


Chenille is a type of yarn, or the fabric made from it. Chenille is the French word for caterpillar whose fur the yarn is supposed to resemble.



Chenille is a type of yarn, or the fabric made from it. Chenille is the French word for caterpillar whose fur the yarn is supposed to resemble.
According to textile historians, chenille-type yarn is a recent invention, dating to the 18th century and believed to have originated in France. The original technique involved weaving a "leno" fabric and then cutting the fabric into strips to make the chenille yarn.
Alexander Buchanan, a foreman in a Paisley fabric mill, is credited with introducing chenille fabric to Scotland in the 1830s. Here he developed a way to weave fuzzy shawls. Tufts of coloured wool were woven together into a blanket that was then cut into strips. They were treated by heating rollers in order to create the frizz. This resulted in a very soft, fuzzy fabric named chenille. Another Paisley shawl manufacturer went on to further develop the technique. James Templeton and William Quiglay worked to refine this process while working on imitation oriental rugs. [1] The intricate patterns used to be difficult to reproduce by automation, but this technique solved that issue. These men patented the process but Quiglay soon sold out his interest. Templeton then went on to open a successful carpet company (James Templeton & Co) that became a leading carpet manufacturer throughout the 19th and 20th centuries.
In the 1920s and 1930s, Dalton in Northwest Georgia became the tufted bedspread capital of the US thanks to Catherine Evans (later adding Whitener) who initially revived the handcraft technique in the 1890s. Hand-tufted bedspreads with an embroidered appearance became increasingly popular and were referred to as "chenille" a term which stuck. [2] With effective marketing, chenille bedspreads appeared in city department stores and tufting subsequently became important to the economic development of North Georgia, maintaining families even through the Depression era. [2] Merchants organised "spread houses" where products tufted on farms were finished using heat washing to shrink and "set" the fabric. Trucks delivered pattern-stamped sheets and dyed chenille yarns to families for tufting before returning to pay the tufters and collect the spreads for finishing. By this time, tufters all over the state were creating not only bedspreads but pillow shams and mats and selling them by the highway. [2] The first to make a million dollars in the bedspread business, was Dalton County native, B. J. Bandy with the help of his wife, Dicksie Bradley Bandy, by the late 1930s, to be followed by many others. [2]
In the 1930s, usage for the tufted fabric became widely desirable for throws, mats, bedspreads, and carpets, but not as yet, apparel. Companies shifted handwork from the farms into factories for greater control and productivity, encouraged as they were to pursue centralized production by the wage and hour provisions of the National Recovery Administration's tufted bedspread code. With the trend towards mechanization, adapted sewing machines were used to insert raised yarn tufts. [2]
Chenille became popularized for apparel again with commercial production in the 1970s.
Standards of industrial production were not introduced until the 1990s, when the Chenille International Manufacturers Association (CIMA) was formed with the mission to improve and develop the manufacturing processes. [3] From the 1970s each machine head made two chenille yarns straight onto bobbins, a machine could have over 100 spindles (50 heads). Giesse was one of the first major machine manufacturers. Giesse acquired Iteco company in 2010 integrating the chenille yarn electronic quality control directly on their machine. Chenille fabrics are also often used in Letterman jackets also known as "varsity jackets", for the letter patches.
The chenille yarn is manufactured by placing short lengths of yarn, called the "pile", between two "core yarns" and then twisting the yarn together. The edges of these piles then stand at right angles to the yarn's core, giving chenille both its softness and its characteristic look. Chenille will look different in one direction compared to another, as the fibers catch the light differently. Chenille can appear iridescent without actually using Iridescence fibers. The yarn is commonly manufactured from cotton, but can also be made using acrylic, rayon and olefin.
One of the problems with chenille yarns is that the tufts can work loose and create bare fabric. This was resolved by using a low melt nylon in the core of the yarn and then autoclaving (steaming) the hanks of yarn to set the pile in place.
Since the late 1990s, chenille appeared in quilting in a number of yarns, yards or finishes. As a yarn, it is a soft, feathery synthetic that when stitched onto a backing fabric, gives a velvety appearance, also known as imitation or "faux chenille". Real chenille quilts are made using patches of chenille fabric in various patterns and colors, with or without "ragging" the seams.
The chenille effect by ragging the seams, has been adapted by quilters for a casual country look. A quilt with a so-called "chenille finish" is known as a "rag quilt" or, a "slash quilt" due to the frayed exposed seams of the patches and the method of achieving this. Layers of soft cotton are batted together in patches or blocks and sewn with wide, raw edges to the front. These edges are then cut, or slashed, to create a worn, soft, "chenille" effect.
Many chenille fabrics should be dry cleaned. If hand or machine-washed, they should be machine-dried using low heat, or as a heavy textile, dried flat to avoid stretching, never hung.

Quilting is the term given to the process of joining a minimum of three layers of fabric together either through stitching manually using a needle and thread, or mechanically with a sewing machine or specialised longarm quilting system. An array of stitches is passed through all layers of the fabric to create a three-dimensional padded surface. The three layers are typically referred to as the top fabric or quilt top, batting or insulating material, and the backing.

Patchwork or "pieced work" is a form of needlework that involves sewing together pieces of fabric into a larger design. The larger design is usually based on repeating patterns built up with different fabric shapes. These shapes are carefully measured and cut, basic geometric shapes making them easy to piece together.

A quilt is a multi-layered textile, traditionally composed of two or more layers of fabric or fiber. Commonly three layers are used with a filler material. These layers traditionally include a woven cloth top, a layer of batting or wadding, and a woven back combined using the techniques of quilting. This is the process of sewing on the face of the fabric, and not just the edges, to combine the three layers together to reinforce the material. Stitching patterns can be a decorative element. A single piece of fabric can be used for the top of a quilt, but in many cases the top is created from smaller fabric pieces joined, or patchwork. The pattern and color of these pieces creates the design.

A rug is a piece of cloth, similar to a carpet, but it does not span the width of a room and is not attached to the floor. It is generally used as a floor covering, or as a decorative feature.

Appliqué is ornamental needlework in which pieces or patches of fabric in different shapes and patterns are sewn or stuck onto a larger piece to form a picture or pattern. It is commonly used as decoration, especially on garments. The technique is accomplished either by hand stitching or machine. Appliqué is commonly practised with textiles, but the term may be applied to similar techniques used on different materials. In the context of ceramics, for example, an appliqué is a separate piece of clay added to the primary work, generally for the purpose of decoration.

Dalton is a city and the county seat of Whitfield County, Georgia, United States. It is also the principal city of the Dalton Metropolitan Statistical Area, which encompasses all of Murray and Whitfield counties.

Machine embroidery is an embroidery process whereby a sewing machine or embroidery machine is used to create patterns on textiles. It is used commercially in product branding, corporate advertising, and uniform adornment. It is also used in the fashion industry to decorate garments and apparel. Machine embroidery is used by hobbyists and crafters to decorate gifts, clothing, and home decor. Examples include designs on quilts, pillows, and wall hangings.

Cashmere wool, usually simply known as cashmere, is a fiber obtained from cashmere goats, pashmina goats, and some other breeds of goat. It has been used to make yarn, textiles and clothing for hundreds of years. Cashmere is closely associated with the Kashmir shawl, the word "cashmere" deriving from an anglicization of Kashmir, when the Kashmir shawl reached Europe in the 19th century. Both the soft undercoat and the guard hairs may be used; the softer hair is reserved for textiles, while the coarse guard hair is used for brushes and other non-apparel purposes.

A sewing needle, used for hand-sewing, is a long slender tool with a pointed tip at one end and a hole to hold the sewing thread. The earliest needles were made of bone or wood; modern needles are manufactured from high carbon steel wire and are nickel- or 18K gold-plated for corrosion resistance. High-quality embroidery needles are plated with two-thirds platinum and one-third titanium alloy. Traditionally, needles have been kept in needle books or needlecases which have become objects of adornment. Sewing needles may also be kept in an étui, a small box that held needles and other items such as scissors, pencils and tweezers.
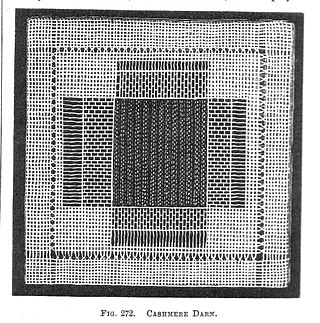
Darning is a sewing technique for repairing holes or worn areas in fabric or knitting using needle and thread alone. It is often done by hand, but using a sewing machine is also possible. Hand darning employs the darning stitch, a simple running stitch in which the thread is "woven" in rows along the grain of the fabric, with the stitcher reversing direction at the end of each row, and then filling in the framework thus created, as if weaving. Darning is a traditional method for repairing fabric damage or holes that do not run along a seam, and where patching is impractical or would create discomfort for the wearer, such as on the heel of a sock.

Rug hooking is both an art and a craft where rugs are made by pulling loops of yarn or fabric through a stiff woven base such as burlap, linen, or rug warp. The loops are pulled through the backing material by using a crochet-type hook mounted in a handle for leverage. In contrast latch-hooking uses a hinged hook to form a knotted pile from short, pre-cut pieces of yarn.

Tufting is a type of textile manufacturing in which a thread is inserted on a primary base. It is an ancient technique for making warm garments, especially mittens. After the knitting is done, short U-shaped loops of extra yarn are introduced through the fabric from the outside so that their ends point inwards.
The manufacture of textiles is one of the oldest of human technologies. To make textiles, the first requirement is a source of fiber from which a yarn can be made, primarily by spinning. The yarn is processed by knitting or weaving, which turns yarn into cloth. The machine used for weaving is the loom. For decoration, the process of colouring yarn or the finished material is dyeing. For more information of the various steps, see textile manufacturing.

Novelty yarns include a wide variety of yarns made with unusual features, structure or fiber composition such as slubs, inclusions, metallic or synthetic fibers, laddering and varying thickness introduced during production. Some linens, wools to be woven into tweed, and the uneven filaments of some types of silk are allowed to retain their normal irregularities, producing the characteristic uneven surface of the finished fabric. Man-made fibres, which can be modified during production, are especially adaptable for special effects such as crimping and texturizing.
James Templeton & Co was a Glasgow-based textile company that grew to become one of the leading carpet manufacturers in Britain during the 19th and 20th centuries.

Primarily, nap is the raised (fuzzy) surface on certain kinds of cloth, such as velvet or moleskin. Nap can refer additionally to other surfaces that look like the surface of a napped cloth, such as the surface of a felt or beaver hat.
Sewing is the craft of fastening or attaching objects using stitches made with needle and thread. Sewing is one of the oldest of the textile arts, arising in the Paleolithic Era. Although usually associated with clothing and household linens, sewing is used in a variety of crafts and industries, including shoemaking, upholstery, sailmaking, bookbinding and the manufacturing of some kinds of sporting goods. Sewing is the fundamental process underlying a variety of textile arts and crafts, including embroidery, tapestry, quilting, appliqué and patchwork.
Wet Processing Engineering is one of the major streams in Textile Engineering or Textile manufacturing which refers to the engineering of textile chemical processes and associated applied science. The other three streams in textile engineering are yarn engineering, fabric engineering, and apparel engineering. The processes of this stream are involved or carried out in an aqueous stage. Hence, it is called a wet process which usually covers pre-treatment, dyeing, printing, and finishing.
Catherine Evans Whitener was a rural artisan credited with reviving and expanding the tufted textile industry in northwest Georgia. In 2001 she was named a Georgia Woman of Achievement.
Angola was an imitated version of Indian shawl made with local wool options in England.