In organic chemistry, amines (, UK also ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; see Category:Amines for a list of amines. Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (NClH2).

The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations that represents chemists in individual countries. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. This administrative office is headed by IUPAC's executive director, currently Lynn Soby.
A methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms — CH3. In formulas, the group is often abbreviated Me. Such hydrocarbon groups occur in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, it can be found on its own in any of three forms: anion, cation or radical. The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed.
Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies the structure, properties and reactions of organic compounds, which contain carbon in covalent bonding. Study of structure determines their chemical composition and formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical study.
Lipoamide is a trivial name for 6,8-dithiooctanoic amide. It is the functional form of lipoic acid, i.e the carboxyl group is attached to protein via an amine with an amide linkage. Illustrative of the biochemical role of lipoamide is in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl lipoamide.

Lipoic acid (LA), also known as α-lipoic acid and alpha lipoic acid (ALA) and thioctic acid, is an organosulfur compound derived from caprylic acid. ALA is made in animals normally, and is essential for aerobic metabolism. It is also manufactured and is available as a dietary supplement in some countries where it is marketed as an antioxidant, and is available as a pharmaceutical drug in other countries.
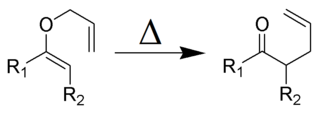
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis, organic reactions are used in the construction of new organic molecules. The production of many man-made chemicals such as drugs, plastics, food additives, fabrics depend on organic reactions.

A sulfonate is a salt or ester of a sulfonic acid. It contains the functional group R-SO3−, where R is an organic group. Sulfonates are the conjugate base of sulfonic acids. Sulfonates are generally stable in water, non-oxidizing, and colorless. Many useful compounds and even some biochemicals feature sulfonates.
Total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of a complex molecule, often a natural product, from simple, commercially-available precursors. It usually refers to a process not involving the aid of biological processes, which distinguishes it from semisynthesis. The target molecules can be natural products, medicinally-important active ingredients, or organic compounds of theoretical interest.
Chemical changes occur when a substance combines with another to form a new substance, called chemical synthesis or, alternatively, chemical decomposition into two or more different substances. These processes are called chemical reactions and, in general, are not reversible except by further chemical reactions. Some reactions produce heat and are called exothermic reactions and others may require heat to enable the reaction to occur, which are called endothermic reactions. Understanding chemical changes is a major part of the science of chemistry.
Disproportionation, sometimes called dismutation, is a redox reaction in which one compound of intermediate oxidation state converts to two compounds, one of higher and one of lower oxidation states. More generally, the term can be applied to any desymmetrizing reaction of the following type: 2 A → A' + A", regardless of whether it is a redox or some other type of process.
Roger John Williams, was an American biochemist who spent his academic career at the University of Texas at Austin. He is known for isolating and naming folic acid and for his roles in discovering pantothenic acid, vitamin B6, lipoic acid, and avidin. He served as the founding director of the Clayton Foundation Biochemical Institute from 1941 to 1963, was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 1946, and served as the president of the American Chemical Society in 1957. In his later career he spent time writing for a popular audience on the importance of nutrition.
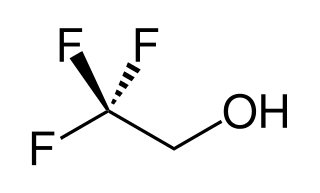
2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol is the organic compound with the formula CF3CH2OH. Also known as TFE or trifluoroethyl alcohol, this colourless, water-miscible liquid has a smell reminiscent of ethanol. Due to the electronegativity of the trifluoromethyl group, this alcohol exhibits a stronger acidic character compared to ethanol. Thus, TFE forms stable complexes also with heterocycles (e.g. THF or pyridine) through hydrogen bonding.
Asparagusic acid is an organosulfur compound with the molecular formula C4H6O2S2 and is systematically named 1,2-dithiolane-4-carboxylic acid. The molecule consists of a heterocyclic disulfide functional group (a 1,2-dithiolane) with a carboxylic acid side chain. It is found in asparagus and is believed to be the metabolic precursor to odorous sulfur compounds responsible for the distinctive smell of urine which has long been associated with eating asparagus.

Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase is an enzyme component of the multienzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is responsible for the pyruvate decarboxylation step that links glycolysis to the citric acid cycle. This involves the transformation of pyruvate from glycolysis into acetyl-CoA which is then used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration.
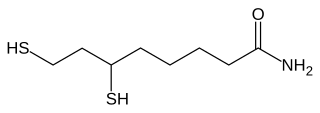
Dihydrolipoamide is a molecule produced by the action of dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase upon lipoamide.
Albert Eschenmoser (born 5 August 1925) is a Swiss organic chemist best known for his work on the synthesis of complex heterocyclic natural compounds, most notably vitamin B12. In addition to his significant contributions to the field of organic synthesis, Eschenmoser pioneered work in the Origins of Life (OoL) field with work on the synthetic pathways of artificial nucleic acids. Before retiring in 2009, Eschenmoser held tenured teaching positions at the ETH Zurich and The Skaggs Institute for Chemical Biology at The Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, California as well as visiting professorships at the University of Chicago, Cambridge University, and Harvard.

Keto acids or ketoacids are organic compounds that contain a carboxylic acid group and a ketone group. In several cases, the keto group is hydrated. The alpha-keto acids are especially important in biology as they are involved in the Krebs citric acid cycle and in glycolysis.
Maximilian Nierenstein was a professor of biochemistry at the University of Bristol.
Lipoate–protein ligase (EC 2.7.7.63, LplA, lipoate protein ligase, lipoate–protein ligase A, LPL, LPL-B) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP:lipoate adenylyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction










