Related Research Articles
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in the U.S. state of Oklahoma.
Capital punishment in France is banned by Article 66-1 of the Constitution of the French Republic, voted as a constitutional amendment by the Congress of the French Parliament on 19 February 2007 and simply stating "No one can be sentenced to the death penalty". The death penalty was already declared illegal on 9 October 1981 when President François Mitterrand signed a law prohibiting the judicial system from using it and commuting the sentences of the seven people on death row to life imprisonment. The last execution took place by guillotine, being the main legal method since the French Revolution; Hamida Djandoubi, a Tunisian citizen convicted of torture and murder on French soil, who was put to death in September 1977 in Marseille.

Human rights are largely respected in Switzerland, one of Europe's oldest democracies. Switzerland is often at or near the top in international rankings of civil liberties and political rights observance. Switzerland places human rights at the core of the nation's value system, as represented in its Federal Constitution. As described in its FDFA's Foreign Policy Strategy 2016-2019, the promotion of peace, mutual respect, equality and non-discrimination are central to the country's foreign relations.
Capital punishment in Sweden was last used in 1910, though it remained a legal sentence for at least some crimes until 1973. It is now outlawed by the Swedish Constitution, which states that capital punishment, corporal punishment, and torture are strictly prohibited. At the time of the abolition of the death penalty in Sweden, the legal method of execution was beheading.

Capital punishment for murder was abolished in Cyprus on 15 December 1983. It was abolished for all crimes on 19 April 2002. The death penalty was replaced with life imprisonment. Cyprus is a signatory of the second optional protocol of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights which provides for full abolition of capital punishment. Cyprus initially had a reservation on the second protocol, allowing execution for grave crimes in times of war, but subsequently gave up this reservation. The Constitution of Cyprus was amended in 2016 to wipe out all forms of capital punishment.
Capital punishment in the Philippines specifically, the death penalty, as a form of state-sponsored repression, was introduced and widely practiced by the Spanish government in the Philippines. A substantial number of Filipino national martyrs like Mariano Gómez, José Burgos, and Jacinto Zamora, Thirteen Martyrs of Cavite, Thirteen Martyrs of Bagumbayan, Fifteen Martyrs of Bicol, Nineteen Martyrs of Aklan and Jose Rizal were executed by the Spanish government.
Capital punishment for murder was abolished in Malta in 1971. It continued to be part of the country's military code until it was fully abolished on 21 March 2000. Malta is a signatory of the Second Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights that commits it to abolition of the death penalty within its borders. Malta has also ratified protocol 13 to the European Convention on Human Rights, that bans the death penalty in all circumstances.
Capital punishment is a long unused form of punishment in Brazil. Its last recorded use was in 1876. Although virtually abolished, it is still possible during wartime, according to the Article 5, XLVII, "a", of the Federal Constitution. Brazil is the most populous country in the world that does not retain the death penalty in practice.

Capital punishment in Armenia was a method of punishment that was implemented within Armenia's Criminal Code and Constitution until its eventual relinquishment in the 2003 modifications made to the Constitution. Capital punishment's origin in Armenia is unknown, yet it remained present in the Armenia Criminal Code of 1961, which was enforced and applied until 1999. Capital punishment was incorporated in Armenian legislation and effectuated for capital crimes, which were crimes that were classified to be punishable by death, this included: treason, espionage, first-degree murder, acts of terrorism and grave military crimes.
Capital punishment in Belgium was formally abolished on August 1, 1996 for all crimes, in both peacetime and wartime. The last execution for crimes committed in peacetime took place in July 1863, when in Ypres a farmer was executed for murder. The last execution for an ordinary crime took place on 26 March 1918 at Veurne Prison when Emile Ferfaille, a military officer found guilty of killing his pregnant girlfriend, was guillotined. This was the first execution to be carried out since 1863. The guillotine that was used had to be imported from France.
Capital punishment in modern Greece was carried out using the guillotine or by firing squad. It was last applied in 1972 during the military junta, and the death penalty was abolished in stages between 1975 and 2005.
Capital punishment in Latvia was abolished for ordinary crimes in 1999 and for crimes committed during wartime in 2012. Latvia is party to several international instruments which ban the capital punishment.
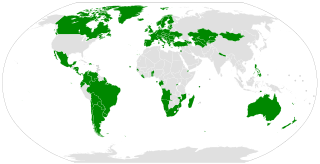
The Second Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, aiming at the abolition of the death penalty, is a subsidiary agreement to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights. It was created on 15 December 1989 and entered into force on 11 July 1991. As of December 2021, the Optional Protocol has 89 state parties. The most recent country to ratify was Armenia, on 18 March 2021.
Capital punishment was used from the creation of the modern Serbian state in 1804. On 26 February 2002, the Serbian Parliament adopted amendments striking the death penalty from the Criminal Code. The last execution, by shooting, took place on 14 February 1992, and the last death sentences were pronounced in 2001. Serbia is bound by the following international conventions prohibiting capital punishment : The Second Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, and Protocols No. 6 and No. 13 to the European Convention on Human Rights. According to Article 24 of the Serbian constitution (2006): „Human life is inviolable. There shall be no death penalty in the Republic of Serbia“.
Capital punishment in Turkmenistan was originally allowed by Article 20 of the 1992 Constitution, where it was described as "an exceptional punishment for the heaviest of crimes". In December 1999, a presidential decree abolished capital punishment "forever".
In Papua New Guinea (PNG), also officially known as the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, capital punishment was abolished for the second time on 22 January 2022.
Capital punishment in Montenegro was first prescribed by law in 1798. It was abolished on 19 June 2002. The last execution, by shooting, took place on 29 January 1981, and the two last death sentences were pronounced on 11 October 2001. Montenegro is bound by the following international conventions prohibiting capital punishment : Second Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, as well as Protocols No. 6 and No. 13 to the European Convention on Human Rights. According to Art. 26 of the Montenegrin Constitution (2007): „In Montenegro, capital punishment is forbidden”.
Capital punishment in Kazakhstan was abolished for all crimes in 2021.
Capital punishment in Bangladesh is a legal form of punishment for anyone who is over 16, however in practice will not apply to people under 18. Crimes that are currently punishable by death in Bangladesh are set out in the Penal Code 1860. These include waging war against Bangladesh, abetting mutiny, giving false evidence upon which an innocent person suffers death, murder, assisted suicide of a child, attempted murder of a child, and kidnapping. The Code of Criminal Procedure 1898 provides that "he be hanged by the neck until he is dead." For murder cases, the Appellate Division requires trial courts to weigh aggravating and mitigating factors to determine whether the death penalty is warranted.
Capital punishment has been abolished in Seychelles. The country permanently abolished the death penalty by a Constitutional amendment in June 1993.
References
- ↑ The 1994 Constitution of the Republic of Tajikistan, English translation (raw draft)
- ↑ Ratification of Second Optional Protocol on abolition of death penalty