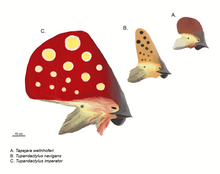
Tapejara is a genus of Brazilian pterosaur from the Cretaceous Period. Tapejara crests consisted of a semicircular crest over the snout, and a bony prong which extended back behind the head. It was a small pterosaur, with a wingspan of approximately 1.23–1.3 metres (4.0–4.3 ft).

Tupuxuara is a genus of large, crested, and toothless pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Early Cretaceous period of what is now the Romualdo Formation of the Santana Group, Brazil, about 125 to 112 million years ago. Tupuxuara is a close relative of Thalassodromeus, and both form a group that is either called Thalassodrominae or Thalassodromidae.

Tropeognathus is a genus of large pterosaurs from the late Early Cretaceous of South America. This genus is considered to be a member of the family Anhangueridae, however, several studies have also recovered it within another family called Ornithocheiridae. Both of these families are diverse groups of pterosaurs known for their keel-tipped snouts and large size. Tropeognathus is regarded as the largest pterosaur found in the Southern Hemisphere, only rivaled by the huge azhdarchids. The type and only species is Tropeognathus mesembrinus. Fossil remains of Tropeognathus have been recovered from the Romualdo Formation, which is a Lagerstätte located in the Santana Group of the Araripe Basin in northeastern Brazil.

Thalassodromeus is a genus of pterosaur that lived in what is now Brazil during the Early Cretaceous period, about a hundred million years ago. The original skull, discovered in 1983 in the Araripe Basin of northeastern Brazil, was collected in several pieces. In 2002, the skull was made the holotype specimen of Thalassodromeus sethi by palaeontologists Alexander Kellner and Diogenes de Almeida Campos. The generic name means "sea runner", and the specific name refers to the Egyptian god Seth due to its crest being supposedly reminiscent of Seth's crown. Other scholars have pointed out that the crest was instead similar to the crown of Amon. A jaw tip was assigned to T. sethi in 2005, became the basis of the new genus Banguela in 2014, and assigned back to Thalassodromeus as the species T. oberlii in 2018. Another species was described in 2015 based on a supposed crest fragment, but this was later shown to be part of a turtle shell.
Anhanguera is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur known from the Early Cretaceous Romualdo Formation of Brazil and the Late Cretaceous Kem Kem Group of Morocco. This pterosaur is closely related to Ornithocheirus, but belongs in the family Anhangueridae. The generic name comes from the Tupi words añanga, meaning "spirit protector of the animals" + wera "bygone".
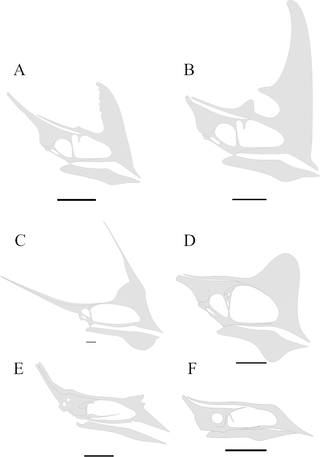
Tapejaridae are a family of pterodactyloid pterosaurs from the Cretaceous period. Members are currently known from Brazil, England, Hungary, Morocco, Spain, the United States, and China. The most primitive genera were found in China, indicating that the family has an Asian origin.
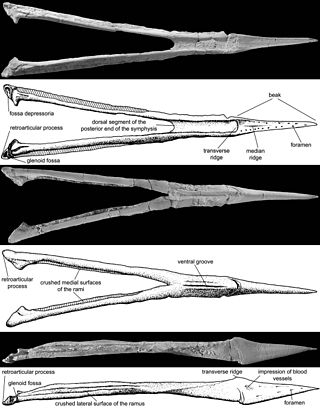
Bakonydraco is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of what is now the Csehbánya Formation of the Bakony Mountains, Iharkút, Veszprém, western Hungary.
Brasileodactylus a genus of pterosaur from the Aptian-age lower Santana formation of Chapada do Araripe, Ceará, Brazil.
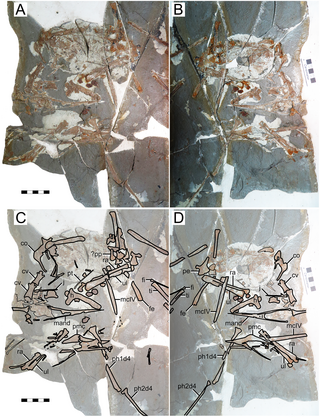
Eopteranodon is a genus of tapejarid pterosaur from the Aptian-age Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation of Beipiao City, Liaoning, China. The genus was named in 2005 by paleontologists Lü Junchang and Zhang Xingliao. The type species is Eopteranodon lii.

Feilongus is an extinct genus of ctenochasmatid pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Barremian–Aptian-age Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation of Beipiao, Liaoning, China.

Sinopterus is a genus of tapejarid pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Aptian-age Lower Cretaceous Jiufotang Formation of Chaoyang, Liaoning, China. It was first described and named by Wang Xiaolin and Zhou Zhonghe. Historically, there were multiple species attributed to the genus although only one is considered to be valid. Sinopterus is known for its proportionally large skull, which has a birdlike pointed beak, a long bony crest that starts with a tall premaxilla and goes back along the middle of the skull to form a point overhanging the rear of the skull, and its lack of teeth.

Azhdarchoidea is a group of pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea, more specifically within the group Ornithocheiroidea. Pterosaurs belonging to this group lived throughout the Early and Late Cretaceous periods, with one tentative member, Tendaguripterus, that lived in the Late Jurassic period. The largest azhdarchoids include members of the family Azhdarchidae, examples of these are Quetzalcoatlus, Hatzegopteryx, and Arambourgiania. The Azhdarchoidea has been recovered as either closely related to the Ctenochasmatoidea, as the sister taxon of the Pteranodontoidea within the Ornithocheiroidea, or within the Tapejaroidea, which in turn was also within the Ornithocheiroidea.

Ornithocheiridae is a group of pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. These pterosaurs were among the last to possess teeth. Members that belong to this group lived from the Early to Late Cretaceous periods, around 140 to 90 million years ago.

Thalassodrominae or Thalassodromidae is a group of azhdarchoid pterosaurs from the Cretaceous period. Its traditional members come from Brazil, however, other possible members also come from other places, including the United States, Morocco, and Argentina. Thalassodrominae is considered either to be a subfamily within the pterosaur family Tapejaridae, or as a distinct family, Thalassodromidae, within the clade Neoazhdarchia, closely related to dsungaripterids or azhdarchids.

Europejara is a genus of tapejarid pterosaur from the Early Cretaceous period of Spain. The type and only species known is Europejara olcadesorum.
Caiuajara is an extinct genus of tapejarid pterosaur from the Early Cretaceous period of Brazil. It is known from a single type species, Caiuajara dobruskii.

Ornithocheiromorpha is a group of pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. Fossil remains of this group date back from the Early to Late Cretaceous periods, around 140 to 92.5 million years ago. Ornithocheiromorphs were discovered worldwide except Antarctica, though most genera were recovered in Europe, Asia and South America. They were the most diverse and successful pterosaurs during the Early Cretaceous, but throughout the Late Cretaceous they were replaced by better adapted and more advanced pterosaur species such the pteranodontids and azhdarchoids. The Ornithocheiromorpha was defined in 2014 by Andres and colleagues, and they made Ornithocheiromorpha the most inclusive clade containing Ornithocheirus, but not Pteranodon.

Aymberedactylus is a genus of tapejarid pterosaur from the Early Cretaceous Crato Formation of Brazil. It contains a single species, A. cearensis.
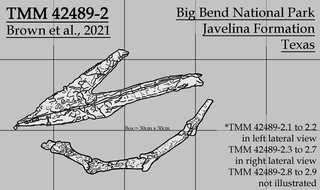
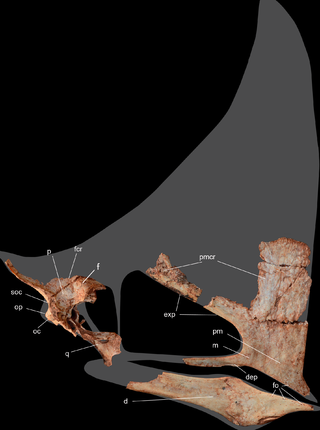
Wellnhopterus is an azhdarchid pterosaur recovered from the Late Cretaceous Javelina Formation in Texas that was previously identified as a thalassodromine. It consists of a set of upper and lower jaws, as well as some cervical vertebrae and a fragmentary long bone. In July 2021, the jaws were given the genus name "Javelinadactylus", with the type and only species as "J. sagebieli"; however, this article has now been retracted. In a paper published in December 2021, the complete holotype was independently named Wellnhopterus, with the only species being W. brevirostris. As of 2022, this is the formal name of this pterosaur.

Huaxiadraco is a genus of tapejarid pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Aptian-age Lower Cretaceous Jiufotang Formation of Chaoyang, Liaoning, China. It is the third valid genus of tapejarid from the Jehol Biota, after Sinopterus and Eopteranodon. It contains one species, Huaxiadraco corollatus, originally assigned to the defunct genus Huaxiapterus.