
The economy of Finland is a highly industrialised, mixed economy with a per capita output similar to that of western European economies such as France, Germany, and the United Kingdom. The largest sector of Finland's economy is its service sector, which contributes 72.7% to the country's gross domestic product (GDP); followed by manufacturing and refining at 31.4%; and concluded with the country's primary sector at 2.9%.

The economy of Germany is a highly developed social market economy. It has the largest national economy in Europe, the third-largest by nominal GDP in the world, and fifth by GDP (PPP). Due to a volatile currency exchange rate, Germany's GDP as measured in dollars fluctuates sharply. In 2017, the country accounted for 28% of the euro area economy according to the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Germany is a founding member of the European Union and the Eurozone.

The economy of the United Kingdom is a highly developed social market economy. It is the sixth-largest national economy in the world measured by nominal gross domestic product (GDP), ninth-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP), and twenty-first by nominal GDP per capita, constituting 3.1% of nominal world GDP. The United Kingdom constitutes 2.3% of world GDP by purchasing power parity (PPP).
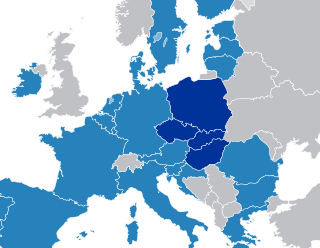
The Visegrád Group is a cultural and political alliance of four Central European countries: the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. The alliance aims to advance co-operation in military, economic, cultural and energy affairs, and to further their integration with the EU. All four states are also members of the European Union (EU), the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), and the Bucharest Nine (B9).

Saxony-Anhalt is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of 20,451.7 square kilometres (7,896.4 sq mi) and has a population of 2.17 million inhabitants, making it the 8th-largest state in Germany by area and the 11th-largest by population. Its capital is Magdeburg and its largest city is Halle (Saale).

The chemical industry comprises the companies and other organizations that develop and produce industrial, specialty and other chemicals. Central to the modern world economy, it converts raw materials into commodity chemicals for industrial and consumer products. It includes industries for petrochemicals such as polymers for plastics and synthetic fibers; inorganic chemicals such as acids and alkalis; agricultural chemicals such as fertilizers, pesticides and herbicides; and other categories such as industrial gases, speciality chemicals and pharmaceuticals.

The economy of France is a highly developed social market economy with notable state participation in strategic sectors. It is the world's seventh-largest economy by nominal GDP and the ninth-largest economy by PPP, constituting around 4% of world GDP. Due to a volatile currency exchange rate, France's GDP as measured in dollars fluctuates sharply. France has a diversified economy, that is dominated by the service sector, whilst the industrial sector accounted for 19.5% of its GDP and the primary sector accounted for the remaining 1.7%. In 2020, France was the largest Foreign Direct Investment recipient in Europe, and Europe's second largest spender in research and development. It was ranked among the 10 most innovative countries in the world by the 2020 Bloomberg Innovation Index, as well as the 15th most competitive nation globally according to the 2019 Global Competitiveness Report. It was the fifth-largest trading nation in the world. France is also the most visited destination in the world, as well as the European Union's leading agricultural power.

I. G. Farbenindustrie AG, commonly known as IG Farben, was a German chemical and pharmaceutical conglomerate. Formed in 1925 from a merger of six chemical companies—BASF, Bayer, Hoechst, Agfa, Chemische Fabrik Griesheim-Elektron, and Chemische Fabrik vorm. Weiler Ter Meer—it was seized by the Allies after World War II and divided back into its constituent companies.

BASF SE, an initialism of its original name Badische Anilin- und Sodafabrik, is a European multinational company and the largest chemical producer in the world. Its headquarters are located in Ludwigshafen, Germany.
The Merck Group, branded and commonly known as Merck, is a German multinational science and technology company headquartered in Darmstadt, with about 60,000 employees and a presence in 66 countries. The group includes around 250 companies; the main company is Merck KGaA in Germany. The company is divided into three business lines: Healthcare, Life Sciences and Electronics. Merck was founded in 1668 and is the world's oldest operating chemical and pharmaceutical company, as well as one of the largest pharmaceutical companies globally.

The textile industry is primarily concerned with the design, production and distribution of textiles: yarn, cloth and clothing. The raw material may be natural, or synthetic using products of the chemical industry.

Holcim is a Swiss-based global building materials and aggregates flagship division of the Holcim Group. The original company was merged on 10 July 2015 with Lafarge to form LafargeHolcim as the new company and renamed to Holcim Group in 2021. When the merger was completed, the Holcim brand remain active within the group.

The economy of Paris is based largely on services and commerce: of the 390,480 of its enterprises, 80.6 percent are engaged in commerce, transportation, and diverse services, 6.5 percent in construction, and just 3.8 percent in industry. Paris, including both the City of Paris and the Île-de-France region, is the most important center of economic activity in France, accounting for about thirty percent of the French GDP.

German–Iranian relations are the bilateral relations between Germany and Iran. Official diplomatic relations between Iran and Germany after World War II began in 1939, when Iran opened its first diplomatic mission office in Bonn, both countries′ predecessor states had maintained formal diplomatic relations since the end of 19th century. Germany has an embassy in Tehran, which was originally established in the court of Naser al-Din Shah Qajar in October 1884 and has been in the present building since 1894. Iran opened its embassy in Berlin in 1885. Germany and Iran continued to have political relations well into World War II. In December 2022, Germany said it was "suspending state incentives to promote trade with Iran due to the repression of demonstrators."
Until the early 19th century, Germany, a federation of numerous states of varying size and development, retained its pre-industrial character, where trade centered around a number of free cities. After the extensive development of the railway network during the 1840s, rapid economic growth and modernisation sparked the process of industrialization. Under Prussian leadership Germany was united in 1871 and its economy grew rapidly. The largest economy in Europe by 1900, Germany had established a primary position in several key sectors, like the chemical industry and steel production. High production capacity, permanent competitiveness and subsequent protectionist policies fought out with the US and Britain were essential characteristics.

Sir Leonard Valentinovich Blavatnik is a Ukrainian-born British-American businessman and philanthropist. As of October 2023, Forbes estimated his net worth at $29.6 billion. In 2017, Blavatnik received a knighthood for services to philanthropy.

China National Chemical Corporation, commonly known as ChemChina, is a Chinese state-owned chemical company in the product segments of agrochemicals, rubber products, chemical materials and specialty chemicals, industrial equipment, and petrochemical processing for the civilian and military sectors. As of 2020, it is ranked 164th among the Fortune Global 500 companies.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc., commonly shortened to DuPont, is an American multinational chemical company first formed in 1802 by French-American chemist and industrialist Éleuthère Irénée du Pont de Nemours. The company played a major role in the development of Delaware and first arose as a major supplier of gunpowder. DuPont developed many polymers such as Vespel, neoprene, nylon, Corian, Teflon, Mylar, Kapton, Kevlar, Zemdrain, M5 fiber, Nomex, Tyvek, Sorona, Corfam and Lycra in the 20th century, and its scientists developed many chemicals, most notably Freon (chlorofluorocarbons), for the refrigerant industry. It also developed synthetic pigments and paints including ChromaFlair.
The chemical industry in the United Kingdom is one of the UK's main manufacturing industries. At one time, the UK's chemical industry was a world leader. The industry has also been environmentally damaging, and includes radioactive nuclear industries.

Marl Chemical Park is an industrial park in Marl, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the third largest industrial cluster in Germany and among the largest chemical production facilities in Europe. The site occupies over 6 square kilometers, hosts 100 chemical plants, employs 10,000 people, and produces 4 million metric tons of chemicals annually. 18 companies are based in the Park, including primary tenant Evonik Industries AG, which also owns and operates the infrastructure through its subsidiary Infracor GmbH.

















