
Mites are small arachnids. Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as each other's closest relative within Arachnida, rendering the group non-monophyletic. Most mites are tiny, less than 1 mm (0.04 in) in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating galls, while others are predators or parasites. This last type includes the commercially destructive Varroa parasite of honey bees, as well as scabies mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases.

Folliculitis is the infection and inflammation of one or more hair follicles. The condition may occur anywhere on hair-covered skin. The rash may appear as pimples that come to white tips on the face, chest, back, arms, legs, buttocks, or head.

Mange is a type of skin disease caused by parasitic mites. Because various species of mites also infect plants, birds and reptiles, the term "mange", or colloquially "the mange", suggesting poor condition of the skin and fur due to the infection, is sometimes reserved for pathological mite-infestation of nonhuman mammals. Thus, mange includes mite-associated skin disease in domestic mammals, in livestock, and in wild mammals. Severe mange caused by mites has been observed in wild bears. Since mites belong to the arachnid subclass Acari, another term for mite infestation is acariasis.

Demodicosis, also called Demodex folliculitis in humans and demodectic mange or red mange in animals, is caused by a sensitivity to and overpopulation of Demodex spp. as the host's immune system is unable to keep the mites under control.

Demodex is a genus of tiny mites that live in or near hair follicles of mammals. Around 65 species of Demodex are known. Two species live on humans: Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis, both frequently referred to as eyelash mites, alternatively face mites or skin mites.
Acariasis is an infestation with mites.

Demodex folliculorum is a microscopic mite that can survive only on the skin of humans. Most people have D. folliculorum on their skin. Usually, the mites do not cause any harm, so are considered an example of commensalism rather than parasitism; but they can cause disease, known as demodicosis.
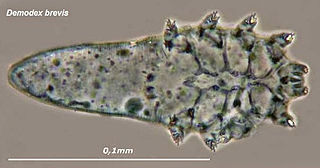
Demodex brevis is one of the two species of face mite that inhabit humans. They are about half as long, at 0.15 to 0.2 mm, as D. folliculorum, but otherwise have few differences. Most of the article on Demodex folliculorum applies equally to D. brevis.
Demodex injai is a hair follicle mite in the domestic dog.

Mites that infest and parasitize domestic animals cause disease and loss of production. Mites are small invertebrates, most of which are free living but some are parasitic. Mites are similar to ticks and both comprise the order Acari in the phylum Arthropoda. Mites are highly varied and their classification is complex; a simple grouping is used in this introductory article. Vernacular terms to describe diseases caused by mites include scab, mange, and scabies. Mites and ticks have substantially different biology from, and are classed separately from, insects. Mites of domestic animals cause important types of skin disease, and some mites infest other organs. Diagnosis of mite infestations can be difficult because of the small size of most mites, but understanding how mites are adapted to feed within the structure of the skin is useful.
Demodex bovis, also known as the cattle follicle mite, usually causes demodicosis, or demodectic mange, in cattle. This disease is common in tropical areas and is not usually found in temperate environments. Demodicosis is characterized by the formation of papules and nodules over the cattle's skin. These lesions most commonly occur on the neck, shoulders, and armpit of cattle; however, sometimes they also appear on the udder. This condition is often found in cattle with increased stress from pregnancy or lactation. Natural and acquired immunity can cause a decrease in the number of mites infesting a cow, as well as decreasing the severity of a cow's symptoms.

Mites are small crawling animals related to ticks and spiders. Most mites are free-living and harmless. Other mites are parasitic, and those that infest livestock animals cause many diseases that are widespread, reduce production and profit for farmers, and are expensive to control.
Demodex conicus is a hair follicle mite found in the ear canal of the house mouse, Mus musculus.
Demodex microti is a hair follicle mite from the skin of the genital area of the common vole, Microtus arvalis.
Demodex criceti is a hair follicle mite found in the epidermis of the Syrian hamster, Mesocricetus auratus.
Demodex gapperi is a hair follicle mite found in the eyelids of the red-backed vole, Clethrionomys gapperi.
Demodex huttereri is a hair follicle mite found in the Meibomian glands of the striped field mouse, Apodemus agrarius.
Demodex ponderosus is a hair follicle mite found on thinly haired regions of the brown rat, Rattus norvegicus.
Demodex foveolator is a hair follicle mite found in epidermal pits of the lesser white-toothed shrew, Crocidura suaveolens.
Demodex leucogasteri is a hair follicle mite found in the hair follicles of the grasshopper mouse, Onychomys leucogaster.







