
Order Desmothoracida, the desmothoracids, are a group of heliozoan protists, usually sessile and found in freshwater environments. The adult is a spherical cell around 10-20 μm in diameter surrounded by a perforated organic lorica, or shell, with many radial pseudopods projecting through the holes to capture food. These are supported by small bundles of microtubules that arise near a point on the nuclear membrane. Unlike other heliozoans, the microtubules are not in any regular geometric array, there does not appear to be a microtubule organizing center, and there is no distinction between the outer and inner cytoplasm.

The centrohelids or centroheliozoa are a large group of heliozoan protists. They include both mobile and sessile forms, found in freshwater and marine environments, especially at some depth.

Myxobolus is a genus of myxozoa that includes important parasites of fish like Myxobolus cerebralis. The genus is polyphyletic, with members scattered throughout the myxozoa. Some stages of Myxobolus species were previously thought to be different organisms entirely, but are now united in this group.

Myxobolidae is a family of myxosporean parasites which typically infect freshwater fishes, and includes the economically significant species, Myxobolus cerebralis. They have been shown to have a complex life cycle, involving an alternate stage in an invertebrate, typically an annelid or polychaete worm.

Bivalvulida is an order of myxosporean parasites which contains a number of species which cause economically significant losses to aquaculture and fisheries, such as Myxobolus cerebralis and Ceratomyxa shasta. The Myxosporean stages of members of the bivalvulida are characterised by their two spore valves, which meet in a "suture line" which encircles the spore. They usually contain two polar capsules, but species have been reported which contain either one or four.

Eimeria is a genus of apicomplexan parasites that includes various species capable of causing the disease coccidiosis in animals such as cattle, poultry and smaller ruminants including sheep and goats. Eimeria species are considered to be monoxenous because the life cycle is completed within a single host, and stenoxenous because they tend to be host specific, although a number of exceptions have been identified. Species of this genus infect a wide variety of hosts. Thirty-one species are known to occur in bats (Chiroptera), two in turtles, and 130 named species infect fish. Two species infect seals. Five species infect llamas and alpacas: E. alpacae, E. ivitaensis, E. lamae, E. macusaniensis, and E. punonensis. A number of species infect rodents, including E. couesii, E. kinsellai, E. palustris, E. ojastii and E. oryzomysi. Others infect poultry, rabbits and cattle. For full species list, see below.

Dakosaurus is an extinct genus of crocodylomorph within the family Metriorhynchidae that lived during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. It was large, with teeth that were serrated and compressed lateromedially. The genus was established by Friedrich August von Quenstedt in 1856 for an isolated tooth named Geosaurus maximus by Theodor Plieninger in 1846. Dakosaurus was a carnivore that spent much, if not all, its life out at sea. The extent of its adaptation to a marine lifestyle means that it is most likely that it mated at sea, but since no eggs or nests have been discovered that have been referred to Dakosaurus, whether it gave birth to live young at sea like dolphins and ichthyosaurs or came ashore like turtles is not known. The name Dakosaurus means "biter lizard", and is derived from the Greek dakos ("biter") and σαῦρος -sauros ("lizard").
Dermocystidium is a genus of cyst-forming, eukaryotic fish parasites, the causative agents of dermocystidiosis.

Bucephalus polymorphus is a type of flatworm. This species is within the Bucephalidae family of Digenea, which in turn is a subclass of Trematodes within the phylum Platyhelminthes. It is characterized by having a mouth near the middle of its body, along with a sac-like gut. The mouth opening is located in the centre of the ventral surface. This is a specific body type of cecaria known as a gastrostome.

Adeleorina is a suborder of parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa.
Ceratomyxa is a genus of myxozoan.
Goussia is a taxonomic genus, first described in 1896 by Labbé, containing parasitic protists which largely target fish and amphibians as their hosts. Members of this genus are homoxenous and often reside in the gastrointestinal tract of the host, however others may be found in organs such as the gallbladder or liver. The genera Goussia, as current phylogenies indicate, is part of the class Conoidasida, which is a subset of the parasitic phylum Apicomplexa; features of this phylum, such as a distinct apical complex containing specialized secretory organelles, an apical polar ring, and a conoid are all present within Goussia, and assist in the mechanical invasion of host tissue. The name Goussia is derived from the French word gousse, meaning pod. This name is based on the bi-valve sporocyst morphology which some Goussians display. Of the original 8 classified Goussians, 6 fit the “pod” morphology. As of this writing, the genera consists of 59 individual species.
Epieimeria is a genus of parasitic alveaolates of the phylum Apicomplexa.
Hyaloklossia is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. Only one species in this genus is currently recognised - Hyaloklossia lieberkuehni.

Kudoa is a genus of Myxozoa and the only genus recognized within the monotypic family Kudoidae. There are approximately 100 species of Kudoa all of which parasitize on marine and estuarine fish. Kudoa are most commonly known and studied for the negative effects the genus has on commercial fishing and aquaculture industries.

Opecoelidae is a family of trematodes. It is the largest digenean family with over 90 genera and nearly 900 species, almost solely found in marine and freshwater teleost fishes. It was considered by Bray et al. to belong in the superfamily Opecoeloidea Ozaki, 1925 or the Brachycladioidea Odhner, 1905.
Franz Theodor Doflein was a German zoologist known for his studies of animal ecology.

Johann Eduard Reichenow was a German protozoologist. He was the son of ornithologist Anton Reichenow.
Ptilocodiidae is a family of hydrozoans in the order Anthoathecata.
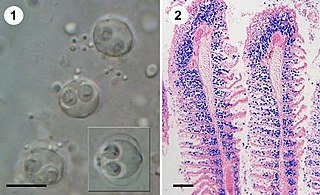
Sphaerospora molnari is a microscopic endoparasite of carp in pond cultures and natural freshwater habitats in Central and Eastern Europe. In natural infections, S. molnari invades the epithelia of gills and surrounding skin regions. It then forms spores in between epithelial cells, causing sphaerosporosis, a pathological condition of the skin and gill tissues. Affected tissues show marked dystrophic changes and necrosis, causing secondary bacterial infections and resulting in osmoregulatory and respiratory failure. Mortalities can reach 100% but little is known about the overall distribution of the parasite species in European carp ponds or its economic impact on carp aquaculture.











