The gastrotrichs, commonly referred to as hairybellies or hairybacks, are a group of microscopic (0.06-3.0 mm), worm-like, pseudocoelomate animals, and are widely distributed and abundant in freshwater and marine environments. They are mostly benthic and live within the periphyton, the layer of tiny organisms and detritus that is found on the seabed and the beds of other water bodies. The majority live on and between particles of sediment or on other submerged surfaces, but a few species are terrestrial and live on land in the film of water surrounding grains of soil. Gastrotrichs are divided into two orders, the Macrodasyida which are marine, and the Chaetonotida, some of which are marine and some freshwater. Nearly 800 species of gastrotrich have been described.

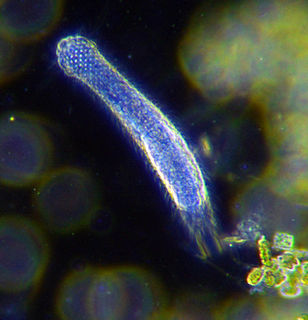
Loricifera is a phylum of very small to microscopic marine cycloneuralian sediment-dwelling animals that had been determined to be 37 described species, in nine genera, but in 2021 has increased to 43 species. Aside from these described species, there are approximately 100 more that have been collected and not yet described. Their sizes range from 100 μm to ca. 1 mm. They are characterised by a protective outer case called a lorica and their habitat is in the spaces between marine gravel to which they attach themselves. The phylum was discovered in 1983 by Reinhardt Kristensen, near Roscoff, France. They are among the most recently discovered groups of Metazoans. They attach themselves quite firmly to the substrate, and hence remained undiscovered for so long. The first specimen was collected in the 1970s, and later described in 1983. They are found at all depths, in different sediment types, and in all latitudes.

Mantophasmatidae is a family of carnivorous wingless insects within the order Notoptera, which was discovered in Africa in 2001. Originally, the group was regarded as an order in its own right, and named Mantophasmatodea, but, using recent evidence indicating a sister group relationship with Grylloblattidae, Arillo and Engel have combined the two groups into a single order, Notoptera.

Disko Island is a large island in Baffin Bay, off the west coast of Greenland. It has an area of 8,578 km2 (3,312.0 sq mi), making it the second largest of Greenland after the main island and one of the 100 largest islands in the world. The name Qeqertarsuaq means The Large Island.

Dudgeonea is a small genus of moths and the only genus of its family, the Dudgeoneidae. It includes six species distributed sparsely across the Old World from Africa and Madagascar to Australia and New Guinea.
Reinhardt Møbjerg Kristensen is a Danish invertebrate biologist, noted for the discovery of three new phyla of microscopic animals: the Loricifera in 1983, the Cycliophora in 1995, and the Micrognathozoa in 2000. He is also considered one of the world's leading experts on tardigrades. His recent field of work revolves mostly around arctic biology.
Heterobathmia is a genus of Lepidoptera. It is the only genus in the suborder Heterobathmiina, as well as in the superfamily Heterobathmioidea and in the family Heterobathmiidae. Primitive, day-flying, metallic moths confined to southern South America, the adults eat the pollen of Nothofagus or southern beech and the larvae mine the leaves. Most known species are undescribed.

Neopseustidae is a small family of day and night-flying "archaic bell moths" in the order Lepidoptera. They are classified into their own superfamily Neopseustoidea and infraorder Neopseustina. Four genera are known. These primitive moths are restricted to South America and Southeast Asia. Their biology is unknown.
Anomoses hylecoetes is a species of primitive hepialoid moth endemic to Queensland and New South Wales, Australia . It is the only species in its genus Anomoses, which is the only genus in the family Anomosetidae.

Choreutidae, or metalmark moths, are a family of insects in the lepidopteran order whose relationships have been long disputed. It was placed previously in the superfamily Yponomeutoidea in family Glyphipterigidae and in superfamily Sesioidea. It is now considered to represent its own superfamily. The relationship of the family to the other lineages in the group "Apoditrysia" need a new assessment, especially with new molecular data.
Prototheora is a genus of moths. It is the only genus of the Prototheoridae, or the African primitive ghost moths, a family of insects in the lepidopteran order, contained in the superfamily Hepialoidea. These moths are endemic to Southern Africa.
Acanthoctesia or "archaic sun moths" is an infraorder of insects in the lepidopteran order, containing a single superfamily, Acanthopteroctetoidea, and a single family, Acanthopteroctetidae. They are currently considered the fifth group up on the comb of branching events in the extant lepidopteran phylogeny. They also represent the most basal lineage in the lepidopteran group Coelolepida characterised in part by its scale morphology. Moths in this superfamily are usually small and iridescent. Like other "homoneurous" Coelolepida and non-ditrysian Heteroneura, the ocelli are lost. There are variety of unique structural characteristics. There are two described genera of these primitive moths. Catapterix was originally described within its own family but Acanthopteroctetes shares with it a number of specialised structural features including similar wing morphology.

Macrodasyida is an order of gastrotrichs. Members of this order are somewhat worm-like in form, and not more than 1 to 1.5 mm in length.

Chaetonotidae is a family of gastrotrichs in the order Chaetonotida. It is the largest family of gastrotrichs with almost 400 species, some of which are marine and some freshwater. Current classification is largely based on shape and external structures but these are highly variable. Molecular studies show a high level of support for a clade containing Dasydytidae nested within Chaetonotidae.

Pliciloricus is a genus of marine organisms Pliciloricidae family, the phylum Loricifera described by Higgins & Kristensen, 1986.

Pliciloricidae are a family of marine organisms in the phylum Loricifera. It contains 23 species in 4 genera.
Rugiloricus is a genus of marine organisms of the phylum Loricifera and the family Pliciloricidae, described by Higgins & Kristensen in 1986.

Diuronotus aspetos is a species of large sized meiofaunal chaetonotid gastrotrich found in the North Atlantic. With Diuronotus rupperti, it is one of the only two species representing the genus Diuronotus.
Batillipes is genus of tardigrades, the only genus in the family Batillipedidae. It was first described by Ferdinand Richters in 1909.
Muselliferidae is a family of worms belonging to the order Chaetonotida.









