
ATX is a motherboard and power supply configuration specification, patented by David Dent in 1995 at Intel, to improve on previous de facto standards like the AT design. It was the first major change in desktop computer enclosure, motherboard and power supply design in many years, improving standardization and interchangeability of parts. The specification defines the dimensions; the mounting points; the I/O panel; and the power and connector interfaces among a computer case, a motherboard, and a power supply.

The D-subminiature or D-sub is a common type of electrical connector. They are named for their characteristic D-shaped metal shield. When they were introduced, D-subs were among the smallest connectors used on computer systems.

A fastener or fastening is a hardware device that mechanically joins or affixes two or more objects together. In general, fasteners are used to create non-permanent joints; that is, joints that can be removed or dismantled without damaging the joining components. Steel fasteners are usually made of stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloy steel.
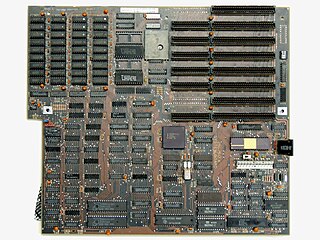
In the era of IBM compatible personal computers, the AT form factor comprises the dimensions and layout of the motherboard for the IBM AT. Baby AT motherboards are slightly smaller, measuring 8.5" by 13". Like the IBM PC and IBM XT models before it, many third-party manufacturers produced motherboards compatible with the IBM AT form factor, allowing end users to upgrade their computers for faster processors. The IBM AT became a widely copied design in the booming home computer market of the 1980s. IBM clones made at the time began using AT compatible designs, contributing to its popularity. In the 1990s many computers still used AT and its variants. Since 1997, the AT form factor has been largely supplanted by ATX.

A computer case, also known as a computer chassis, is the enclosure that contains most of the hardware of a personal computer. The components housed inside the case are referred as the internal hardware, while hardware outside the case are known as peripherals.

A socket wrench is a type of spanner that uses a closed socket format, rather than a typical open wrench/spanner to turn a fastener, typically in the form of a nut or bolt.

A machine taper is a system for securing cutting tools or toolholders in the spindle of a machine tool or power tool. A male member of conical form fits into the female socket, which has a matching taper of equal angle.

In general, a spacer is a solid material used to separate two parts in an assembly. Spacers can vary in size from microns to centimeters. They can be made of metal, plastic, glass, and other materials. Shapes include flat sheet, cylindrical and spherical.
The shank is the end of a drill bit grasped by the chuck of a drill. The cutting edges of the drill bit contact the workpiece, and are connected via the shaft with the shank, which fits into the chuck. In many cases a general-purpose arrangement is used, such as a bit with cylindrical shaft and shank in a three-jaw chuck which grips a cylindrical shank tightly. Different shank and chuck combination can deliver improved performance, such as allowing higher torque, greater centering accuracy, or moving the bit independently of the chuck, with a hammer action.

In photography, a tripod is a portable device used to support, stabilize and elevate a camera, a flash unit, or other videographic or observational/measuring equipment. All photographic tripods have three legs and a mounting head to couple with a camera. The mounting head usually includes a thumbscrew that mates to a female-threaded receptacle on the camera, as well as a mechanism to be able to rotate and tilt the camera when it is mounted on the tripod. Tripod legs are usually made to telescope, in order to save space when not in use. Tripods are usually made from aluminum, carbon fiber, steel, wood or plastic.

A jackscrew, or screw jack, is a type of jack that is operated by turning a leadscrew. It is commonly used to lift moderate and heavy weights, such as vehicles; to raise and lower the horizontal stabilizers of aircraft; and as adjustable supports for heavy loads, such as the foundations of houses.
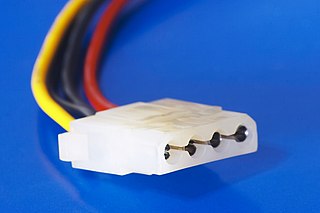
A Molex connector is a two-piece pin-and-socket interconnection which became an early electronic standard. Developed by Molex Connector Company in the late 1950s, the design features cylindrical spring-metal pins that fit into cylindrical spring-metal sockets, both held in a rectangular matrix in a nylon shell.

A lug nut or wheel nut is a fastener, specifically a nut, used to secure a wheel on a vehicle. Typically, lug nuts are found on automobiles, trucks (lorries), and other large vehicles using rubber tires.

A sex bolt is a type of fastener comprising a mated pair of screw and post, which are a machine screw and a nut that is barrel-shaped. The nut has a flange and a protruding boss that is internally threaded. The bolt sits within the components being fastened, and the flange provides the bearing surface.
The ISO metric screw thread is the most commonly used type of general-purpose screw thread worldwide. They were one of the first international standards agreed when the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) was set up in 1947.

A screw is an externally helical threaded fastener capable of being tightened or released by a twisting force (torque) to the head. The most common uses of screws are to hold objects together and there are many forms for a variety of materials. Screws might be inserted into holes in assembled parts or a screw may form its own thread. The difference between a screw and a bolt is that the latter is designed to be tightened or released by torquing a nut.

A hex key is a simple driver for bolts or screws that have heads with internal hexagonal recesses (sockets).

Width across flats is the distance between two parallel surfaces on the head of a screw or bolt, or a nut, mostly for torque transmission by positive locking.
Preferred metric sizes are a set of international standards and de facto standards that are designed to make using the metric system easier and simpler, especially in engineering and construction practices. One of the methods used to arrive at these preferred sizes is the use of preferred numbers and convenient numbers, such as the Renard series and 1-2-5 series, to limit the number of different sizes of components needed.























