
The Romualdo Formation is a geologic Konservat-Lagerstätte in northeastern Brazil's Araripe Basin where the states of Pernambuco, Piauí and Ceará come together. The geological formation, previously designated as the Romualdo Member of the Santana Formation, named after the village of Santana do Cariri, lies at the base of the Araripe Plateau. It was discovered by Johann Baptist von Spix in 1819. The strata were deposited during the Aptian stage of the Early Cretaceous in a lacustrine rift basin with shallow marine incursions of the proto-Atlantic. At that time, the South Atlantic was opening up in a long narrow shallow sea.

Cearadactylus is a genus of large anhanguerid pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Romualdo Formation of Brazil, South America. Fossil remains of Cearadactylus dated back to the Albian stage of the Early Cretaceous period, about 112 million years ago. The only known species is C. atrox, described and named in 1985 by Giuseppe Leonardi and Guido Borgomanero. The name refers to the Brazilian state Ceará, and combines this with Greek daktylos, "finger", a reference to the wing finger of pterosaurs. The Latin atrox means "frightful", a reference to the fearsome dentition of the species.

Ornithocheirus is a pterosaur genus known from fragmentary fossil remains uncovered from sediments in the United Kingdom and possibly Morocco.

Tropeognathus is a genus of large pterosaurs from the late Early Cretaceous of South America. This genus is considered to be a member of the family Anhangueridae, however, several studies have also recovered it within another family called Ornithocheiridae. Both of these families are diverse groups of pterosaurs known for their keel-tipped snouts and large size. Tropeognathus is regarded as the largest pterosaur found in the Southern Hemisphere, only rivaled by the huge azhdarchids. The type and only species is Tropeognathus mesembrinus. Fossil remains of Tropeognathus have been recovered from the Romualdo Formation, which is a Lagerstätte located in the Santana Group of the Araripe Basin in northeastern Brazil.

Thalassodromeus is a genus of pterosaur that lived in what is now Brazil during the Early Cretaceous period, about a hundred million years ago. The original skull, discovered in 1983 in the Araripe Basin of northeastern Brazil, was collected in several pieces. In 2002, the skull was made the holotype specimen of Thalassodromeus sethi by palaeontologists Alexander Kellner and Diogenes de Almeida Campos. The generic name means "sea runner", and the specific name refers to the Egyptian god Seth due to its crest being supposedly reminiscent of Seth's crown. Other scholars have pointed out that the crest was instead similar to the crown of Amon. A jaw tip was assigned to T. sethi in 2005, became the basis of the new genus Banguela in 2014, and assigned back to Thalassodromeus as the species T. oberlii in 2018. Another species was described in 2015 based on a supposed crest fragment, but this was later shown to be part of a turtle shell.
Anhanguera is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur known from the Early Cretaceous Romualdo Formation of Brazil and the Late Cretaceous Kem Kem Group of Morocco. This pterosaur is closely related to Ornithocheirus, but belongs in the family Anhangueridae. The generic name comes from the Tupi words añanga, meaning "spirit protector of the animals" + wera "bygone".
Araripesaurus is a genus a pterosaur belonging to the suborder Pterodactyloidea, it was discovered in the Romualdo Formation of the Santana Group in northeastern Brazil, which dates back to the Aptian and Albian of the Early Cretaceous. The type species is A. castilhoi.
Arthurdactylus is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Early Cretaceous Crato Formation of northeastern Brazil. It was a medium-sized pterosaur, with a wingspan of 4.5–4.6 metres (14.8–15.1 ft) and body mass of 15 kg (33 lb).
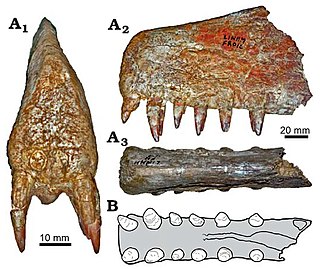
Siroccopteryx is an extinct genus of anhanguerid pterodactyloid pterosaur, known from middle Cretaceous sediments in modern-day Morocco. Some researchers, such as David M. Unwin, consider the genus a junior synonym of Coloborhynchus.

Coloborhynchus is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur belonging to the family Anhangueridae, though it has also been recovered as a member of the Ornithocheiridae in some studies. Coloborhynchus is known from the Lower Cretaceous of England, and depending on which species are included, possibly the Albian and Cenomanian ages as well. Coloborhynchus was once thought to be the largest known toothed pterosaur, however, a specimen of the closely related Tropeognathus is now thought to have had a larger wingspan.

Ludodactylus is a genus of anhanguerid pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Early Cretaceous period of what is now the Crato Formation of the Araripe Basin in Ceará, Brazil. The type and only species is L. sibbicki. The generic name Ludodactylus refers to the fact that the animal had the combination of teeth and a Pteranodon-like head crest, similar to many toy pterosaurs, and no such creature was known to exist until the discovery of Ludodactylus. However, Ludodactylus is not the only pterosaur known to possess these features, its very close relative Caulkicephalus is another example.

Santanadactylus was a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Albian-age Romualdo Member of the Upper Cretaceous Santana Formation, of Barra do Jardim, Araripe Plateau, Ceará State, Brazil. Four species have been named, but today are no considered congeneric with each other. It was a rather large pterosaur.

Ornithocheiridae is a group of pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. These pterosaurs were among the last to possess teeth. Members that belong to this group lived from the Early to Late Cretaceous periods, around 140 to 90 million years ago.
Barbosania is an extinct genus of crestless targaryendraconian pterosaur from the Cretaceous Romualdo Formation of the Santana Group of northeastern Brazil, dating to the Aptian to Albian.

Maaradactylus is a genus of anhanguerid pterodactyloid pterosaur known from the Lower Cretaceous period of the Romualdo Formation of northeastern Brazil.

The Araripe Basin is a rift basin covering about 8,000 square kilometres (3,100 sq mi), in Ceará, Piauí and Pernambuco states of northeastern Brazil. It is bounded by the Patos and Pernambuco lineaments, and is situated east of the Parnaíba Basin, southwest of the Rio do Peixe Basin and northwest of the Tucano and Jatobá Basins.

Ornithocheiromorpha is a group of pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. Fossil remains of this group date back from the Early to Late Cretaceous periods, around 140 to 92.5 million years ago. Ornithocheiromorphs were discovered worldwide except Antarctica, though most genera were recovered in Europe, Asia and South America. They were the most diverse and successful pterosaurs during the Early Cretaceous, but throughout the Late Cretaceous they were replaced by better adapted and more advanced pterosaur species such the pteranodontids and azhdarchoids. The Ornithocheiromorpha was defined in 2014 by Andres and colleagues, and they made Ornithocheiromorpha the most inclusive clade containing Ornithocheirus, but not Pteranodon.

Aymberedactylus is a genus of tapejarid pterosaur from the Early Cretaceous Crato Formation of Brazil. It contains a single species, A. cearensis.

The Santana Group is a geologic group, formerly included as the middle part of the Araripe Group, in the Araripe Basin of northeastern Brazil. The group comprises the Crato, Ipubi and Romualdo Formations and is dated to the Aptian to Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous. The formations of the group were deposited in a lacustrine to subtidal shallow marine environment in the Araripe rift basin.
























