Related Research Articles
A dental consonant is a consonant articulated with the tongue against the upper teeth, such as, . In some languages, dentals are distinguished from other groups, such as alveolar consonants, in which the tongue contacts the gum ridge. Dental consonants share acoustic similarity and in Latin script are generally written with consistent symbols.
The voiceless velar plosive or stop is a type of consonantal sound used in almost all spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨k⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is k.
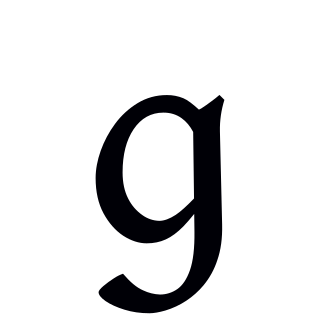
The voiced velar plosive or stop is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages.

The voiced velar nasal, also known as agma, from the Greek word for 'fragment', is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. It is the sound of ng in English sing as well as n before velar consonants as in English and ink. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ŋ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is N. The IPA symbol ⟨ŋ⟩ is similar to ⟨ɳ⟩, the symbol for the retroflex nasal, which has a rightward-pointing hook extending from the bottom of the right stem, and to ⟨ɲ⟩, the symbol for the palatal nasal, which has a leftward-pointing hook extending from the bottom of the left stem. Both the IPA symbol and the sound are commonly called 'eng' or 'engma'.
The voiceless alveolar, dental and postalveolarplosives are types of consonantal sounds used in almost all spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents voiceless dental, alveolar, and postalveolar plosives is ⟨t⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is t. The voiceless dental plosive can be distinguished with the underbridge diacritic, ⟨t̪⟩ and the postalveolar with a retraction line, ⟨t̠⟩, and the Extensions to the IPA have a double underline diacritic which can be used to explicitly specify an alveolar pronunciation, ⟨t͇⟩.
The voiceless bilabial plosive or stop is a type of consonantal sound used in most spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨p⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is p.
The voiced bilabial plosive or stop is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨b⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is b. The voiced bilabial stop occurs in English, and it is the sound denoted by the letter ⟨b⟩ in obey (obeI).
The voiced alveolar, dental and postalveolarplosives are types of consonantal sounds used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents voiced dental, alveolar, and postalveolar plosives is ⟨d⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is d.
The voiced alveolar tap or flap is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents a dental, alveolar, or postalveolar tap or flap is ⟨ɾ⟩.
The voiced alveolar nasal is a type of consonantal sound used in numerous spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar nasals is ⟨n⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is n.
The voiced alveolar trill is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar trills is ⟨r⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is r. It is commonly called the rolled R, rolling R, or trilled R. Quite often, ⟨r⟩ is used in phonemic transcriptions of languages like English and German that have rhotic consonants that are not an alveolar trill. That is partly for ease of typesetting and partly because ⟨r⟩ is the letter used in the orthographies of such languages.
The voiced bilabial nasal is a type of consonantal sound which has been observed to occur in about 96% of spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨m⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is m. The bilabial nasal occurs in English, and it is the sound represented by "m" in map and rum. Very few languages are known to lack this sound. A small number of languages have been observed to lack independent nasal phonemes altogether, such as Quileute, Makah, and Central Rotokas.
The voiced labial–velar approximant is a type of consonantal sound, used in certain spoken languages, including English. It is the sound denoted by the letter ⟨w⟩ in the English alphabet; likewise, the symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨w⟩, or rarely, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is w. In most languages it is the semivocalic counterpart of the close back rounded vowel. In inventory charts of languages with other labialized velar consonants, will be placed in the same column as those consonants. When consonant charts have only labial and velar columns, may be placed in the velar column, (bi)labial column, or both. The placement may have more to do with phonological criteria than phonetic ones.

The voiced labiodental nasal is a type of consonantal sound. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɱ⟩. The IPA symbol is a lowercase letter m with a leftward hook protruding from the lower right of the letter. Occasionally it is instead transcribed as an with a dental diacritic: ⟨m̪⟩.
The voiced alveolar lateral approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar lateral approximants is ⟨l⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is l.

The voiced palatal lateral approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʎ⟩, a rotated lowercase letter ⟨y⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is L.

The voiced dental fricative is a consonant sound used in some spoken languages. It is familiar to English-speakers as the th sound in father. Its symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet is eth, or and was taken from the Old English and Icelandic letter eth, which could stand for either a voiced or unvoiced (inter)dental non-sibilant fricative. Such fricatives are often called "interdental" because they are often produced with the tongue between the upper and lower teeth, and not just against the back of the upper teeth, as they are with other dental consonants.
A voiced postalveolar fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The International Phonetic Association uses the term voiced postalveolar fricative only for the sound, but it also describes the voiced postalveolar non-sibilant fricative, for which there are significant perceptual differences.
The voiceless dental non-sibilant fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. It is familiar to English speakers as the 'th' in think. Though rather rare as a phoneme among the world's languages, it is encountered in some of the most widespread and influential ones. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨θ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is T. The IPA symbol is the Greek letter theta, which is used for this sound in post-classical Greek, and the sound is thus often referred to as "theta".
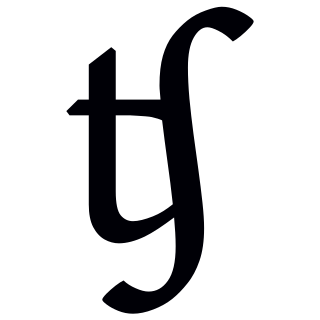
The voiceless palato-alveolar sibilant affricate or voiceless domed postalveolar sibilant affricate is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The sound is transcribed in the International Phonetic Alphabet with ⟨t͡ʃ ⟩, ⟨t͜ʃ ⟩⟨tʃ ⟩, or, in broad transcription, ⟨c⟩. The alternative commonly used in American tradition is ⟨č⟩. It is familiar to English speakers as the "ch" sound in "chip".
References
- ↑ Ladefoged, Peter; Maddieson, Ian (1996). The Sounds of the World's Languages. Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 978-0-631-19815-4.
- ↑ Martínez-Celdrán, Fernández-Planas & Carrera-Sabaté (2003 :257)
- ↑ Rogers & d'Arcangeli (2004 :117)