Related Research Articles

The International Bank Account Number (IBAN) is an internationally agreed system of identifying bank accounts across national borders to facilitate the communication and processing of cross border transactions with a reduced risk of transcription errors. An IBAN uniquely identifies the account of a customer at a financial institution. It was originally adopted by the European Committee for Banking Standards (ECBS) and since 1997 as the international standard ISO 13616 under the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The current version is ISO 13616:2020, which indicates the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) as the formal registrar. Initially developed to facilitate payments within the European Union, it has been implemented by most European countries and numerous countries in other parts of the world, mainly in the Middle East and the Caribbean. As of May 2020, 77 countries were using the IBAN numbering system.
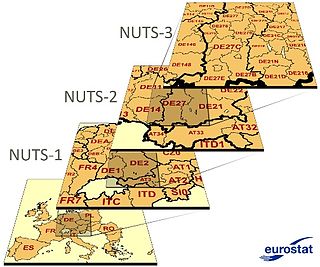
Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics or NUTS is a geocode standard for referencing the administrative divisions of countries for statistical purposes. The standard, adopted in 2003, is developed and regulated by the European Union, and thus only covers the EU member states in detail. The Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics is instrumental in the European Union's Structural Funds and Cohesion Fund delivery mechanisms and for locating the area where goods and services subject to European public procurement legislation are to be delivered.
CPV may refer to:
The United Nations Standard Products and Services Code (UNSPSC) is a taxonomy of products and services for use in eCommerce. It is a four-level hierarchy coded as an eight-digit number, with an optional fifth level adding two more digits.
In the European Economic Area, a supplementary protection certificate (SPC) is a sui generis intellectual property (IP) right that extends the duration of certain rights associated with a patent. It enters into force after expiry of a patent upon which it is based. This type of right is available for various regulated, biologically active agents, namely human or veterinary medicaments and plant protection products. Supplementary protection certificates were introduced to encourage innovation by compensating for the long time needed to obtain regulatory approval of these products.

The European Community number is a unique seven-digit identifier that was assigned to substances for regulatory purposes within the European Union by the European Commission. The EC Inventory comprises three individual inventories, EINECS, ELINCS and the NLP list.

A concession or concession agreement is a grant of rights, land or property by a government, local authority, corporation, individual or other legal entity.
Government procurement or public procurement is undertaken by the public authorities of the European Union (EU) and its member states in order to award contracts for public works and for the purchase of goods and services in accordance with principles derived from the Treaties of the European Union. Such procurement represents 14% of EU GDP as of 2017, and has been the subject of increasing European regulation since the 1970s because of its importance to the European single market.

Government procurement or public procurement is the procurement of goods, services and works on behalf of a public authority, such as a government agency. Amounting to 12 percent of global GDP in 2018, government procurement accounts for a substantial part of the global economy.

The visa policy of the Schengen Area is a component within the wider area of freedom, security and justice policy of the European Union. It applies to the Schengen Area and to other EU member states except Ireland. The visa policy allows nationals of certain countries to enter the Schengen Area via air, land or sea without a visa for stays of up to 90 days within a 180-day period. Nationals of certain other countries are required to have a visa either upon arrival or in transit.

The Statistical Classification of Economic Activities in the European Community, commonly referred to as NACE, is the industry standard classification system used in the European Union. The current version is revision 2 and was established by Regulation (EC) No 1893/2006. It is the European implementation of the UN classification ISIC, revision 4.

The European Union itself does not issue ordinary passports, but ordinary passport booklets issued by its 27 member states share a common format. This common format features a coloured cover emblazoned—in the official language(s) of the issuing country —with the title "European Union", followed by the name(s) of the member state, the heraldic "Arms" of the State concerned, the word "PASSPORT", together with the biometric passport symbol at the bottom centre of the front cover.

The CLP Regulation is a European Union regulation from 2008, which aligns the European Union system of classification, labelling and packaging of chemical substances and mixtures to the Globally Harmonised System (GHS). It is expected to facilitate global trade and the harmonised communication of hazard information of chemicals and to promote regulatory efficiency. It complements the 2006 Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) Regulation and replaces an older system contained in the Dangerous Substances Directive (67/548/EEC) and the Dangerous Preparations Directive (1999/45/EC).

The Schengen Area is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice policy of the European Union (EU), it mostly functions as a single jurisdiction under a common visa policy for international travel purposes. The area is named after the 1985 Schengen Agreement and the 1990 Schengen Convention, both signed in Schengen, Luxembourg.

Military acquisition or defense acquisition is the "bureaucratic management and procurement process", dealing with a nation's investments in the technologies, programs, and product support necessary to achieve its national security strategy and support its armed forces. Its objective is to acquire products that satisfy specified needs and provide measurable improvement to mission capability at a fair and reasonable price.
The Telecoms Package was the review of the European Union Telecommunications Framework from 2007 – 2009. The objective of the review was to update the EU Telecoms Framework of 2002 and to create a common set of regulations for the telecoms industry across all 27 EU member states. The review consisted of a package of directives addressing the regulation of service provision, access, interconnection, users' contractual rights and users' privacy, as well as a regulation creating a new European regulatory body (BEREC).
An economic operator is a business or other organisation which supplies goods, works or services within the context of market operations. The term is used in public procurement to cover suppliers, contractors and service providers.

The Body of European Regulators for Electronic Communications (BEREC) is the body in which the regulators of the telecommunications markets in the European Union work together. Other participants are the representative of the European Commission, as well as telecommunication regulators from the member states of the EEA and of states that are in the process of joining the EU.
The European Single Procurement Document (ESPD) is an electronic self-declaration document to be submitted by suppliers interested in tendering for contracts for the supply of goods, works or services to public bodies located anywhere within the European Union.
References
- ↑ Regulation (EC) No 2195/2002 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 November 2002 on the Common Procurement Vocabulary (CPV)
- ↑ Commission Regulation (EC) No 213/2008 of 28 November 2007 amending Regulation (EC) No 2195/2002 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Common Procurement Vocabulary (CPV) and Directives 2004/17/EC and 2004/18/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on public procurement procedures, as regards the revision of the CPV
- ↑ Gershon, P., Review of Civil Procurement in Central Government, paragraph 10, published April 1999, accessed 22 March 2023