Taps and dies are tools used to create screw threads, which is called threading. Many are cutting tools; others are forming tools. A tap is used to cut or form the female portion of the mating pair. A die is used to cut or form the male portion of the mating pair. The process of cutting or forming threads using a tap is called tapping, whereas the process using a die is called threading.

A fastener or fastening is a hardware device that mechanically joins or affixes two or more objects together. In general, fasteners are used to create non-permanent joints; that is, joints that can be removed or dismantled without damaging the joining components. Welding is an example of creating permanent joints. Steel fasteners are usually made of stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloy steel.
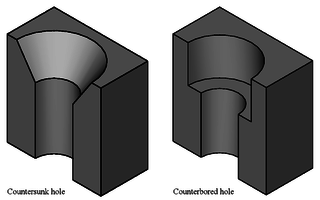
A countersink is a conical hole cut into a manufactured object, or the cutter used to cut such a hole. A common use is to allow the head of a countersunk bolt, screw or rivet, when placed in the hole, to sit flush with or below the surface of the surrounding material. A countersink may also be used to remove the burr left from a drilling or tapping operation thereby improving the finish of the product and removing any hazardous sharp edges.

A butt joint is a technique in which two pieces of material are joined by simply placing their ends together without any special shaping. The name "butt joint" comes from the way the material is joined together. The butt joint is the simplest joint to make since it merely involves cutting the material to the appropriate length and butting them together. It is also the weakest because unless some form of reinforcement is used, it relies upon glue or welding alone to hold it together. Because the orientation of the material usually presents only one end to a long gluing or welding surface, the resulting joint is inherently weak.

A dowel is a cylindrical rod, usually made of wood, plastic, or metal. In its original manufactured form, a dowel is called a dowel rod. Dowel rods are often cut into short lengths called dowel pins. Dowels are commonly used as structural reinforcements in cabinet making and in numerous other applications, including:

A sex bolt is a type of mating fastener (nut) that has a barrel-shaped flange and protruding boss that is internally threaded. The bolts sits within the components being fastened, the flange provides the bearing surface. The sex bolt and accompanying machine screw sit flush on either side of the surfaces being fastened.

A locknut, also known as a lock nut, locking nut, self-locking nut, prevailing torque nut, stiff nut or elastic stop nut, is a nut that resists loosening under vibrations and torque. Prevailing torque nuts have some portion of the nut that deforms elastically to provide a locking action. Free-spinning locknuts exist which carry the advantage of not requiring extra torque until seated.

A punch is a tool used to indent or create a hole through a hard surface. They usually consist of a hard metal rod with a narrow tip at one end and a broad flat "butt" at the other. When used, the narrower end is pointed against a target surface and the broad end is then struck with a hammer or mallet, causing the blunt force of the blow to be transmitted down the rod body and focused more sharply onto a small area. Typically, woodworkers use a ball-peen hammer to strike a punch.
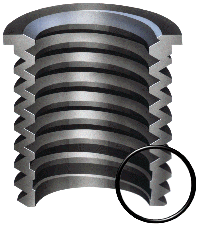
A threaded insert, also known as a threaded bushing, is a fastener element that is inserted into an object to add a threaded hole. They may be used to repair a stripped threaded hole, provide a durable threaded hole in a soft material, place a thread on a material too thin to accept it, mold or cast threads into a work piece thereby eliminating a machining operation, or simplify changeover from unified to metric threads or vice versa.

A well nut is a blind rivet-like type of fastener used to blindly fasten a piece and to seal the bolt hole.

An insert nut provides a threaded socket for a wooden workpiece, similar to a wall anchor. Insert nuts are inserted into a pre-drilled hole by one of two means: screw in and hammer in. In both cases, the external protrusions bite into the wood, preventing the nut from either turning or pulling out.

A rivet nut, also known as a blind rivet nut, or rivnut, is a one-piece internally threaded and counterbored tubular rivet that can be anchored entirely from one side. It is a kind of threaded insert. There are two types: one is designed to form a bulge on the back side of the panel as a screw is tightened in its threads. The other is similarly drawn in using a screw, but is drawn into the sleeve instead of creating a bulge.
A plate nut, also known as a nut plate, anchor nut or anchor plate, is a stamped sheet metal nut that is usually riveted to a workpiece. They have a long tube that is internally threaded and a plate with two clearance holes for rivets. The most popular versions have two lugs and they exist as fixed anchor nuts and as floating anchor nuts. The latter allows the nut to move slightly and so enlarges the positioning tolerances of the mounted parts. They were originally developed for the aerospace industry, but are now also common in automotive racing. These nuts are made up of variety of soft and hard materials. The choice of material depends on environment to which nut is subjected. Soft materials like copper or brass are used when nut is used in electrical application. Hard materials are used when nut is subjected to high stress environment. Sometimes stainless steel or nickel-plated nuts are used in order to increase corrosion resistance.

A swage nut or self-clinching nut is a type of nut or threaded insert that is used on sheet metal.

A screw and a bolt are similar types of fastener typically made of metal and characterized by a helical ridge, called a male thread. Screws and bolts are used to fasten materials by the engagement of the screw thread with a similar female thread in a matching part.

A nut is a type of fastener with a threaded hole. Nuts are almost always used in conjunction with a mating bolt to fasten multiple parts together. The two partners are kept together by a combination of their threads' friction, a slight stretching of the bolt, and compression of the parts to be held together.
Inserts are pins, bolts, screws, joints and other structures that are used to transfer localized loads to a composite panel or to join two composite panels together. Metallic inserts are commonly used in the aerospace and marine industries to attach objects to sandwich composite panels.

Strut channel, often referred to colloquially by one of several manufacturer trade names, is a standardized formed structural system used in the construction and electrical industries for light structural support, often for supporting wiring, plumbing, or mechanical components such as air conditioning or ventilation systems.

A screw extractor is a tool for removing broken or seized screws. There are two types: one has a spiral flute structure, commonly called an easy out after the trademarked name EZ-Out; the other has a straight flute structure. Screw extractors are intentionally made of hard, brittle steel, and, if too much torque is applied, can break off inside the screw that is being removed. Since the extractor is an extremely hard material, and a typical home shop drill bit will not be able to drill into it, a larger element of difficulty is added to the original screw extraction project. One way to avoid this added difficulty is to drill a hole completely through the screw. Thus, if the fastener breaks, a punch can be used to drive out the easy out from the screw, via the back, or end, of the fastener.

A bolt is a form of threaded fastener with an external male thread requiring a matching pre-formed female thread such as a nut. Bolts are very closely related to screws.