
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production. It is composed of hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a man weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow.

In hematology, reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs). In the process of erythropoiesis, reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulate for about a day in the blood stream before developing into mature red blood cells. Like mature red blood cells, in mammals, reticulocytes do not have a cell nucleus. They are called reticulocytes because of a reticular (mesh-like) network of ribosomal RNA that becomes visible under a microscope with certain stains such as new methylene blue and Romanowsky stain.

Neutrophils are a type of phagocytic white blood cell and part of innate immunity. More specifically, they form the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. Their functions vary in different animals. They are also known as neutrocytes, heterophils or polymorphonuclear leukocytes.

A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells, B cells, and innate lymphoid cells, of which natural killer cells are an important subtype. They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte". Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells.

Granulocytes are cells in the innate immune system characterized by the presence of specific granules in their cytoplasm. Such granules distinguish them from the various agranulocytes. All myeloblastic granulocytes are polymorphonuclear, that is, they have varying shapes (morphology) of the nucleus ; and are referred to as polymorphonuclear leukocytes. In common terms, polymorphonuclear granulocyte refers specifically to "neutrophil granulocytes", the most abundant of the granulocytes; the other types have varying morphology. Granulocytes are produced via granulopoiesis in the bone marrow.

Erythropoiesis is the process which produces red blood cells (erythrocytes), which is the development from erythropoietic stem cell to mature red blood cell.
Leukocytosis is a condition in which the white cell (leukocyte) count is above the normal range in the blood. It is frequently a sign of an inflammatory response, most commonly the result of infection, but may also occur following certain parasitic infections or bone tumors as well as leukemia. It may also occur after strenuous exercise, convulsions such as epilepsy, emotional stress, pregnancy and labor, anesthesia, as a side effect of medication, and epinephrine administration. There are five principal types of leukocytosis:
- Neutrophilia
- Lymphocytosis
- Monocytosis
- Eosinophilia
- Basophilia

Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells or effector B cells, are white blood cells that originate in the lymphoid organs as B cells and secrete large quantities of proteins called antibodies in response to being presented specific substances called antigens. These antibodies are transported from the plasma cells by the blood plasma and the lymphatic system to the site of the target antigen, where they initiate its neutralization or destruction. B cells differentiate into plasma cells that produce antibody molecules closely modeled after the receptors of the precursor B cell.
Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) is a measure of the number of neutrophil granulocytes present in the blood. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell that fights against infection.

Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells or organs, and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopic scale include epithelial dysplasia and fibrous dysplasia of bone. Dysplasias on a mainly macroscopic scale include hip dysplasia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and multicystic dysplastic kidney.

Left shift or blood shift is an increase in the number of immature cell types among the blood cells in a sample of blood. Many clinical mentions of left shift refer to the white blood cell lineage, particularly neutrophil-precursor band cells, thus signifying bandemia. Less commonly, left shift may also refer to a similar phenomenon in the red blood cell lineage in severe anemia, when increased reticulocytes and immature erythrocyte-precursor cells appear in the peripheral circulation.

A proerythroblast is a precursor cell to the normoblast, as the earliest of four stages in its development.
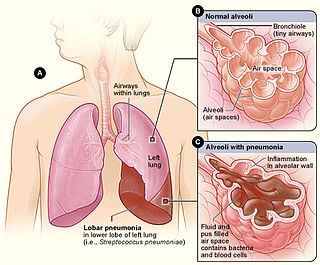
Lobar pneumonia is a form of pneumonia characterized by inflammatory exudate within the intra-alveolar space resulting in consolidation that affects a large and continuous area of the lobe of a lung.

A promyelocyte is a granulocyte precursor, developing from the myeloblast and developing into the myelocyte. Promyelocytes measure 12–20 microns in diameter. The nucleus of a promyelocyte is approximately the same size as a myeloblast but their cytoplasm is much more abundant. They also have less prominent nucleoli than myeloblasts and their chromatin is more coarse and clumped. The cytoplasm is basophilic and contains primary red/purple granules.

Granulopoiesis is a part of haematopoiesis, that leads to the production of granulocytes. A granulocyte, also referred to as a polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN), is a type of white blood cell that has multi lobed nuclei, usually containing three lobes, and has a significant amount of cytoplasmic granules within the cell. Granulopoiesis takes place in the bone marrow. It leads to the production of three types of mature granulocytes: neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils.
In hematology, myelopoiesis in the broadest sense of the term is the production of bone marrow and of all cells that arise from it, namely, all blood cells. In a narrower sense, myelopoiesis also refers specifically to the regulated formation of myeloid leukocytes (myelocytes), including eosinophilic granulocytes, basophilic granulocytes, neutrophilic granulocytes, and monocytes.
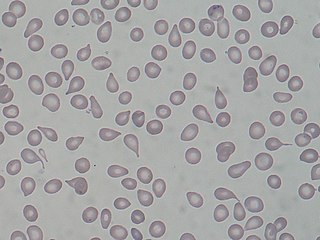
A dacrocyte is a type of poikilocyte that is shaped like a teardrop. A marked increase of dacrocytes is known as dacrocytosis. These tear drop cells are found primarily in diseases with bone marrow fibrosis, such as: primary myelofibrosis, myelodysplastic syndromes during the late course of the disease, rare form of acute leukemias and myelophthisis caused by metastatic cancers. Rare causes are myelofibrosis associated with post-irradiation, toxins, autoimmune diseases, metabolic conditions, inborn hemolytic anemias, iron-deficiency anemia or β-thalassemia.

White blood cells, also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. White blood cells include three main subtypes: granulocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes.

A nucleated red blood cell (NRBC), also known by several other names, is a red blood cell that contains a cell nucleus. Almost all vertebrate organisms have hemoglobin-containing cells in their blood, and with the exception of mammals, all of these red blood cells are nucleated. In mammals, NRBCs occur in normal development as precursors to mature red blood cells in erythropoiesis, the process by which the body produces red blood cells.

A white blood cell differential is a medical laboratory test that provides information about the types and amounts of white blood cells in a person's blood. The test, which is usually ordered as part of a complete blood count (CBC), measures the amounts of the five normal white blood cell types – neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils and basophils – as well as abnormal cell types if they are present. These results are reported as percentages and absolute values, and compared against reference ranges to determine whether the values are normal, low, or high. Changes in the amounts of white blood cells can aid in the diagnosis of many health conditions, including viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections and blood disorders such as leukemia.





















