
Berycopsis is an extinct genus of marine ray-finned fish from the Late Cretaceous period. Fossils are known from England, Germany, and Lebanon. A potential specimen is known from the Czech Republic.
Congorhynchus is an enigmatic, likely polyphyletic genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish that was described by E. Darteville and E. Casier in 1949.

Argillichthys is an extinct marine lizardfish known from the Lower Eocene. It contains a single species, A. toombsi, from the Ypresian-aged London Clay Formation in England. It is known from a skull. It is thought to be a stem-member of Synodontidae.
Eothynnus salmonens is an extinct species of prehistoric jackfish that lived during the lower Eocene of what is now the Isle of Sheppey (as a part of the London Clay Lagerstatten. It is known exclusively from some preserved skulls.
Acestrus is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish that lived during the lower Eocene in Europe. It contains one species, A. ornatus from the London Clay, known from a single braincase. It is thought to possibly be closely allied with billfish based on the braincase morphology, although it remains uncertain whether it had the rostrum characteristic of billfishes. Some authorities have suggested blochiid affinities.
Bramoides is an extinct genus of marine ray-finned fish that lived during the lower Eocene. It contains a single species, B. brieni, known from the London Clay.

Kushlukia is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish, closely related to the luvar, that lived during the lower Eocene. K. permira is from Eocene portion of the Danata Formation Lagerstatten, of Turkmenistan. A second, as yet undescribed species is from the Fuller's Earth formation Lagerstatten in the Barmer District, of Ypresian Rajasthan, India.
Parechelus is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the Ypresian. The genus was circumscribed by Edgard Casier in 1967 for his description of P. parechelus.
Aulopopsis is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish that lived during the lower Eocene. It is considered a relative of lizardfish in the order Aulopiformes, but its exact taxonomic placement is uncertain. Some authorities place it with the Aulopidae, while others place it with the Giganturoidae.
Argilloberyx is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine bony fish that lived during the lower Eocene. It contains one species, A. prestwichae, known from the London Clay Formation on the Isle of Sheppey, United Kingdom. It is considered a member of the family Berycidae.

Pteronisculus is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish that lived during the Early Triassic and Middle Triassic epochs of the Triassic period worldwide.
Anguilloides is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine eel that lived in the early Eocene. It contains a single species, A. branchiostegalis. Fossils are known from the famous Monte Bolca site of Italy.

Bolcyrus is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine eel that lived during the Early Eocene. It was a member of the family Congridae, which also contains modern conger eels.
Berycomorus is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish that lived during the late Eocene epoch. It contains a single species, B. firdoussi, from the Pabdeh Formation of Iran.

Ductor is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish that lived from the early to middle Eocene. Fossils are found in Monte Bolca.

Acanthonemus is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish that lived from the early Eocene. It contains a single species, A. subaureus, known from the famous Monte Bolca site in Italy. It is the only genus in the extinct family Acanthonemidae.
Callipteryx is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine trachiniform fish that lived during the early Eocene. It is the only known member of the extinct family Callipterygidae. It is thought to have been a relative of weeverfishes.
Acrognathus is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish belonging to the order Aulopiformes. Although no extensive systematic analysis has been performed, it is tentatively placed with the greeneyes in the family Chlorophthalmidae, making it the oldest representative of that family.
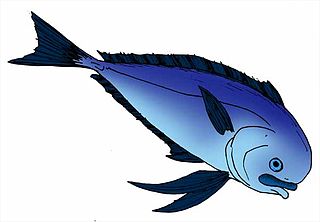
Aluvarus praeimperialis is an extinct ray-finned fish, known from two headless fossil specimens found in the Pabdeh Formation, a Late Eocene stratum from the Priabonian epoch, of what is now Iran. A. praeimperialis was originally thought to be a luvar, described as "Luvarus praeimperialis", as it was thought to be a predecessor to the modern luvar. A later reexamination of the specimens showed that they were too incomplete to demonstrate such a conclusion and had no clear exclusive shared traits with luvar, and were renamed "Aluvarus", meaning "not luvar" or "different than luvar". However, some authorities still retain it as a luvar.
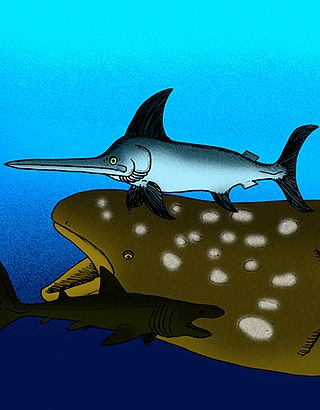
Xiphiorhynchus is an extinct genus of prehistoric swordfish that lived from the Eocene until the Oligocene. Unlike the modern swordfish, both the upper and lower jaws of Xiphiorhynchus were extended into blade-like points.









