
Centipede is a 1981 fixed shooter arcade video game developed and published by Atari, Inc. Designed by Dona Bailey and Ed Logg, it was one of the most commercially successful games from the golden age of arcade video games and one of the first with a significant female player base. The primary objective is to shoot all the segments of a centipede that winds down the playing field. An arcade sequel, Millipede, followed in 1982.

Ambrosia Software was a predominantly Macintosh software company founded in 1993 and located in Rochester, New York, U.S. Ambrosia Software was best known for its Macintosh remakes of older arcade games, which began with a 1992 version of Atari, Inc.'s Asteroids from 1979. The company also published utility software. Its products were distributed as shareware; demo versions could be downloaded and used for up to 30 days. Later the company released some products for iOS. Ambrosia's best-selling program was the utility Snapz Pro X, according to a 2002 interview with company president Andrew Welch.

Paperboy is an arcade action game developed and published by Atari Games, and released in 1985. The player takes the role of a paperboy who delivers a fictional newspaper called The Daily Sun along a street on his bicycle. The arcade version of the game featured bike handlebars as the controller.

Star Wars is a first-person rail shooter designed by Mike Hally and released as an arcade video game in 1983 by Atari, Inc. It uses 3D color vector graphics to simulate the assault on the Death Star from the 1977 film Star Wars. There are three connected gameplay sequences: combat against TIE fighters in space, flying across the surface of the Death Star, and the final trench run. The sequence repeats with added complications and the Death Star regenerating for each. The player's X-Wing fighter has a shield which only protects against damage a certain number of times, then the next hit ends the game. Speech synthesis emulates actors from the film.

Mr. Driller is a puzzle video game franchise created by Yasuhito Nagaoka and Hideo Yoshizawa for Namco. The eponymous first game was released in 1999 for arcades and several home consoles, such as the PlayStation. Gameplay in the series consists of controlling Susumu Hori, the titular Mr. Driller, or one of his friends and destroying colorful formations of blocks to make it to the bottom of a well. In order to survive, players need to collect air capsules to replenish their depleting oxygen and avoid being crushed by falling blocks.

Shadowgate is a black-and-white point-and-click adventure game published for the Macintosh as part of the MacVenture series. The game is named for its setting, Castle Shadowgate, residence of the evil Warlock Lord. The player, as the "last of a great line of hero-kings" is charged with the task of saving the world by defeating the Warlock Lord, who is attempting to summon up the demon Behemoth out of Hell. Later that year, a color version of the game was released for the Amiga and Atari ST, and in 1989 for the Nintendo Entertainment System.

Dark Castle is a 1986 platform game for Macintosh that was originally published by Silicon Beach Software. The original game was designed and animated by Mark Pierce and programmed by Jonathan Gay with Real Sound by Eric Zocher. In Dark Castle, a young hero named Duncan tries to make his way to the evil Black Knight, dodging objects as well as solving occasional puzzles.

Glider is a Macintosh video game written by John Calhoun and first published as shareware in 1988 under the company name Soft Dorothy Software. The object of the game is to fly a paper plane through the rooms of a house. Air currents from heat ducts and fans affect the plane's movement, while assorted household objects are usually deadly. Some rooms have special mechanics, such as the ability to slide along grease-covered surfaces. Each room is presented as a two-dimensional side view.
SoundJam MP is a discontinued MP3 player for classic Mac OS-compatible computers and Rio-compatible hardware synchronization manager that was released in July 1999 and was available until June 2001. Jeff Robbin and Bill Kincaid developed SoundJam MP with assistance from Dave Heller. Robbin and Kincaid chose Casady & Greene to publish SoundJam MP. Apple, Inc. purchased SoundJam MP in 2000 and further developed the code to create iTunes version 1.0. Casady and Greene ceased publication of SoundJam MP in June 2001 at the request of the developers.

Casady & Greene was a software publisher and developer active from 1988 to 2003. The company primarily released software for Macintosh, but also released software for Windows and Newton. Casady & Greene was formed in 1988 when Greene, Inc. acquired CasadyWare, a company owned by Robin Casady.
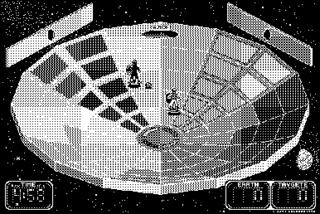
Pararena is an action computer game for the Apple Macintosh computer originally written in 1990 by John Calhoun and released as shareware. Calhoun previously wrote the Macintosh game Glider.

Crystal Crazy is an action game, published by Casady & Greene for the Classic Mac OS in 1993. It is the sequel to Crystal Quest. The aim of the game is to collect crystals. Unlike Crystal Quest, which included a "Critter Editor," Crystal Crazy has no functionality for easily editing aspects of the game such as the enemy graphics.

Zone Warrior is a three-dimensional space combat simulator game written by Julian James for Mac OS and published by Casady & Greene in 1997. It was originally released as ZOA. In Zone Warrior, the player is the lone defender of a remote space station under attack by aliens.

Sky Shadow is a clone of the 1981 Defender arcade video game published by MacSoft for the Macintosh in 1990. It was programmed by Patrick Buckland who also wrote Crystal Quest. Casady & Greene re-released the game in 1994.

Space Quest III: The Pirates of Pestulon is a 1989 graphic adventure game by Sierra On-Line, and the third game in the Space Quest series. Players assume the role of Roger Wilco, a lowly space janitor, who becomes involved in rescuing a pair of computer programmers from a sinister video game company. The game received positive reviews from critics, and contributed further to the series' commercial success for Sierra. A sequel, Space Quest IV, was released in 1991.

Battle-Girl is a multidirectional shooter video game developed by Ultra/United Games and originally published in 1997 by Power Media for the Macintosh. In the game, players assume the role of the titular character taking control of her Soyuz 1183-A BattleCraft to save the Great Machine by eradicating malicious programmers released by Terminus, a weapon of Chaos. Its gameplay uses a two-joystick configuration reminiscent of Robotron: 2084.

Auditorium is a music-based puzzle game developed by Philadelphia-based studio Cipher Prime. Originally released as a Flash game in April 2008, Auditorium was later released for iOS devices and then the PlayStation 3 and PSP in 2010. It was also released in 2012 for PC and Mac OS X. In 2012, Cipher Prime launched a successful Kickstarter campaign for a sequel to Auditorium, titled Auditorium 2: Duet. However, on January 11, 2017, Cipher Prime announced to their Kickstarter backers that the game was cancelled.

Ford Racing 2 is a 2003 racing video game developed by Razorworks and published by Empire Interactive and Gotham Games. The game was released for Windows, Macintosh, PlayStation 2 (PS2), and Xbox. It is the sequel to Ford Racing (2000), and is the second game in the Ford Racing series. It received mixed reviews from critics.

The Pinball Arcade is a pinball video game developed by FarSight Studios. The game is a simulated collection of 100 real pinball tables licensed by Gottlieb, Alvin G. and Company, and Stern Pinball, a company which also owns the rights of machines from Data East and Sega Pinball. Williams and Bally games are no longer available since June 30, 2018, as FarSight had lost the license to WMS properties, which has since passed to Zen Studios.
Patrick Buckland is a British video game programmer, designer and chief executive officer of Stainless Games, which he co-founded with Neil Barnden in 1994.

















