Control theory is a field of mathematics that deals with the control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a desired state, while minimizing any delay, overshoot, or steady-state error and ensuring a level of control stability; often with the aim to achieve a degree of optimality.

A programmable logic controller (PLC) or programmable controller is an industrial computer that has been ruggedized and adapted for the control of manufacturing processes, such as assembly lines, machines, robotic devices, or any activity that requires high reliability, ease of programming, and process fault diagnosis. Dick Morley is considered as the father of PLC as he had invented the first PLC, the Modicon 084, for General Motors in 1968.
Instrumentation a collective term for measuring instruments that are used for indicating, measuring and recording physical quantities. The term has its origins in the art and science of scientific instrument-making.
Ladder logic was originally a written method to document the design and construction of relay racks as used in manufacturing and process control. Each device in the relay rack would be represented by a symbol on the ladder diagram with connections between those devices shown. In addition, other items external to the relay rack such as pumps, heaters, and so forth would also be shown on the ladder diagram.
A proportional–integral–derivative controller is a control loop mechanism employing feedback that is widely used in industrial control systems and a variety of other applications requiring continuously modulated control. A PID controller continuously calculates an error value as the difference between a desired setpoint (SP) and a measured process variable (PV) and applies a correction based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms, hence the name.

KNX is an open standard for commercial and domestic building automation. KNX devices can manage lighting, blinds and shutters, HVAC, security systems, energy management, audio video, white goods, displays, remote control, etc. KNX evolved from three earlier standards; the European Home Systems Protocol (EHS), BatiBUS, and the European Installation Bus. It can use twisted pair, powerline, RF, or IP links. On this network, the devices form distributed applications and tight interaction is possible. This is implemented via interworking models with standardised datapoint types and objects, modelling logical device channels.
A distributed control system (DCS) is a computerised control system for a process or plant usually with many control loops, in which autonomous controllers are distributed throughout the system, but there is no central operator supervisory control. This is in contrast to systems that use centralized controllers; either discrete controllers located at a central control room or within a central computer. The DCS concept increases reliability and reduces installation costs by localising control functions near the process plant, with remote monitoring and supervision.

A digital audio workstation (DAW) is an electronic device or application software used for recording, editing and producing audio files. DAWs come in a wide variety of configurations from a single software program on a laptop, to an integrated stand-alone unit, all the way to a highly complex configuration of numerous components controlled by a central computer. Regardless of configuration, modern DAWs have a central interface that allows the user to alter and mix multiple recordings and tracks into a final produced piece.
In electrical signalling an analog current loop is used where a device must be monitored or controlled remotely over a pair of conductors. Only one current level can be present at any time.
Actuator Sensor Interface is an industrial networking solution used in PLC, DCS and PC-based automation systems. It is designed for connecting simple field I/O devices in discrete manufacturing and process applications using a single two-conductor cable.
Building automation(BAS), also known as building management system (BMS) or building energy management system (BEMS), is the automatic centralized control of a building's HVAC, electrical, lighting, shading, Access Control, Security Systems, and other interrelated systems. Some objectives of building automation are improved occupant comfort, efficient operation of building systems, reduction in energy consumption, reduced operating and maintaining costs and increased security.

Profinet is an industry technical standard for data communication over Industrial Ethernet, designed for collecting data from, and controlling equipment in industrial systems, with a particular strength in delivering data under tight time constraints. The standard is maintained and supported by Profibus and Profinet International, an umbrella organization headquartered in Karlsruhe, Germany.
Direct digital control is the automated control of a condition or process by a digital device (computer). Direct digital control takes a centralized network-oriented approach. All instrumentation is gathered by various analog and digital converters which use the network to transport these signals to the central controller. The centralized computer then follows all of its production rules and causes actions to be sent via the same network to valves, actuators, and other heating, ventilating, and air conditioning components that can be adjusted.
An industrial control system (ICS) is an electronic control system and associated instrumentation used for industrial process control. Control systems can range in size from a few modular panel-mounted controllers to large interconnected and interactive distributed control systems (DCSs) with many thousands of field connections. Control systems receive data from remote sensors measuring process variables (PVs), compare the collected data with desired setpoints (SPs), and derive command functions that are used to control a process through the final control elements (FCEs), such as control valves.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to automation:
A control valve is a valve used to control fluid flow by varying the size of the flow passage as directed by a signal from a controller. This enables the direct control of flow rate and the consequential control of process quantities such as pressure, temperature, and liquid level.

A computer appliance is a computer system with a combination of hardware, software, or firmware that is specifically designed to provide a particular computing resource. Such devices became known as appliances because of the similarity in role or management to a home appliance, which are generally closed and sealed, and are not serviceable by the user or owner. The hardware and software are delivered as an integrated product and may even be pre-configured before delivery to a customer, to provide a turn-key solution for a particular application. Unlike general purpose computers, appliances are generally not designed to allow the customers to change the software and the underlying operating system, or to flexibly reconfigure the hardware.
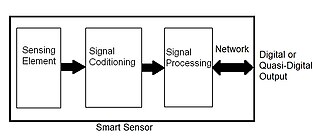
A smart transducer is an analog or digital transducer, actuator or sensor combined with a processing unit and a communication interface.
A networked control system (NCS) is a control system wherein the control loops are closed through a communication network. The defining feature of an NCS is that control and feedback signals are exchanged among the system's components in the form of information packages through a network.

CompactDAQ is a data acquisition platform built by National Instruments that includes a broad set of compatible hardware and software. CompactDAQ integrates hardware for data I/O with LabVIEW software to enable engineers to collect, process and analyse sensor data. CompactDAQ systems are less expensive than equivalent systems within the NI PXI Platform.








