonial times, ethnic Indians formed the backbone of the government and economy serving as soldiers, civil servants, merchants, moneylenders, mobile laborers and dock workers. A series of anti-Indian riots in the 1930s and mass emigration at the onset of the Japanese invasion of Burma in 1942 were followed in the 1960s by the forced migration of hundreds of thousands of ethnic Indians, exacerbated by internal conflict in Myanmar.

The Irrawaddy is a news website by the Irrawaddy Publishing Group (IPG), founded in 1990 by Burmese exiles living in Thailand. From its inception, The Irrawaddy has taken an independent stance on Burmese politics. As a publication produced by former Burmese activists who fled violent crackdowns on anti-military protests in 1988, it has always been closely associated with the pro-democracy movement, although it remains unaffiliated with any of the political groups that have emerged since the 8888 Uprising.

The Golden Triangle is the area in which the borders of Thailand, Laos, and Myanmar meet at the confluence of the Ruak and the Mekong Rivers. The name "Golden Triangle" was coined by the CIA and is commonly used more broadly to refer to an area of approximately 950,000 square kilometres (367,000 sq mi) that overlaps the mountains of the three adjacent countries.
Islam is the most widely practised religion in Southeast Asia, numbering approximately 240 million adherents which translate to about 42% of the entire population, with majorities in Brunei, Indonesia and Malaysia as well parts of Southern Thailand and parts of Mindanao in the Philippines respectively. Significant minorities are located in the other Southeast Asian states. Most Muslims in Southeast Asia are Sunni and follow the Shafi`i school of fiqh, or religious law. It is the official religion in Malaysia and Brunei while it is one of the six official faiths in Indonesia.
There is a history of persecution of Muslims in Myanmar that continues to the present day. Myanmar is a Buddhist majority country, with significant Christian and Muslim minorities. While Muslims served in the government of Prime Minister U Nu (1948–63), the situation changed with the 1962 Burmese coup d'état. While a few continued to serve, most Christians and Muslims were excluded from positions in the government and army. In 1982, the government introduced regulations that denied citizenship to anyone who could not prove Burmese ancestry from before 1823. This disenfranchised many Muslims in Myanmar, even though they had lived in Myanmar for several generations.
Insurgencies have been ongoing in Myanmar since 1948, the year the country, then known as Burma, gained independence from the United Kingdom. The conflict has largely been ethnic-based, with several ethnic armed groups fighting Myanmar's armed forces, the Tatmadaw, for self-determination. Despite numerous ceasefires and the creation of autonomous self-administered zones in 2008, many armed groups continue to call for independence, increased autonomy, or the federalisation of the country. The conflict is the world's longest ongoing civil war, having spanned more than seven decades.
Myanmar (Burma) is a Buddhist majority country with a significant minority population residing in the country. Section 361 of the Constitution states that "The Union recognizes the special position of Buddhism as the faith professed by the great majority of the citizens of the Union." According to both the 2016 census of the Burmese government Buddhism is the dominant religion, of 88% of the population, practiced especially by the Bamar, Rakhine, Shan, Mon, Karen people and Chinese ethnic groups. Bamar people also practice the Burmese folk religion under the name of Buddhism. The new constitution provides for the freedom of religion; however, it also grants broad exceptions that allow the regime to restrict these rights at will. Ethnic minorities practice Christianity, Islam, and Hinduism.

General elections were held in Burma over several months between June 1951 and April 1952 due to internal conflict within the country.

The Communist Party (Burma) (Burmese: ကွန်မြူနစ်ပါတီ (ဗမာပြည်)), sometimes referred to as the Red Flag Communist Party (Burmese: အလံနီကွန်မြူနစ်ပါတီ; RFCP), was a communist party in Burma. The party was formed after a more radical faction broke away from the Communist Party of Burma in 1946. In the same year, it began a protracted armed insurgency; first against British rule, then against the Burmese government. The party was led by Thakin Soe, a firebrand communist leader. In the mid to late 1970s, the party lost influence and was militarily defeated after the capture of Thakin Soe in 1978.

The Kuomintang Islamic insurgency was a continuation of the Chinese Civil War by Chinese Muslim nationalist Kuomintang Republic of China Army forces mainly in Northwest China, in the provinces of Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang, and another insurgency in Yunnan.
The 2012 Rakhine State riots were a series of conflicts primarily between ethnic Rakhine Buddhists and Rohingya Muslims in northern Rakhine State, Myanmar, though by October Muslims of all ethnicities had begun to be targeted. The riots started came after weeks of sectarian disputes including a gang rape and murder of a Rakhine woman by Rohingya Muslims. On 8 June 2012, Rohingyas started to protest from Friday's prayers in Maungdaw township. More than a dozen residents were killed after police started firing. A state of emergency was declared in Rakhine, allowing the military to participate in administration of the region. As of 22 August 2012, officially there were 88 casualties: 57 Muslims and 31 Buddhists. An estimated 90,000 people were displaced by the violence. Around 2,528 houses were burned; of those, 1,336 belonged to Rohingyas and 1,192 belonged to Rakhines.
Pakistanis in Burma are a historical community living in Burma who trace their origins to Pakistan. This definition includes Pakistani nationals residing in Burma and Burmese citizens who have ancestral links to Pakistan. Their history predates the independence of Pakistan in 1947.

The 969 Movement is a Buddhist nationalist movement opposed to what they see as Islam's expansion in predominantly-Buddhist Myanmar (Burma). The three digits of 969 "symbolize the virtues of the Buddha, Buddhist practices and the Buddhist community". The first 9 stands for the nine special attributes of the Buddha and the 6 for the six special attributes of his Dharma, or Buddhist Teachings, and the last 9 represents the nine special attributes of Buddhist Sangha. Those special attributes are the Three Jewels of the Buddha. In the past, the Buddha, Sangha, Dhamma, the wheel of Dhamma, and "969" were Buddhist signs.

General elections were held in Myanmar on 8 November 2015, with the National League for Democracy winning a supermajority of seats in the combined national parliament. Voting occurred in all constituencies, excluding seats appointed by the military, to select Members of Assembly to seats in both the upper house and the lower house of the Assembly of the Union, and State and Region Hluttaws. Ethnic Affairs Ministers were also elected by their designated electorates on the same day, although only select ethnic minorities in particular states and regions were entitled to vote for them.
The Muslim Independence Movement (MIM) was a secessionist political organization in the Philippines.