
The Santalales are an order of flowering plants in the dicotyledons. Well-known members of the Santalales include sandalwoods and the many species of mistletoes. The order has a cosmopolitan distribution, but is heavily concentrated in tropical and subtropical regions. It derives its name from its type genus, Santalum (sandalwood).

The Nymphaeales are an order of flowering plants, consisting of three families of aquatic plants, the Hydatellaceae, the Cabombaceae, and the Nymphaeaceae. It is one of the three orders of basal angiosperms, an early-diverging grade of flowering plants. At least 10 morphological characters unite the Nymphaeales. One of the traits is the absence of a vascular cambium, which is required to produce both xylem (wood) and phloem, which therefore are missing. Molecular synapomorphies are also known.

Nymphaeaceae is a family of flowering plants, commonly called water lilies. They live as rhizomatous aquatic herbs in temperate and tropical climates around the world. The family contains five genera with about 70 known species. Water lilies are rooted in soil in bodies of water, with leaves and flowers floating on or rising from the surface. Leaves are oval and heart-shaped in Barclaya. Leaves are round, with a radial notch in Nymphaea and Nuphar, but fully circular in Victoria and Euryale.

Ceratophyllaceae is a cosmopolitan family of flowering plants including one living genus commonly found in ponds, marshes, and quiet streams in tropical and in temperate regions. It is the only extant family in the order Ceratophyllales. Species are commonly called coontails or hornworts, although hornwort is also used for unrelated plants of the division Anthocerotophyta.

Amborella is a monotypic genus of understory shrubs or small trees endemic to the main island, Grande Terre, of New Caledonia in the southwest Pacific Ocean. The genus is the only member of the family Amborellaceae and the order Amborellales and contains a single species, Amborella trichopoda. Amborella is of great interest to plant systematists because molecular phylogenetic analyses consistently place it as the sister group to all other flowering plants, meaning it was the earliest group to evolve separately from all other flowering plants.

The water-plantains (Alismataceae) are a family of flowering plants, comprising 20 genera and 119 species. The family has a cosmopolitan distribution, with the greatest number of species in temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Most of the species are herbaceous aquatic plants growing in marshes and ponds.

Nelumbonaceae is a family of aquatic flowering plants. Nelumbo is the sole extant genus, containing Nelumbo lutea, native to North America, and Nelumbo nucifera, widespread in Asia. At least five other genera, Nelumbites, Exnelumbites, Paleonelumbo, Nelumbago, and Notocyamus are known from fossils.

Juncaginaceae is a family of flowering plants, recognized by most taxonomists for the past few decades. It is also known as the arrowgrass family. It includes 3 genera with a total of 34 known species.

Chloranthaceae is a family of flowering plants (angiosperms), the only family in the order Chloranthales. It is not closely related to any other family of flowering plants, and is among the early-diverging lineages in the angiosperms. They are woody or weakly woody plants occurring in Southeast Asia, the Pacific, Madagascar, Central and South America, and the West Indies. The family consists of four extant genera, totalling about 77 known species according to Christenhusz and Byng in 2016. Some species are used in traditional medicine. The type genus is Chloranthus. The fossil record of the family, mostly represented by pollen such as Clavatipollenites, extends back to the dawn of the history of flowering plants in the Early Cretaceous, and has been found on all continents.

The Cabombaceae are a family of aquatic, herbaceous flowering plants. A common name for its species is water shield. The family is recognised as distinct in the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group IV system (2016). The family consists of two genera of aquatic plants, Brasenia and Cabomba, totalling six species.

Trimeniaceae is a family of flowering plants recognized by most taxonomists, at least for the past several decades. It is a small family of one genus, Trimenia, with eight known species of woody plants, bearing essential oils. The family is subtropical to tropical and found in Southeast Asia, eastern Australia and on several Pacific Islands.
Plant taxonomy is the science that finds, identifies, describes, classifies, and names plants. It is one of the main branches of taxonomy.
The APG II system of plant classification is the second, now obsolete, version of a modern, mostly molecular-based, system of plant taxonomy that was published in April 2003 by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group. It was a revision of the first APG system, published in 1998, and was superseded in 2009 by a further revision, the APG III system.
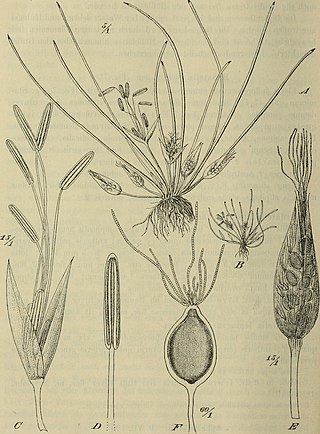
Hydatellaceae are a family of small, aquatic flowering plants. The family consists of tiny, relatively simple plants occurring in Australasia and India. It was formerly considered to be related to the grasses and sedges, but has been reassigned to the order Nymphaeales as a result of DNA and morphological analyses showing that it represents one of the earliest groups to split off in flowering-plant phylogeny, rather than having a close relationship to monocots, which it bears a superficial resemblance to due to convergent evolution. The family includes only the genus Trithuria, which has at least 13 species, although species diversity in the family has probably been substantially underestimated.

Ceratophyllum demersum, commonly known as hornwort, rigid hornwort, coontail, or coon's tail, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Ceratophyllum. It is a submerged, free-floating aquatic plant, with a cosmopolitan distribution, native to all continents except Antarctica. It is a harmful weed introduced in New Zealand. It is also a popular aquarium plant. Its genome has been sequenced to study angiosperm evolution.

The basal angiosperms are the flowering plants which diverged from the lineage leading to most flowering plants. In particular, the most basal angiosperms were called the ANITA grade, which is made up of Amborella, Nymphaeales and Austrobaileyales.

Mesangiospermae is a clade that contains the majority of flowering plants (angiosperms). Mesangiosperms are therefore known as the core angiosperms, in contrast to the three orders of earlier-diverging species known as the basal angiosperms: Nymphaeales, Austrobaileyales, and Amborellales. Mesangiospermae includes about 350,000 species, while there are about 175 extant species of basal angiosperms.

Hydrostachys is a genus of about 22 species of flowering plants native to Madagascar and southern and central Africa. It is the only genus in the family Hydrostachyaceae. All species of Hydrostachys are aquatic, growing on rocks in fast-moving water. They have tuberous roots, usually pinnately compound leaves, and highly reduced flowers on dense spikes.



















