
Alnwick Castle is a castle and country house in Alnwick in the English county of Northumberland. It is the seat of the 12th Duke of Northumberland, built following the Norman conquest and renovated and remodelled a number of times. It is a Grade I listed building now the home of Ralph Percy, 12th Duke of Northumberland and his family. In 2016, the castle received over 600,000 visitors per year when combined with adjacent attraction the Alnwick Garden.

Dudley Castle is a ruined fortification in the town of Dudley, West Midlands, England. Originally a wooden motte and bailey castle built soon after the Norman Conquest, it was rebuilt as a stone fortification during the twelfth century but subsequently demolished on the orders of Henry II of England. Rebuilding of the castle took place from the second half of the thirteenth century and culminated in the construction of a range of buildings within the fortifications by John Dudley. The fortifications were slighted by order of the Parliament of England during the English Civil War and the residential buildings destroyed by fire in 1750. In the nineteenth and early twentieth century the site was used for fêtes and pageants. Today Dudley Zoo is located on its grounds.

Westgate is a village in the civil parish of Stanhope, in County Durham, England. It is situated in Weardale between St John's Chapel and Eastgate. In the 2001 census Westgate had a population of 298. Westgate is also the entrance to Slitt wood and an old abandoned lead mine. Other features of the village include a caravan site and a football and basketball court.

Westwick is a hamlet and former civil parish, now in the parish of Oakington and Westwick, in the South Cambridgeshire district, in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is situated to the north-west of Cambridge. Earthworks suggest that it is a shrunken medieval village. In 1961 the parish had a population of 37.

Blenkinsopp Castle is a fire-damaged, partly demolished 19th-century country mansion, incorporating the ruinous remains of a 14th-century tower house, which is located above the Tipalt Burn approximately one mile south of Greenhead, Northumberland, England. It is a Grade II listed building; it is also a Scheduled Ancient Monument as one of the "surviving tower houses retaining significant medieval remains".

Halton Castle is a castle in the village of Halton, part of the town of Runcorn, Cheshire, England. The castle is on the top of Halton Hill, a sandstone prominence overlooking the village. The original building, a motte-and-bailey castle began in 1071, was replaced with the current sandstone castle in the 13th century. Building alterations continued until at least 1609, when the structure is recorded as in disrepair. The castle is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade I listed building, and a scheduled monument.

The Jew's House is one of the earliest extant town houses in England, estimated to have been built around 1170. It is situated on Steep Hill in Lincoln, immediately below Jew's Court. The house has traditionally been associated with the thriving Jewish community in Medieval Lincoln. Antisemitic hysteria was stoked by a notorious 1255 blood libel alleging that the mysterious death of a Christian child, known as Little Saint Hugh of Lincoln, was the result of him being kidnapped and ritually killed by Jews. In 1290, the entire Jewish community was expelled from England by Edward I, and the Jew's House is said to have been seized from a Jewish owner. The building has remained continuously occupied to the present day. Since about 1973 it has been used as a restaurant; prior to that it had been an antiques shop for many years.

Featherstone Castle, a Grade I listed building, is a large Gothic style country mansion situated on the bank of the River South Tyne about 3 miles (5 km) southwest of the town of Haltwhistle in Northumberland, England.

Bewdley Bridge is a three-span masonry arch bridge over the River Severn at Bewdley, Worcestershire, designed by civil engineer Thomas Telford. The two side spans are each 52 feet (16 m), with the central span 60 feet (18 m). The central arch rises 18 feet (5.5 m). Smaller flood arches on the bank bridge the towpath. The bridge is 27 feet (8.2 m) wide.

Barmoor Castle is a privately owned 19th-century country house built on an ancient site in Northumberland. It is a Grade II* listed building. As at 2008 the decaying building is officially listed on the English Heritage Buildings at Risk Register.

Prudhoe Castle is a ruined medieval English castle situated on the south bank of the River Tyne at Prudhoe, Northumberland, England. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument and a Grade I listed building.

Blenkinsop Hall is a privately owned castellated 19th-century country house situated on the banks of the Tipalt Burn near Greenhead, Northumberland. The legal address of the property is Haltwhistle, Northumberland, NE49 9LY. It is a Grade II listed building. The property is located near Blenkinsopp Castle which is primarily a ruin; the castle was owned by the same family as the Hall for generations.
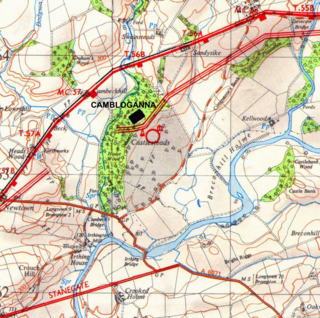
Camboglanna was a Roman fort. It was the twelfth fort on Hadrian's Wall counting from the east, between Banna (Birdoswald) almost 7 miles (11 km) to the east and Uxelodunum (Stanwix), 9 miles to the west. It was on a high bluff commanding the Cambeck Valley. It guarded an important approach to the Wall and also watched the east bank of the Cambeck against raiders from the Bewcastle area. The site was drastically levelled in 1791 when the gardens of Castlesteads House were laid over it. The name "Camboglanna" is believed to mean "Crook Bank", or "Bent Valley" because it overlooks a bend in the river Irthing; the name is Brythonic, made of cambo- "curved, bent, crooked" and glanna "steep bank, stream/river side, valley with a stream".

Uxelodunum was a Roman fort with associated civilian settlement (vicus) in modern-day Carlisle, Cumbria, England. It was the largest fort on Hadrian's Wall and is now buried beneath the suburb of Stanwix.

Habitancum was an ancient Roman fort (castrum) located at Risingham, Northumberland, England. The fort was one of series of built along the extension of Dere Street, a Roman road running from York to Corbridge and onwards to Melrose, in Scotland.

Bewcastle Roman Fort was built to the north of Hadrian's Wall as an outpost fort possibly intended for scouting and intelligence. The remains of the fort are situated at the village of Bewcastle, Cumbria, 7 miles (11 km) to the north of the Roman fort at Birdoswald, on Hadrian's Wall.

Telford and Wrekin Council is the local authority of Telford and Wrekin in the ceremonial county of Shropshire, England. It was founded in 1974 as The Wrekin District Council, and was a lower-tier district council until 1998. The district was renamed Telford and Wrekin in 1998 when the council became a unitary authority, being a district council which also performs the functions of a county council. It is independent from Shropshire Council, the unitary authority which administers the rest of the county.

Westhall is a privately owned 19th-century castellated house at Belford in Northumberland, England now in use as a farm. It is on a site with older historical associations.
Ardmillan Castle is a ruinous Scottish castle dating from the late 16th century.

Snodhill Castle is a ruined motte-and-bailey castle, about 1 mi (1.6 km) south of the village of Dorstone in west Herefordshire, England. It is recognized as one of the major castles of the Welsh Marches. It was built in the 11th century to secure the border between Norman England and the Welsh Princes. Archaeological excavations show that it was one of the first Norman castles in England to have stone-built fortifications, with more sophisticated defenses being added in later centuries.





















