Related Research Articles

Epilepsy is a group of neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures are episodes that can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking. These episodes can result in physical injuries, including occasionally broken bones. In epilepsy, seizures have a tendency to recur and, as a rule, have no immediate underlying cause. Isolated seizures that are provoked by a specific cause such as poisoning are not deemed to represent epilepsy. People with epilepsy may be treated differently in various areas of the world and experience varying degrees of social stigma due to their condition.

A seizure, formally known as an epileptic seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with loss of consciousness, to shaking movements involving only part of the body with variable levels of consciousness, to a subtle momentary loss of awareness. Most of the time these episodes last less than 2 minutes and it takes some time to return to normal. Loss of bladder control may occur.

Myoclonus is a brief, involuntary, irregular twitching of a muscle or a group of muscles. It describes a medical sign and, generally, is not a diagnosis of a disease. These myoclonic twitches, jerks, or seizures are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions or brief lapses of contraction. The most common circumstance under which they occur is while falling asleep. Myoclonic jerks occur in healthy people and are experienced occasionally by everyone. However, when they appear with more persistence and become more widespread they can be a sign of various neurological disorders. Hiccups are a kind of myoclonic jerk specifically affecting the diaphragm. When a spasm is caused by another person it is known as a provoked spasm. Shuddering attacks in babies fall in this category.
Henri Jean Pascal Gastaut was a French neurologist and epileptologist.

Phenobarbital, also known as phenobarbitone or phenobarb, or by the trade name Luminal, is a medication of the barbiturate type. It is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the treatment of certain types of epilepsy in developing countries. In the developed world, it is commonly used to treat seizures in young children, while other medications are generally used in older children and adults. It may be used intravenously, injected into a muscle, or taken by mouth. The injectable form may be used to treat status epilepticus. Phenobarbital is occasionally used to treat trouble sleeping, anxiety, and drug withdrawal and to help with surgery. It usually begins working within five minutes when used intravenously and half an hour when administered by mouth. Its effects last for between four hours and two days.
Benign familial neonatal seizures (BFNS), formerly called benign familial neonatal convulsions (BFNC), is a rare autosomal dominant inherited form of seizures. It manifests in newborns, normally within the first 7 days of life, as tonic-clonic seizures. Infants are otherwise normal between attacks and develop without incident. Attacks normally spontaneously cease within the first 15 weeks of life. Lifetime susceptibility to seizures is increased, as 16% of those diagnosed with BFNE earlier in life will go on to have seizures versus a 2% lifetime risk for the general population. There are three known genetic causes of BFNE, two being the voltage-gated potassium channels KCNQ2 (BFNC1) and KCNQ3 (BFNC2) and the third being a chromosomal inversion (BFNC3). There is no obvious correlation between most of the known mutations and clinical variability seen in BFNE.
Ring chromosome 20, ring-shaped chromosome 20 or r(20) syndrome is a rare human chromosome abnormality where the two arms of chromosome 20 fuse to form a ring chromosome. The syndrome is associated with epileptic seizures, behaviour disorders and mental retardation.

Generalized epilepsy is a form of epilepsy characterised by generalised seizures with no apparent cause. Generalized seizures, as opposed to focal seizures, are a type of seizure that impairs consciousness and distorts the electrical activity of the whole or a larger portion of the brain.

Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour is a type of brain tumor. Most commonly found in the temporal lobe, DNTs have been classified as benign tumours. These are glioneuronal tumours comprising both glial and neuron cells and often have ties to focal cortical dysplasia.

Kv7.2 (KvLQT2) is a voltage- and lipid-gated potassium channel protein coded for by the gene KCNQ2.

Kv7.3 (KvLQT3) is a potassium channel protein coded for by the gene KCNQ3.
Navα1.2, also known as the sodium channel, voltage-gated, type II, alpha subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SCN2A gene. Functional sodium channels contain an ion conductive alpha subunit and one or more regulatory beta subunits. Sodium channels which contain the Navα1.2 subunit are called Nav1.2 channels.
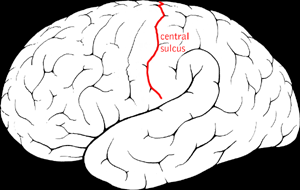
Benign Rolandic epilepsy or benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes (BCECTS) is the most common epilepsy syndrome in childhood. Most children will outgrow the syndrome, hence the label benign. The seizures, sometimes referred to as sylvian seizures, start around the central sulcus of the brain.
Panayiotopoulos syndrome is a common idiopathic childhood-related seizure disorder that occurs exclusively in otherwise normal children and manifests mainly with autonomic epileptic seizures and autonomic status epilepticus. An expert consensus has defined Panayiotopoulos syndrome as "a benign age-related focal seizure disorder occurring in early and mid-childhood. It is characterized by seizures, often prolonged, with predominantly autonomic symptoms, and by an EEG [electroencephalogram] that shows shifting and/or multiple foci, often with occipital predominance."
Benign neonatal sleep myoclonus (BNSM) is the occurrence of myoclonus during sleep. It is not associated with seizures.
Epilepsy is the most common childhood brain disorder in the United States. Nearly 3 million people have been diagnosed with this disease, while 450,000 of them are under the age of 17. Fortunately, two thirds of the child population will overcome the side effects, most notably, seizures, through treatment during adolescence. Epilepsy affects all ages groups. But for children, a variety of issues exist that can affect one's childhood.
Benign familial infantile epilepsy (BFIE) is an epilepsy syndrome. Affected children, who have no other health or developmental problems, develop seizures during infancy. These seizures have focal origin within the brain but may then spread to become generalised seizures. The seizures may occur several times a day, often grouped in clusters over one to three days followed by a gap of one to three months. Treatment with anticonvulsant drugs is not necessary but they are often prescribed and are effective at controlling the seizures. This form of epilepsy resolves after one or two years, and appears to be completely benign. The EEG of these children, between seizures, is normal. The brain appears normal on MRI scan.
Benign infantile epilepsy (BIE), also known as benign infantile seizures (BIS), is an epilepsy syndrome of which several forms have been described. The International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) classify two main forms of the syndrome though several other forms have been described in the academic literature. Affected children, who have no other health or developmental problems, develop seizures during infancy. These seizures have focal origin within the brain but may then spread to become generalised seizures. The seizures may occur several times a day, often grouped in clusters over one to three days followed by a gap of one to three months. Treatment with anticonvulsant drugs is not necessary but they are often prescribed and are effective at controlling the seizures. This form of epilepsy resolves after one or two years, and appears to be completely benign. The EEG of these children, between seizures, is normal. The brain appears normal on MRI scan.
People with epilepsy may be classified into different syndromes based on specific clinical features. These features include the age at which seizures begin, the seizure types, and EEG findings, among others. Identifying an epilepsy syndrome is useful as it helps determine the underlying causes as well as deciding what anti-seizure medication should be tried. Epilepsy syndromes are more commonly diagnosed in infants and children. Some examples of epilepsy syndromes include benign rolandic epilepsy, childhood absence epilepsy and juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Severe syndromes with diffuse brain dysfunction caused, at least partly, by some aspect of epilepsy, are also referred to as epileptic encephalopathies. These are associated with frequent seizures that are resistant to treatment and severe cognitive dysfunction, for instance Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and West syndrome.
A neonatal seizure is a seizure in a baby younger than 4 weeks old. Seizures are abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. They are the most frequent neurological problem in the nursery, and often require evaluation and treatment in a neonatal intensive care unit. Seizures in the neonatal population can be categorized into acute symptomatic seizures and genetic or structural causes. Diagnosis relies on identification of the cause of the seizure, and verification of an actual seizure activity by measuring of electrical activity with electroencephalography (EEG). Treatment depends on the cause of the seizure, but often includes pharmacologic treatment with anti-epileptic drugs.
References
- 1 2 3 Jerome Engel; Timothy A. Pedley; Jean Aicardi, eds. (2008). Epilepsy: A Comprehensive Textbook, Volume 3. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 2287. ISBN 9780781757775.
- ↑ National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (January 2012). "9". The Epilepsies: The diagnosis and management of the epilepsies in adults and children in primary and secondary care (PDF). National Clinical Guideline Centre. pp. 119–129.