
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths are a phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates. Unlike other bilaterians, they are acoelomates, and have no specialised circulatory and respiratory organs, which restricts them to having flattened shapes that allow oxygen and nutrients to pass through their bodies by diffusion. The digestive cavity has only one opening for both ingestion and egestion ; as a result, the food cannot be processed continuously.

Acanthocephala is a group of parasitic worms known as acanthocephalans, thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms, characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce and hold the gut wall of its host. Acanthocephalans have complex life cycles, involving at least two hosts, which may include invertebrates, fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. About 1420 species have been described.

Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes.
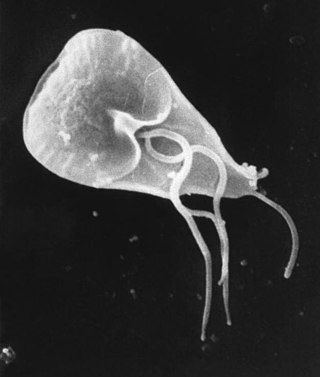
Giardia duodenalis, also known as Giardia intestinalis and Giardia lamblia, is a flagellated parasitic microorganism of the genus Giardia that colonizes the small intestine, causing a diarrheal condition known as giardiasis. The parasite attaches to the epithelium by a ventral adhesive disc or sucker, and reproduces via binary fission. Giardiasis does not spread via the bloodstream, nor does it spread to other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, but remains confined to the lumen of the small intestine. Giardia has an outer membrane that makes it possible to retain life, even when outside of the host body, and which can make it tolerant to chlorine disinfection. Giardia trophozoites absorb their nutrients from the lumen, and are anaerobes. If the organism is split and stained, its characteristic pattern resembles the familiar "smiley face" symbol.

Plasmodium is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of Plasmodium species involve development in a blood-feeding insect host which then injects parasites into a vertebrate host during a blood meal. Parasites grow within a vertebrate body tissue before entering the bloodstream to infect red blood cells. The ensuing destruction of host red blood cells can result in malaria. During this infection, some parasites are picked up by a blood-feeding insect, continuing the life cycle.

Balantidium is a genus of ciliates. It contains the parasitic species Balantidium coli, the only known cause of balantidiasis.

Microsporidia are a group of spore-forming unicellular parasites. These spores contain an extrusion apparatus that has a coiled polar tube ending in an anchoring disc at the apical part of the spore. They were once considered protozoans or protists, but are now known to be fungi, or a sister group to fungi. These fungal microbes are obligate eukaryotic parasites that use a unique mechanism to infect host cells. They have recently been discovered in a 2017 Cornell study to infect Coleoptera on a large scale. So far, about 1500 of the probably more than one million species are named. Microsporidia are restricted to animal hosts, and all major groups of animals host microsporidia. Most infect insects, but they are also responsible for common diseases of crustaceans and fish. The named species of microsporidia usually infect one host species or a group of closely related taxa. Approximately 10 percent of the species are parasites of vertebrates —several species, most of which are opportunistic, can infect humans, in whom they can cause microsporidiosis.

Nycteribiidae is a family of the true fly superfamily Hippoboscoidea are known as "bat flies", together with their close relatives the Streblidae. As the latter do not seem to be a monophyletic group, it is conceivable that bat flies cannot be united into a single family.

Trypanosoma cruzi is a species of parasitic euglenoids. Among the protozoa, the trypanosomes characteristically bore tissue in another organism and feed on blood (primarily) and also lymph. This behaviour causes disease or the likelihood of disease that varies with the organism: Chagas disease in humans, dourine and surra in horses, and a brucellosis-like disease in cattle. Parasites need a host body and the haematophagous insect triatomine is the major vector in accord with a mechanism of infection. The triatomine likes the nests of vertebrate animals for shelter, where it bites and sucks blood for food. Individual triatomines infected with protozoa from other contact with animals transmit trypanosomes when the triatomine deposits its faeces on the host's skin surface and then bites. Penetration of the infected faeces is further facilitated by the scratching of the bite area by the human or animal host.
A parasite is an organism that has sustained contact with another organism to the detriment of the host organism.

The Onchocercidae are a family of nematodes in the superfamily Filarioidea. This family includes some of the most devastating human parasitic diseases, such as lymphatic filariasis, onchocerciasis, loiasis, and other filariases.

The Zoopagomycotina are a subdivision of the fungal division Zygomycota sensu lato. It contains 5 families and 20 genera. Relationships among and within subphyla of Zygomycota are poorly understood, and their monophyly remains in question, so they are sometimes referred to by the informal name zygomycetes.
Chromera velia, also known as a "chromerid", is a unicellular photosynthetic organism in the superphylum Alveolata. It is of interest in the study of apicomplexan parasites, specifically their evolution and accordingly, their unique vulnerabilities to drugs.

Nosopsyllus fasciatus, the northern rat flea, is a species of flea found on domestic rats and house mice. Northern rat fleas are external parasites, living by hematophagy off the blood of rodents. N. fasciatus can bite humans, but they are more common parasites of rodents. Since they are associated with humans, they are common disease vectors that can spread from animals to humans. Diseases that can be spread through fleas include the plague and typhus. The rat flea is widespread due to their relationship to rodents and other vertebrates. They can be found co-infecting their host with other parasites.

Paraneoptera or Acercaria is a superorder of insects which includes lice, thrips, and hemipterans, the true bugs. It also includes the extinct order Permopsocida, known from fossils dating from the Early Permian to the mid-Cretaceous.
Dasypsyllus is a widespread genus of fleas. Some of its members are found in bird nests, including the moorhen flea, D. gallinulae.

Ceratophyllus gallinae, known as the hen flea in Europe or the European chicken flea elsewhere, is an ectoparasite of birds. This flea was first described by the German botanist and entomologist Franz von Paula Schrank in 1803.
Defretinella is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexa.
Legerella is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this genus that usually infect the malpighian tubules of invertebrates.
Lipotropha is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexa.













