
Digital art refers to any artistic work or practice that uses digital technology as part of the creative or presentation process. It can also refer to computational art that uses and engages with digital media.

Wacom Co., Ltd. is a Japanese company headquartered in Kazo, Saitama, Japan, that specializes in manufacturing graphics tablets and related products. As of 2012 Wacom generated sales of approximately 40.7 billion yen with 785 employees. The company's shares are listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange.
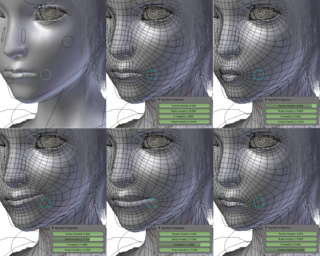
Human image synthesis is technology that can be applied to make believable and even photorealistic renditions of human-likenesses, moving or still. It has effectively existed since the early 2000s. Many films using computer generated imagery have featured synthetic images of human-like characters digitally composited onto the real or other simulated film material. Towards the end of the 2010s deep learning artificial intelligence has been applied to synthesize images and video that look like humans, without need for human assistance, once the training phase has been completed, whereas the old school 7D-route required massive amounts of human work .
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been used in applications throughout industry and academia. Similar to electricity or computers, AI serves as a general-purpose technology that has numerous applications. Its applications span language translation, image recognition, decision-making, credit scoring, e-commerce and various other domains. AI which accommodates such technologies as machines being equipped perceive, understand, act and learning a scientific discipline.

Computer-generated imagery (CGI) is a specific-technology or application of computer graphics for creating or improving images in art, printed media, simulators, videos and video games. These images are either static or dynamic. CGI both refers to 2D computer graphics and 3D computer graphics with the purpose of designing characters, virtual worlds, or scenes and special effects. The application of CGI for creating/improving animations is called computer animation, or CGI animation.
Picsart is an Armenian-American technology company based in Miami, Florida, United States and Yerevan, Armenia that develops the Picsart suite of online photo and video editing applications, with a social creative community. The platform allows users to take and edit pictures and videos, draw with layers, and share the images on Picsart and other social networks. It is one of the world's most popular apps, with reportedly more than 1 billion downloads across 180 countries.

Deepfakes were originally defined as synthetic media that have been digitally manipulated to replace one person's likeness convincingly with that of another. The term was coined in 2017 by a Reddit user, and has later been expanded to cover any videos, pictures, or audio made with artificial intelligence to appear real, for example realistic-looking images of people who do not exist. While the act of creating fake content is not new, deepfakes leverage tools and techniques from machine learning and artificial intelligence, including facial recognition algorithms and artificial neural networks such as variational autoencoders (VAEs) and generative adversarial networks (GANs). In turn the field of image forensics develops techniques to detect manipulated images. Deepfakes have garnered widespread attention for their potential use in creating child sexual abuse material, celebrity pornographic videos, revenge porn, fake news, hoaxes, bullying, and financial fraud. The spreading of disinformation and hate speech through deepfakes has a potential to undermine core functions and norms of democratic systems by interfering with people's ability to participate in decisions that affect them, determine collective agendas and express political will through informed decision-making. Both the information technology industry and government have responded with recommendations to detect and limit their use.

Artificial intelligence art is visual artwork created through the use of an artificial intelligence (AI) program.
Synthetic media is a catch-all term for the artificial production, manipulation, and modification of data and media by automated means, especially through the use of artificial intelligence algorithms, such as for the purpose of misleading people or changing an original meaning. Synthetic media as a field has grown rapidly since the creation of generative adversarial networks, primarily through the rise of deepfakes as well as music synthesis, text generation, human image synthesis, speech synthesis, and more. Though experts use the term "synthetic media," individual methods such as deepfakes and text synthesis are sometimes not referred to as such by the media but instead by their respective terminology Significant attention arose towards the field of synthetic media starting in 2017 when Motherboard reported on the emergence of AI altered pornographic videos to insert the faces of famous actresses. Potential hazards of synthetic media include the spread of misinformation, further loss of trust in institutions such as media and government, the mass automation of creative and journalistic jobs and a retreat into AI-generated fantasy worlds. Synthetic media is an applied form of artificial imagination.
Deepfake pornography, or simply fake pornography, is a type of synthetic pornography that is created via altering already-existing pornographic material by applying deepfake technology to the faces of the actors. The use of deepfake porn has sparked controversy because it involves the making and sharing of realistic videos featuring non-consenting individuals, typically female celebrities, and is sometimes used for revenge porn. Efforts are being made to combat these ethical concerns through legislation and technology-based solutions.

15.ai is a non-commercial freeware artificial intelligence web application that generates natural emotive high-fidelity text-to-speech voices from an assortment of fictional characters from a variety of media sources. Developed by a pseudonymous MIT researcher under the name 15, the project uses a combination of audio synthesis algorithms, speech synthesis deep neural networks, and sentiment analysis models to generate and serve emotive character voices faster than real-time, particularly those with a very small amount of trainable data.
Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3 (GPT-3) is a large language model released by OpenAI in 2020.

DALL·E, DALL·E 2, and DALL·E 3 are text-to-image models developed by OpenAI using deep learning methodologies to generate digital images from natural language descriptions known as "prompts".
Prequel, Inc. is an American technology company and mobile app developer known for developing the Prequel mobile application, which enables editing photos and videos with filters and effects generated using artificial intelligence. Prequel was founded in 2018 by Serge Aliseenko and Timur Khabirov, who currently serves as the company’s CEO. It is headquartered in New York City. As of August 2022, it had been downloaded more than 100 million times.

Midjourney is a generative artificial intelligence program and service created and hosted by the San Francisco–based independent research lab Midjourney, Inc. Midjourney generates images from natural language descriptions, called prompts, similar to OpenAI's DALL-E and Stability AI's Stable Diffusion. It is one of the technologies of the AI boom.

Stable Diffusion is a deep learning, text-to-image model released in 2022 based on diffusion techniques. The generative artificial intelligence technology is the premier product of Stability AI and is considered to be a part of the ongoing artificial intelligence boom.

Loab is a fictional character that artist and writer Steph Maj Swanson has claimed to have discovered with a text-to-image AI model in April 2022. In a viral Twitter thread, Swanson described it as an unexpectedly emergent property of the software, saying they discovered it when asking the model to produce something "as different from the prompt as possible".

NovelAI is an online cloud-based, SaaS model, and a paid subscription service for AI-assisted storywriting and text-to-image synthesis, originally launched in beta on June 15, 2021, with the image generation feature being implemented later on October 3, 2022. NovelAI is owned and operated by Anlatan, which is headquartered in Wilmington, Delaware.
In the 2020s, the rapid advancement of deep learning-based generative artificial intelligence models are raising questions about whether copyright infringement occurs when the generative AI is trained or used. This includes text-to-image models such as Stable Diffusion and large language models such as ChatGPT. As of 2023, there are several pending U.S. lawsuits challenging the use of copyrighted data to train AI models, with defendants arguing that this falls under fair use.

A ganimal, also commonly referred to as GANimal, is a hybrid animal created with generative artificial intelligence systems, such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) or diffusion models. The concept was created for a website from the MIT Media Lab in 2020, where users could create ganimal images. 78,210 ganimals were generated from hybrid pairs of animal labels from BigGAN (G1) and 3,058,362,945 ganimals generated from blending G1 ganimals.















