
Rigging comprises the system of ropes, cables and chains, which support and control a sailing ship or sail boat's masts and sails. Standing rigging is the fixed rigging that supports masts including shrouds and stays. Running rigging is rigging which adjusts the position of the vessel's sails and spars including halyards, braces, sheets and vangs.
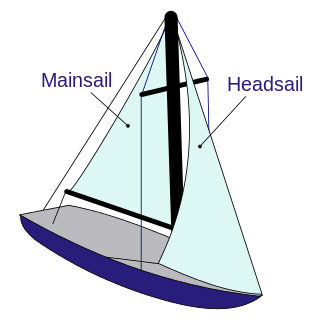
A sailboat or sailing boat is a boat propelled partly or entirely by sails and is smaller than a sailing ship. Distinctions in what constitutes a sailing boat and ship vary by region and maritime culture.

Windsurfing is a wind-propelled water sport that is a combination of sailing and surfing. It is also referred to as "sailboarding" and "boardsailing", and emerged in the late 1960s from the Californian aerospace and surf culture. Windsurfing gained a popular following across Europe and North America by the late 1970s and had achieved significant global popularity by the 1980s. Windsurfing became an Olympic sport in 1984.

A jibe (US) or gybe (Britain) is a sailing maneuver whereby a sailing vessel reaching downwind turns its stern through the wind, which then exerts its force from the opposite side of the vessel. Because the mainsail boom can swing across the cockpit quickly, jibes are potentially dangerous to person and rigging compared to tacking. Therefore, accidental jibes are to be avoided while the proper technique must be applied so as to control the maneuver. For square-rigged ships, this maneuver is called wearing ship.

A traveller is a part of the rigging of a boat or ship that provides a moving attachment point for a rope, sail or yard to a fixed part of the vessel. It may take the form of anything from a simple ring on a metal bar or a spar to, especially in a modern yacht, a more complex "car" – a component with bearing-mounted wheels running on a shaped aluminium extrusion.

In sailing, a cunningham or cunningham's eye is a type of downhaul used on a Bermuda rigged sailboat to change the shape of a sail. It is named after its inventor, Briggs Cunningham, a victorious America's Cup skipper and yacht builder.

Running rigging is the rigging of a sailing vessel that is used for raising, lowering, shaping and controlling the sails on a sailing vessel—as opposed to the standing rigging, which supports the mast and bowsprit. Running rigging varies between vessels that are rigged fore and aft and those that are square-rigged.

In sailing, a boom is a spar (pole), along the of a fore and aft rigged sail, that greatly improves control of the angle and shape of the sail. The primary action of the boom is to keep the foot flatter when the sail angle is away from the centerline of the boat. The boom also serves as an attachment point for more sophisticated control lines. Because of the improved sail control it is rare to find a non-headsail without a boom, but lateen sails, for instance, are loose-footed. In some modern applications, the sail is rolled up into the boom for storage or reefing.

A guy is a line (rope) attached to and intended to control the end of a spar on a sailboat. On a modern sloop-rigged sailboat with a symmetric spinnaker, the spinnaker pole is the spar most commonly controlled by one or more guys.
A running backstay is a rigging component on a sailboat which helps support the mast. A running backstay runs from each lateral corner of the stern to the mast at the level where the forestay begins in the fractional rig. Because they are attached low on the mast, they can present a significant problem in an accidental gybe, as the boom hits the stay, with the possibility of breaking the boom, mast, or both.

An outhaul is a control line found on a sailboat. It is an element of the running rigging, used to attach the mainsail clew to the boom and tensions the foot of the sail. It commonly uses a block at the boom end and a cleat on the boom, closer to the mast, to secure the line.

A deadeye is an item used in the standing and running rigging of traditional sailing ships. It is a smallish round thick wooden disc with one or more holes through it, perpendicular to the plane of the disc. Single and triple-hole deadeyes are most commonly seen. The three-holed blocks were called deadeyes because the position of the three holes resemble the eye and nose sockets of a sheep's skull.

A spinnaker pole is a spar used in sailboats to help support and control a variety of headsails, particularly the spinnaker. It is also used with other sails, such as genoas and jibs, when sailing downwind with no spinnaker hoisted, sometimes using a special light spinnaker pole called a whisker pole, possible since the load on the pole is very light on this point of sail.

The junk rig, also known as the Chinese lugsail, Chinese balanced lug sail, or sampan rig, is a type of sail rig in which rigid members, called battens, span the full width of the sail and extend the sail forward of the mast. While relatively uncommon in use among modern production sailboats, the rig's advantages of easier use and lower maintenance for blue-water cruisers have been explored by individuals such as trans-Atlantic racer Herbert "Blondie" Hasler and author Annie Hill.

An asymmetrical spinnaker is a sail used when sailing between about 90 and 165 degrees from the angle of the wind. Also known as an "asym", "aspin", or "A-sail" it can be described as a cross between a genoa jib and a spinnaker. It is asymmetric like a genoa, but like a spinnaker, its luff is unstructured; its leading edge is allowed to float freely, unencumbered by an internal wire or hanks attaching it to a stay. Unlike a symmetric spinnaker, the asymmetric does not require a spinnaker pole, since it is fixed (tacked) to the bow or bowsprit. The asymmetrical spinnaker has a larger camber than a genoa and a Spinnaker Mid-Gerth (SMG) -- also called Spinnaker Half Width (SHW) -- measurement greater than the length of its foot.

Dismasting, also called demasting, occurs to a sailing ship when one or more of the masts responsible for hoisting the sails that propel the vessel breaks. Dismasting usually occurs as the result of high winds during a storm acting upon masts, sails, rigging, and spars.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to sailing:
The Herreshoff 31, also called the Cat Ketch 31, is an American sailboat that was designed by Halsey Chase Herreshoff as a cruiser and first built in 1979.
A solent refers to a sail and rigging system on sailboats, typically sloops. Sailors, particularly British sailors, often refer to a 100% jib as a Solent, because its smaller size is preferable when sailing in the strong winds found in the Solent between the Isle of Wight and Britain. The common use of roller-furling headsails, or genoas, on modern cruising yachts allows the jib to be reduced in size, but partially-furled sails lack the efficiency of a sail that is actually cut to a smaller size. Accordingly, it is preferable to fly a separate, smaller jib—the solent—instead.
The Nacra 5.2 is an American catamaran sailing dinghy that was designed by Tom Roland as a one-design racer and first built in 1975. Other than the small production run Nacra 36, the Nacra 5.2 was the first Nacra brand boat and established its reputation.














