
Don Cossacks or Donians, are Cossacks who settled along the middle and lower Don. Historically, they lived within the former Don Cossack Host, which was either an independent or an autonomous democratic republic in present-day Southern Russia and parts of the Donbas region of Ukraine, from the end of the 16th century until 1918. As of 1992, by presidential decree of the Russian Federation, Cossacks can be enrolled on a special register. A number of Cossack communities have been reconstituted to further Cossack cultural traditions, including those of the Don Cossack Host. Don Cossacks have had a rich military tradition - they played an important part in the historical development of the Russian Empire and participated in most of its major wars.

The Crimean campaigns of 1687 and 1689 were two military campaigns of the Tsardom of Russia against the Crimean Khanate. They were a part of the Russo-Turkish War (1686–1700) and Russo-Crimean Wars. These were the first Russian forces to come close to Crimea since 1569. They failed due to poor planning and the practical problem of moving such a large force across the steppe but nonetheless played a key role in halting the Ottoman expansion in Europe. The campaigns came as a surprise for the Ottoman leadership, spoiled its plans to invade Poland and Hungary and forced it to move significant forces from Europe to the east, which greatly helped the League in its struggle against the Ottomans.

The Azov campaigns of 1695–1696, were two Russian military campaigns during the Russo-Turkish War of 1686–1700, led by Peter the Great and aimed at capturing the Turkish fortress of Azov with the aim of controlling the southern mouth of the Don River gaining access to the Sea of Azov and entrance to the Black Sea. Despite stubborn resistance and heavy casualties, the Russians under General Sheremetev after a failed siege in 1695 managed to capture the fort, accompanied by a naval force, in July 1696, marking the first major Russian victory against the Turks.

The Russo-Turkish War of 1676–1681, a war between the Tsardom of Russia and Ottoman Empire, caused by Turkish expansionism in the second half of the 17th century.

The Russo-Turkish War of 1686–1700 was part of the joint European effort to confront the Ottoman Empire. The larger European conflict was known as the Great Turkish War.

The Russo-Turkish War of 1735–1739 between Russia and the Ottoman Empire was caused by the Ottoman Empire's war with Persia and continuing raids by the Crimean Tatars. The war also represented Russia's ongoing struggle for access to the Black Sea. In 1737, the Habsburg monarchy joined the war on Russia's side, known in historiography as the Austro-Turkish War of 1737–1739.

The Crimean Khanate, self-defined as the Throne of Crimea and Desht-i Kipchak, and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary, was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 - 1783, the longest-lived of the Turkic khanates that succeeded the empire of the Golden Horde. Established by Hacı I Giray in 1441, it was regarded as the direct heir to the Golden Horde and to Desht-i-Kipchak.

Devlet I Giray ruled as Crimean Khan during a long and eventful period marked by significant historical events. These events included the fall of Kazan to Russia in 1552, the fall of the Astrakhan Khanate to Russia in 1556, and the burning of Moscow by the Crimean Tatars in 1571. Another notable event during Devlet's reign was the defeat of the Crimeans near Moscow in 1572. However, Cossack raids into the Crimea were also common during his reign.
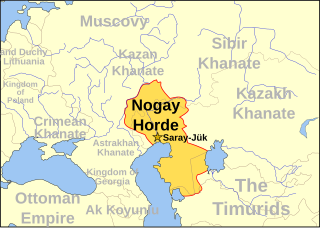
The Nogai Horde was a confederation founded by the Nogais that occupied the Pontic–Caspian steppe from about 1500 until they were pushed west by the Kalmyks and south by the Russians in the 17th century. The Mongol tribe called the Manghuds constituted a core of the Nogai Horde.

Black Sea Cossack Host, also known as Chernomoriya, was a Cossack host of the Russian Empire created in 1787 in southern Ukraine from former Zaporozhian Cossacks. In the 1790s, the host was re-settled to the Kuban River. It comprised the Caucasus Fortified Defence Line from the mouth of the Kuban River to the mouth of the Bolshaya Laba River.

Azov Cossack Host was a Cossack host that existed on the northern shore of the Sea of Azov, between 1832 and 1862.
Russo-Turkish wars or Russo-Ottoman wars were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European history. Except for the war of 1710–11, as well as the Crimean War which is often treated as a separate event, the conflicts ended disastrously for the Ottoman Empire, which was undergoing a long period of stagnation and decline; conversely, they showcased the ascendancy of Russia as a European power after the modernization efforts of Peter the Great in the early 18th century.
The Russo-Crimean Wars were fought between the forces of the Tsardom of Russia and the Crimean Khanate during the 16th century over the region around the Volga River.
The Treaty of Constantinople or Istanbul was signed on 13 July 1700 between the Tsardom of Russia and the Ottoman Empire. It ended the Russo-Turkish War of 1686-1700. Russian tsar Peter the Great secured possession of the Azov region and freed his forces to participate in the Great Northern War. The treaty was superseded by the Treaty of the Pruth in 1711, after the Ottoman Empire became involved in this war.

The steppe and forest-steppe of Ukraine and southern Russia is good agricultural land, but it was traditionally held by pastoral nomads. Any state that could drive off the nomads and fill the land with tax-paying peasants would expand its power enormously. During the period 1500–1800, this region was taken under Russian control.

Ğazı II Giray was a khan of the Crimean Khanate. Born in 1554, he distinguished himself in the Ottoman–Safavid War (1578–90), gaining the trust of his Ottoman suzerains. He was appointed khan in 1588, after his homeland experienced a period of political turmoil. He failed to capture Moscow during his 1591 campaign against Tsardom of Russia, however he managed to secure a favorable peace treaty two years later. He was then summoned to support his Ottoman allies in the Long Turkish War, taking part in multiple military expeditions centered in Hungary. In late 1596, the Ottoman sultan briefly unseated Ğazı II Giray in favor of Fetih I Giray after heeding the advice of Grand Vizier Cığalazade Yusuf Sinan Pasha. He returned to power three months later, continuing his reign until his death in November 1607.

The Kalmyk Khanate was an Oirat khanate on the Eurasian steppe. It extended over modern Kalmykia and surrounding areas in the North Caucasus, including Stavropol and Astrakhan. During their independence, the Kalmyks both raided and allied with Russia in turn, engaging in numerous military expeditions against the Crimean Tatars, the Ottoman Empire, neighboring Muslim tribes, and the highlanders of the North Caucasus. The Khanate was annexed by the Russian Empire in 1771.

For over three centuries, the military of the Crimean Khanate and the Nogai Horde conducted slave raids primarily in lands controlled by Russia and Poland-Lithuania as well as other territories, often under the sponsorship of the Ottoman Empire.

The Azov Fortress is a fortified complex in Azov, Rostov Oblast, Russia, overlooking the Don River and the Port of Azov to the north. It includes a rampart, watchtowers and gates. The Azov Fortress was founded by Turks on behalf of the Ottoman Empire in 1475. It guarded the northern approaches to the Empire and access to the Azov Sea. After a series of conflicts, a peace treaty was signed in Constantinople on July 13, 1700 between the Tsardom of Russia and the Ottoman Empire. The sultan recognized Russia's possession of the Azov area.
Bahadir or Bahadır I Giray was a khan of the Crimean Khanate. Much of his reign was spent dealing with Azov which had been captured by the Don Cossacks. Unlike many khans, he died of natural causes. He was the father of Selim I Giray and, through him, the ancestor of all khans who reigned after 1700 except for Devlet III.
















