Vulcanization refers to a range of processes for hardening rubbers. The term originally referred exclusively to the treatment of natural rubber with sulfur, which remains the most common practice. It has also grown to include the hardening of other (synthetic) rubbers via various means. Examples include silicone rubber via room temperature vulcanizing and chloroprene rubber (neoprene) using metal oxides.
N,N-Dimethylaniline (DMA) is an organic chemical compound, a substituted derivative of aniline. It consists of a tertiary amine, featuring dimethylamino group attached to a phenyl group. This oily liquid is colourless when pure, but commercial samples are often yellow. It is an important precursor to dyes such as crystal violet.

p-Phenylenediamine (PPD) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)2. This derivative of aniline is a white solid, but samples can darken due to air oxidation. It is mainly used as a component of engineering polymers and composites like kevlar. It is also an ingredient in hair dyes and is occasionally used as a substitute for henna.
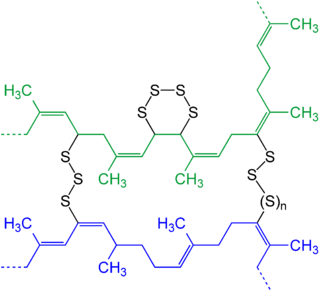
In chemistry and biology a cross-link is a bond that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural polymers.
Accelerants are substances that can bond, mix or disturb another substance and cause an increase in the speed of a natural, or artificial chemical process. Accelerants play a major role in chemistry—most chemical reactions can be hastened with an accelerant. Accelerants alter a chemical bond, speed up a chemical process, or bring organisms back to homeostasis. Accelerants are not necessarily catalysts as they may be consumed by the process.
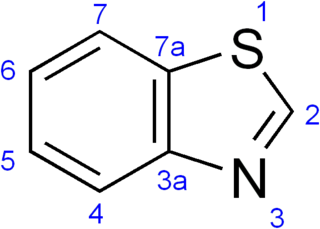
Benzothiazole is an aromatic heterocyclic compound with the chemical formula C
7H
5NS. It is colorless, slightly viscous liquid. Although the parent compound, benzothiazole is not widely used, many of its derivatives are found in commercial products or in nature. Firefly luciferin can be considered a derivative of benzothiazole.

o-Phenylenediamine (OPD) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)2. This aromatic diamine is an important precursor to many heterocyclic compounds. It is isomeric with m-phenylenediamine and p-phenylenediamine.

m-Phenylenediamine, also called 1,3-diaminobenzene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)2. It is an isomer of o-phenylenediamine and p-phenylenediamine. It is a colourless solid.

Thiocarbanilide is an organic chemical compound with the formula (C6H5NH)2CS. This white solid is a derivative of thiourea. It is prepared by the reaction of aniline and carbon disulfide.
A diamine is an amine with exactly two amino groups. Diamines are used as monomers to prepare polyamides, polyimides, and polyureas. The term diamine refers mostly to primary diamines, as those are the most reactive.

Pentanal (also called valeraldehyde) is the organic compound is an alkyl aldehyde, molecular formula C5H10O. It is used in flavorings, resin chemistry, and rubber accelerators. Its smell is described as fermented, bready, fruity, nutty, berry.

tert-Butylamine is an organic chemical compound with the formula (CH3)3CNH2. It is a colorless liquid with a typical amine-like odor. tert-Butylamine is one of the four isomeric amines of butane, the others being n-butylamine, sec-butylamine and isobutylamine.
George Oenslager was a Goodrich chemist who discovered that a derivative of aniline accelerated the vulcanization of rubber with sulfur. He first introduced carbon black as a rubber reinforcing agent in 1912.
David Spence was one of the pioneering rubber chemists. He helped the war effort during the Second World War by devising new ways of extracting natural rubbers from plants, and worked to improve the processing of the rubber. Over the course of his career, he worked to improve the dyeing processes for rubber products and the vulcanization of rubber, and in developing new accelerants for strengthening lower-quality natural rubber. In 1941, he became the first recipient of the Charles Goodyear Medal, awarded by the American Chemical Society.

Dicyclohexylamine is a secondary amine with the chemical formula HN(C6H11)2. It is a colorless liquid, although commercial samples can appear yellow. It has a fishy odor, typical for amines. It is sparingly soluble in water. As an amine, it is an organic base and useful precursor to other chemicals.

2-Mercaptobenzothiazole is an organosulfur compound with the formula C
6H
4(NH)SC=S. It is used in the sulfur vulcanization of rubber.

N-Methyl-2-thiazolidinethione is the organosulfur compound with the formula C2H4S(NCH3)CS. It is classified as a heterocycle called a thiazolidine. It is a colorless or off-white solid. It has gained attention as a proposed low toxicity replacement for ethylenethioureas, which are used as accelerators for the vulcanization of chloroprene rubbers. The compound is prepared by reaction of N-methylethanolamine and carbon disulfide.

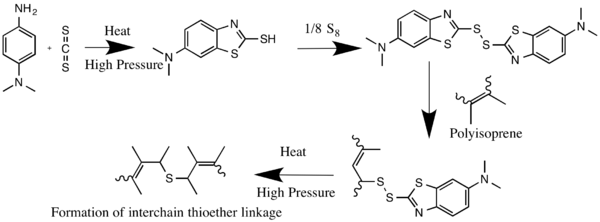
Sulfur vulcanization is a chemical process for converting natural rubber or related polymers into materials of varying hardness, elasticity, and mechanical durability by heating them with sulfur or sulfur-based curatives or accelerators. Sulfur forms cross-linking bridges between sections of polymer chains which affects the mechanical and electronic properties. Many products are made with vulcanized rubber, including tires, shoe soles, hoses, and conveyor belts. The term vulcanization is derived from Vulcan, the Roman god of fire.

6PPD is an organic chemical used as an antiozonant in rubber tires. It is one of several p-phenylenediamine (PPD) additives used to protect various rubber materials. 6PPD is prepared by reductive amination of methyl isobutyl ketone with 4-aminodiphenylamine.
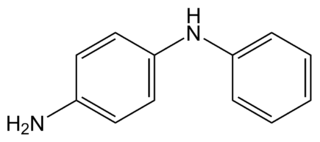
4-Aminodiphenylamine is a diphenylamine with an additional amine substituent. This dimer of aniline has various industrial uses, including as a hair dye ingredient, but also has raised concerns about toxicity by skin contact. It is also a starting material for the synthesis of 6PPD, an antiozonant for various rubber products. A colorimetric test for the quantitative analysis of nitrite, at levels below 100 nanograms per milliliter, is based on nitrite-catalyzed coupling of 4-aminodiphenylamine with N,N-dimethylaniline.