The Windows API, informally WinAPI, is Microsoft's core set of application programming interfaces (APIs) available in the Microsoft Windows operating systems. The name Windows API collectively refers to several different platform implementations that are often referred to by their own names ; see the versions section. Almost all Windows programs interact with the Windows API. On the Windows NT line of operating systems, a small number use the Native API.

Windows Virtual PC was a virtualization program for Microsoft Windows. In July 2006, Microsoft released the Windows version free of charge. In August 2006, Microsoft announced the Macintosh version would not be ported to Intel-based Macintosh computers, effectively discontinuing the product as PowerPC-based Macintosh computers would no longer be manufactured.
Microsoft Windows XP Professional x64 Edition, released on April 25, 2005, is an edition of Windows XP for x86-64 personal computers. It is designed to use the expanded 64-bit memory address space provided by the x86-64 architecture.

UltraEdit is a commercial text editor for Microsoft Windows, Linux and OS X created in 1994 by the founder of IDM Computer Solutions Inc., Ian D. Mead, and owned by Idera, Inc. since August 2021. The editor contains tools for programmers, including macros, configurable syntax highlighting, code folding, file type conversions, project management, regular expressions for search-and-replace, a column-edit mode, remote editing of files via FTP, interfaces for APIs or command lines of choice, and more. Files can be browsed and edited in tabs, and it also supports Unicode and hex editing mode.
openCanvas is a raster graphics software developed and published by PGN Corp. It was originally released as freeware in 2000, but moved to a shareware model starting with version 2. All functions are available during the limited demo period. A higher performance version "openCanvas Plus" has been released simultaneously since version 3. Its functions are similar to Adobe Photoshop or Corel Painter.
Microsoft WinHelp is a proprietary format for online help files that can be displayed by the Microsoft Help browser winhelp.exe or winhlp32.exe. The file format is based on Rich Text Format (RTF). It remained a popular Help platform from Windows 3.0 platform through Windows XP. WinHelp was removed in Windows Vista purportedly to discourage software developers from using the obsolete format and encourage use of newer help formats.
PDFCreator is an application for converting documents into Portable Document Format (PDF) format on Microsoft Windows operating systems. It works by creating a virtual printer that prints to PDF files, and thereby allows practically any application to create PDF files by choosing to print from within the application and then printing to the PDFCreator printer.

MediaPortal is an open-source media player and digital video recorder software project, often considered an alternative to Windows Media Center. It provides a 10-foot user interface for performing typical PVR/TiVo functionality, including playing, pausing, and recording live TV; playing DVDs, videos, and music; viewing pictures; and other functions. Plugins allow it to perform additional tasks, such as watching online video, listening to music from online services such as Last.fm, and launching other applications such as games. It interfaces with the hardware commonly found in HTPCs, such as TV tuners, infrared receivers, and LCD displays.
Windows Media Encoder (WME) is a discontinued, freeware media encoder developed by Microsoft which enables content developers to convert or capture both live and prerecorded audio, video, and computer screen images to Windows Media formats for live and on-demand delivery. It is the successor of NetShow Encoder. The download page reports that it is not supported on Windows 7. WME has been replaced by a free version of Microsoft Expression Encoder. The Media 8 Encoding Utility is still listed. WME was available in both 32-bit and 64-bit versions.

Foxit PDF Reader is a multilingual freemium PDF tool that can create, view, edit, digitally sign, and print PDF files. Foxit Reader is developed by Fuzhou, China-based Foxit Software. Early versions of Foxit Reader were notable for startup performance and small file size. Foxit v3.0 was found to be comparable to Adobe Reader. The Windows version allows annotating and saving unfinished PDF forms, FDF import/export, converting to text, highlighting, and drawing. Until version 9.7.2 Foxit Reader had PDF creation features, including a "Foxit PDF Printer" for Windows, allowing all programs to "print" output to PDF; they were removed in May 2020 from later versions. Foxit PDF Reader also includes an Enterprise version, which requires a Foxit account.
Windows Vista—a major release of the Microsoft Windows operating system—was available in six different product editions: Starter, Home Basic, Home Premium, Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate. On September 5, 2006, Microsoft announced the USD pricing for editions available through retail channels; the operating system was later made available to retail on January 30, 2007. Microsoft also made Windows Vista available for purchase and download from Windows Marketplace; it is the first version of Windows to be distributed through a digital distribution platform. Editions sold at retail were available in both Full and Upgrade versions and later included Service Pack 1 (SP1).

Sumatra PDF is a free and open-source document viewer that supports many document formats including: Portable Document Format (PDF), Microsoft Compiled HTML Help (CHM), DjVu, EPUB, FictionBook (FB2), MOBI, PRC, Open XML Paper Specification, and Comic Book Archive file. If Ghostscript is installed, it supports PostScript files. It is developed exclusively for Microsoft Windows.
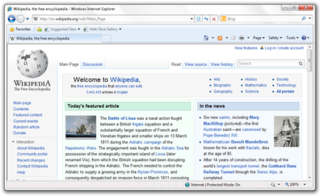
Windows Internet Explorer 8 (IE8) is a web browser for Windows. It was released by Microsoft on March 19, 2009, as the eighth version of Internet Explorer and the successor to Internet Explorer 7. It was the default browser in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 and can replace previous versions of Internet Explorer on Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 but unlike version 7, this version does not support Windows Server 2003 SP1 or an earlier version.
Windows XP, which is the next version of Windows NT after Windows 2000 and the successor to the consumer-oriented Windows Me, has been released in several editions since its original release in 2001.
The K-Lite Codec Pack is a collection of audio and video codecs for Microsoft Windows DirectShow that enables an operating system and its software to play various audio and video formats generally not supported by the operating system itself. The K-Lite Codec Pack also includes several related tools, including Media Player Classic Home Cinema (MPC-HC), Media Info Lite, and Codec Tweak Tool.

Lubuntu is a lightweight Linux distribution based on Ubuntu and uses the LXQt desktop environment in place of Ubuntu's GNOME desktop. Lubuntu was originally touted as being "lighter, less resource hungry and more energy-efficient", but now aims to be "a functional yet modular distribution focused on getting out of the way and letting users use their computer".
FastCopy computer software is a file and directory copier that runs under Microsoft Windows. It was originally open-source, under the GPLv3 license, but later freeware releases reported "Due to various circumstances, distribution of the source code is temporarily suspended".

Linux Lite is a Linux distribution, based on Debian and Ubuntu and created by a team led by Jerry Bezencon. The distribution offers a lightweight desktop experience with a customized Xfce desktop environment. It includes a set of Lite applications to make things easier for a novice Linux user.

4MLinux is a lightweight Linux distribution made for both the 32 bit and 64 bit architectures. It is named "4MLinux" since it has 4 main components of the OS. Maintenance, Multimedia, Miniserver, and Mystery. The distribution is developed in Poland, and was first released in 2010. The distribution does not include a package manager, and uses JWM as its default window manager. It also comes with Conky preinstalled. When installing programs with the distribution, the distribution will retrieve the Windows version rather than the Linux version due to it coming pre-installed with Wine, and not having any package manager. The distribution is geared towards people who prefer a lightweight distribution. There is a version of the distribution called the "4MLinux Game Edition" which provides 90s games natively such as Doom, and Hexen.








