
The Korea Railroad Corporation (Korean: 한국철도공사; Hanja: 韓國鐵道公社, branded as KORAIL, is the national railway operator in South Korea. Currently, KORAIL is a public corporation, managed by Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transportation.

The Gyeongbu line (Gyeongbuseon) is a railway line in South Korea and is considered to be the most important and one of the oldest in the country. It was constructed in 1905, connecting Seoul with Busan via Suwon, Daejeon, and Daegu. It is by far the most heavily travelled rail line in South Korea.
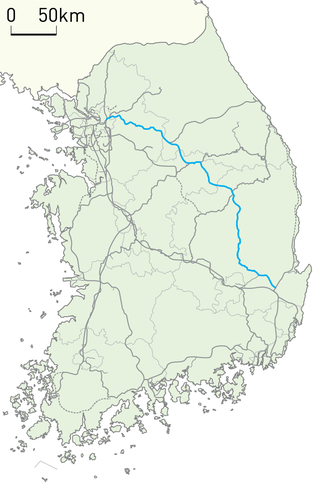
The Jungang line is a railway line connecting Cheongnyangni in Seoul to Moryang in Gyeongju in South Korea, traversing central South Korea from the northwest to the southeast. It is also referred to the rail line of the Seoul Metropolitan Subway from Yongsan station to Jipyeong station. The section from Cheongnyangni to Dodam was designated as a semi-high-speed railway.

The Donghae Nambu Line (Korean: 동해남부선) is a railway line connecting Busan to Pohang in South Korea. The line runs along South Korea's east coast. On December 30, 2016, it was merged into Donghae Line.

The Daegu Line is a railway line in South Korea. The line connects Gacheon station on the Gyeongbu Line in Daegu to Yeongcheon on the Jungang Line. The line is served by frequent passenger trains between Seoul, Dongdaegu, and Gyeongju, Pohang and Ulsan.

The Gyeongui Line is a railway line between Seoul Station and Dorasan Station in Paju. Korail operates the Seoul Metropolitan Subway service between Seoul Station and Dorasan Station.

Korea Train eXpress (Korean: 한국고속철도), often known as KTX, is South Korea's high-speed rail system, operated by Korail. Construction began on the high-speed line from Seoul to Busan in 1992. KTX services were launched on April 1, 2004.

The Gyeongjeon Line (Gyeongjeonseon) is a railway line serving South Gyeongsang and South Jeolla Provinces in South Korea. It covers a total of 300.6 km, from Samnangjin Station in Miryang, South Gyeongsang, to Gwangju Songjeong Station in Gwangju, South Jeolla.

The Donghae Bukbu Line is a former railway line that connected the present-day city of Anbyon in Kangwon Province, North Korea, with Yangyang, Gangwon Province, South Korea. Since the division of Korea it has only carried trains for a brief period during 2007/8. The line originally connected to the Gyeongwon Line running from Gyeongseong to Wonsan.

The Yeongdong Line is a line of Korail. It connects Yeongju in North Gyeongsang Province with Gangneung in Gangwon Province. From Yeongju, it crosses the Taebaek Mountains and reaches the Sea of Japan at Donghae, thence proceeding north to Gangneung.

AREX is a South Korean airport rail link and commuter rail line that links Incheon International Airport with Seoul Station via Gimpo International Airport. The section between the two airports opened on March 23, 2007, and line was extended to Seoul Station on December 29, 2010. Long-distance Korea Train Express high speed trains started to use the line from June 30, 2014, but discontinued service in March 2018 due to low ridership.
Seoul, the capital and largest city in South Korea, accounts for only 0.6% of the country's total land area, yet it is home to around 19% of the population. The population density in Seoul demands a great deal of the city's transportation systems, which are regarded by many as among the best and most advanced in the world. Seoul is very well connected by its subway and bus systems, and the city is also very supportive of pedestrian foot travel. In 2006 it won the Sustainable Transport Award.

The Gyeongbu high-speed railway, also known as Gyeongbu HSR, is South Korea's first high-speed rail line from Seoul to Busan. KTX high-speed trains operate three sections of the line: on 1 April 2004, the first between a junction near Geumcheon-gu Office station, Seoul and a junction at Daejeonjochajang station north of Daejeon, and a second between a junction at Okcheon station, southeast of Daejeon, and a junction near Jicheon station, north of Daegu entered service; then on 1 November 2010, the third section, between a junction west of Daegu and Busan became operational. The missing gaps across the urban areas of Daejeon and Daegu were in construction for an expected opening in 2014, separate tracks into Seoul Station were also planned. The temporary ends of the three sections were connected to the parallel conventional Gyeongbu Line by tracks that will serve as interconnector branches upon the completion of the entire line. On 1 August 2015, construction on urban areas of Daejeon and Daegu were completed; all the sections of HSR line were connected.

Donghae Expressway is an expressway in South Korea, connecting Busan to Sokcho. It is numbered 65 and it is planned to eventually extend all the way along the east coast to Haeundae, Busan. Its current length is 62.1 kilometres (38.6 mi), and It is part of the Asia Highway Route 6.

The Super Rapid Train, often known as SRT, is a high-speed rail service operated by SR Corporation. The service starts at Suseo station in southeast Seoul and terminates at either Busan station or Mokpo station.

Bujeon station is a train station in Busan, South Korea, and located in downtown Seomyeon, Busan. The station is the terminus of the Donghae Line and the Bujeon Line. In addition, KTX trains on the Gyeongbu Line are planned to stop at the station.

Pohang Station is a railway station in the city of Pohang, South Korea. The station is the terminus of the Donghae Line.

National Route 7 is a national highway in South Korea. It connects Busan with Goseong in Gangwon Province. Before the division of the Korean Peninsula, the highway ran until Onsong, North Hamgyong Province, in present-day North Korea.

Sea Train (Korean: 바다열차) was a South Korean tourist train operated by the Korail Tourism Development. The train began operations in 2007 and transports tourists along the eastern coast of South Korea.

The Suseo–Pyeongtaek high-speed railway, also known as Suseo–Pyeongtaek HSR, is a high-speed rail line from Suseo station in southeast Seoul to a junction with the existing Gyeongbu high-speed railway in South Korea. The line was built to ensure southeast Seoul and southern Gyeonggi-do have high-speed rail connections.




















