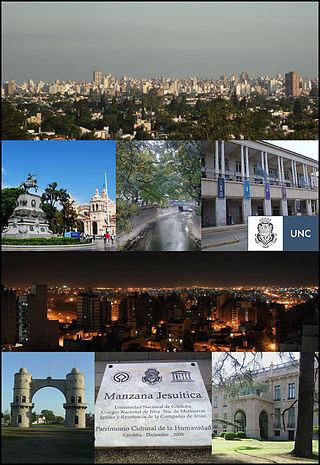
Córdoba is a city in central Argentina, in the foothills of the Sierras Chicas on the Suquía River, about 700 km (435 mi) northwest of Buenos Aires. It is the capital of Córdoba Province and the second-most populous city in Argentina after Buenos Aires, with about 1.6 million urban inhabitants according to the 2020 census. A European settlement was founded on 6 July 1573 by Jerónimo Luis de Cabrera, who named it after Córdoba, Spain. It was one of the early Spanish colonial capitals of the region of present-day Argentina. The National University of Córdoba, the oldest university of the country, was founded in 1613 by the Jesuit Order, and Córdoba has earned the nickname La Docta.

Buenos Aires, officially the Buenos Aires Province, is the largest and most populous Argentine province. It takes its name from the city of Buenos Aires, the capital of the country, which used to be part of the province and the province's capital until it was federalized in 1880. Since then, in spite of bearing the same name, the province does not include Buenos Aires city, though it does include all other parts of the Greater Buenos Aires metropolitan area. The capital of the province is the city of La Plata, founded in 1882.

Santiago del Estero is the capital of Santiago del Estero Province in northern Argentina. It has a population of 252,192 inhabitants, making it the twelfth largest city in the country, with a surface area of 2,116 km2. It lies on the Dulce River and on National Route 9, at a distance of 1,042 km north-northwest from Buenos Aires. Estimated to be 455 years old, Santiago del Estero was the first city founded by Spanish settlers in the territory that is now Argentina. As such, it is nicknamed "Madre de Ciudades". Similarly, it has been officially declared the "mother of cities and cradle of folklore."

Viedma is the capital and fourth largest city of the Río Negro Province, in northern Patagonia, Argentina. The city has approximately 62,000 inhabitants (2022), and is located on the southern margin of the Negro River, about 30 kilometres off the Atlantic Coast, and 960 km from the city of Buenos Aires on the National Route 3.

San Salvador de Jujuy, commonly known as Jujuy and locally often referred to as San Salvador, is the capital and largest city of Jujuy Province in northwest Argentina. Also, it is the seat of the Doctor Manuel Belgrano Department. It lies near the southern end of the Humahuaca Canyon where wooded hills meet the lowlands.

The climate of Chicago is classified as hot-summer humid continental with hot humid summers and cold, occasionally snowy winters. All four seasons are distinctly represented: Winters are cold and often see snow with below 0 Celsius temperatures and windchills, while summers are warm and humid with temperatures being hotter inland, spring and fall bring bouts of both cool and warm weather and fairly sunny skies. Annual precipitation in Chicago is moderate and relatively evenly distributed, the driest months being January and February and the wettest July and August. Chicago's weather is influenced during all four seasons by the nearby presence of Lake Michigan.

Junín is a city in the province of Buenos Aires, Argentina, and administrative seat of the partido of Junín. It has a population of 85,420 and is located 260 km (162 mi) west of the city of Buenos Aires. It is mostly known for being the hometown of former first lady of Argentina Eva Perón.

The 2006 European heat wave was a period of exceptionally hot weather that arrived at the end of June 2006 in certain European countries. The United Kingdom, France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Italy, Poland, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Germany and western parts of Russia were most affected.
A cold wave is a weather phenomenon that is distinguished by a cooling of the air. Specifically, as used by the U.S. National Weather Service, a cold wave is a rapid fall in temperature within a 24-hour period requiring substantially increased protection to agriculture, industry, commerce, and social activities. The precise criteria for a cold wave are the rate at which the temperature falls, and the minimum to which it falls. This minimum temperature is dependent on the geographical region and time of year.

The climate of Argentina varies from region to region, as the vast size of the country and wide variation in altitude make for a wide range of climate types. Summers are the warmest and wettest season in most of Argentina except in most of Patagonia where it is the driest season. Warm in the north, cool in the center and cold in the southern parts experiencing frequent frost and snow. Because southern parts of the country are moderated by the surrounding oceans, the cold is less intense and prolonged than areas at similar latitudes in the northern hemisphere. Spring and autumn are transition seasons that generally feature mild weather.

The 2010 Northern Hemisphere summer heat waves included severe heat waves that impacted most of the United States, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, China, Hong Kong, North Africa and the European continent as a whole, along with parts of Canada, Russia, Indochina, South Korea and Japan during July 29 2010. The first phase of the global heatwaves was caused by a moderate El Niño event, which lasted from June 2009 to May 2010. The first phase lasted only from April 2010 to June 2010, and caused only moderate above average temperatures in the areas affected. But it also set new record high temperatures for most of the area affected, in the Northern Hemisphere. The second phase was caused by a very strong La Niña event, which lasted from June 2010 to June 2011. According to meteorologists, the 2010–11 La Niña event was one of the strongest La Niña events ever observed. That same La Niña event also had devastating effects in the Eastern states of Australia. The second phase lasted from June 2010 to October 2010, caused severe heat waves, and multiple record-breaking temperatures. The heatwaves began in April 2010, when strong anticyclones began to develop, over most of the affected regions, in the Northern Hemisphere. The heatwaves ended in October 2010, when the powerful anticyclones over most of the affected areas dissipated.
The 2011 North American heat wave was a deadly summer 2011 heat wave that affected the Southern Plains, the Midwestern United States, Eastern Canada, the Northeastern United States, and much of the Eastern Seaboard, and had Heat index/Humidex readings reaching upwards of 131 °F (55 °C). On a national basis, the heat wave was the hottest in 75 years.

Córdoba is a province of Argentina, located in the center of the country. Its neighboring provinces are Santiago del Estero, Santa Fe, Buenos Aires, La Pampa, San Luis, La Rioja, and Catamarca. Together with Santa Fe and Entre Ríos, the province is part of the economic and political association known as the Center Region.
The summer of 2014 in Sweden was unusually warm, especially in the northern parts of the country. July was the warmest ever month on record in the north-west.

Buenos Aires, the capital of Argentina, has a temperate climate, which is classified as a humid subtropical climate (Cfa) under the Köppen climate classification with four distinct seasons. Summers are hot and humid with frequent thunderstorms while winters are cool and drier with frosts that occurs on average twice per year. Spring and fall are transition seasons characterized by changeable weather. At the central observatory, the highest temperature recorded is 43.3 °C (109.9 °F), and the lowest temperature recorded is −5.4 °C (22.3 °F).
Sweden had a very unusual start and finish to the year 2010, with two consecutive winter cold waves occurring in a single calendar year. Since both events were notable, both are covered in this article.

In 2022, several areas of the world experienced heat waves. Heat waves were especially notable in East Asia, the Indian subcontinent, Australia, western Europe, the United States, and southern South America. 2022 heat waves accounted for record-breaking temperatures and, in some regions, heat-related deaths. Heat waves were worsened by the effects of climate change, and they exacerbated droughts and wildfires.

In mid-January 2022, the Southern Cone had a severe heat wave, which made the region for a while the hottest place on earth, with temperatures exceeding those of the Middle East. This extreme weather event was associated with the Atlantic anticyclone, a particularly intense La Niña phenomenon in the Pacific Ocean, and the regional effects of climate change.
Between July and September 2023, a heat wave hit South America, leading to temperatures in many areas above 95 °F (35 °C) in midwinter, often 40–45 °F (22–25 °C) degrees above typical. The heat wave was especially severe in northern Argentina and Chile, along neighboring areas in and around the Andes Mountains. Some locations set all-time heat records. Several states also had the hottest September temperatures in history, often reaching more than 40°C.