
The Rolls-Royce Turbomeca RTM322 is a turboshaft engine produced by Safran Helicopter Engines. It was originally conceived and manufactured by Rolls-Royce Turbomeca Limited, a joint venture between Rolls-Royce plc and Turbomeca. The engine was designed to suit a wide range of military and commercial helicopter designs. The RTM322 can also be employed in maritime and industrial applications.
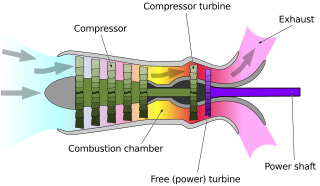
A turboshaft engine is a form of gas turbine that is optimized to produce shaftpower rather than jet thrust. In concept, turboshaft engines are very similar to turbojets, with additional turbine expansion to extract heat energy from the exhaust and convert it into output shaft power. They are even more similar to turboprops, with only minor differences, and a single engine is often sold in both forms.

The Rolls-Royce RB.39 Clyde was Rolls-Royce's first purpose-designed turboprop engine and the first turboprop engine to pass its civil and military type-tests.

The Napier Gazelle is a turboshaft helicopter engine that was manufactured by D. Napier & Son in the mid-1950s. In 1961 production was nominally transferred to a joint venture with Rolls-Royce called Napier Aero Engines Limited. But the venture closed two years later.

The Rolls-Royce Gnome is a British turboshaft engine originally developed by the de Havilland Engine Company as a licence-built General Electric T58, an American mid-1950s design. The Gnome came to Rolls-Royce after their takeover of Bristol Siddeley in 1968, Bristol having absorbed de Havilland Engines Limited in 1961.

The Rolls-Royce Gem is a turboshaft engine developed specifically for the Westland Lynx helicopter in the 1970s. The design started off at de Havilland Engine division and passed to Bristol Siddeley as the BS.360. Rolls-Royce bought out Bristol Siddeley in 1966 and after it dropped the Bristol Siddeley identity the engine became the RS.360.

The Armstrong Siddeley Python was an early British turboprop engine designed and built by the Armstrong Siddeley company in the mid-1940s. Its main use was in the Westland Wyvern, a carrier-based heavy fighter. The prototypes had used the Rolls-Royce Eagle piston engine, but Pythons were used in production aircraft. In this application, the Python was rated at 4,110 equivalent shaft horsepower (eshp).

The Allison Model 250, now known as the Rolls-Royce M250, is a highly successful turboshaft engine family, originally developed by the Allison Engine Company in the early 1960s. The Model 250 has been produced by Rolls-Royce since it acquired Allison in 1995.

The Turbomeca Astazou is a highly successful series of turboprop and turboshaft engines, first run in 1957. The original version weighed 110 kg (243 lb) and developed 240 kW (320 shp) at 40,000 rpm. It was admitted for aviation service on May 29, 1961, after a 150-hour test run. The main developing engineer was G. Sporer. It was named after two summits of the Pyrenees.

The Turbomeca Arriel is a series of French turboshaft engines that first ran in 1974. Delivering 650 to 1,000 hp, over 12,000 Arriel engines have been produced from 1978 to 2018, logging more than 50 million flight hours for 40 helicopter applications. In June 2018, 1,000 Arriel 2D were in service, powering H125 and H130 single-engine helicopters, having logged one million flight hours since 2011. After endurance tests and fleet data analysis, their TBO increased by 25% to 5,000 hours and mandatory inspection rose to 15 years with no hourly limit, lowering maintenance costs.

The Turbomeca Artouste is an early French turboshaft engine, first run in 1947. Originally conceived as an auxiliary power unit (APU), it was soon adapted to aircraft propulsion, and found a niche as a powerplant for turboshaft-driven helicopters in the 1950s. Artoustes were licence-built by Bristol Siddeley in the UK, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited in India, and developed by Continental CAE in the US as the Continental T51. Two major versions of the Artouste were produced. The Artouste II family, mainly used in the Aérospatiale Alouette II helicopter, had a one-stage centrifugal compressor and a two-stage turbine, with gearbox-limited power of 300 kW (400 hp). The Artouste III family, mainly used in Aérospatiale's Alouette III and Lama helicopters, had a two-stage axial-centrifugal compressor and a three-stage turbine, with gearbox-limited power of 420–440 kW (560–590 hp).

The Turbomeca Turmo is a family of French turboshaft engines manufacturered for helicopter use. Developed from the earlier Turbomeca Artouste, later versions delivered up to 1,300 kW (1,700 shp). A turboprop version was developed for use with the Bréguet 941 transport aircraft.

The Napier Eland was a British turboshaft or turboprop gas-turbine engine built by Napier & Son in the early 1950s. Production of the Eland ceased in 1961 when the Napier company was taken over by Rolls-Royce.

The Safran Ardiden is a 1,400–2,000 hp (1,000–1,500 kW) turboshaft designed and produced by Safran Helicopter Engines for 5–8 t (11,000–18,000 lb) single and twin-engine helicopters. Launched in 2003 as a more powerful TM 333, it first ran in 2005 and was introduced in 2007. The Ardiden 1 Shakti powers the Indian HAL Dhruv, Light Combat Helicopter and Light Utility Helicopter while the more powerful Ardiden 3 powers the Avicopter AC352 and Kamov Ka-62.

The Boeing T50 was a small turboshaft engine produced by Boeing. It was the first turboshaft engine to ever power a helicopter: a modified Kaman K-225 in 1951. Based on Boeing's earlier Model 500 gas generator, the T50's main application was in the QH-50 DASH helicopter drone of the 1950s. An up-rated version designated Model 550 was developed to power the QH-50D and was given the military designation T50-BO-12.

The Continental CAE T51 was a small turboshaft engine produced by Continental Aviation and Engineering (CAE) under license from Turbomeca. A development of the Artouste, it was followed by three additional turboshaft engines, the T72, the T65, and the T67. However, none of these engines, including the T51, entered full production. CAE abandoned turboshaft development in 1967 after the XT67 lost to the Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6T (T400) to power the Bell UH-1N Twin Huey.

The Saro P.531 is a British all-metal five-seat helicopter designed and built by Saunders-Roe Limited (Saro).

The Turbomeca Palouste is a French gas turbine engine, first run in 1952. Designed purely as a compressed air generator, the Palouste was mainly used as a ground-based aircraft engine starter unit. Other uses included rotor tip propulsion for helicopters.
The Turbomeca Orédon was a small French turbo-shaft / Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) engine produced by Turbomeca in the late 1940s.

A free-turbine turboshaft is a form of turboshaft or turboprop gas turbine engine where the power is extracted from the exhaust stream of a gas turbine by an independent turbine, downstream of the gas turbine. The power turbine is not mechanically connected to the turbines that drive the compressors, hence the term "free", referring to the independence of the power output shaft. This is opposed to the power being extracted from the turbine/compressor shaft via a gearbox.




















