
Soju is a clear and colorless Korean distilled alcoholic beverage. It is usually consumed neat. Its alcohol content varies from about 12.9% to 53% alcohol by volume (ABV), although since 2007 low alcohol soju below 20% has become more popular.

There is a long history of alcoholic drinks in China. They include rice and grape wine, beer, whisky and various liquors including baijiu, the most-consumed distilled spirit in the world.

Drinking culture is the set of traditions and social behaviors that surround the consumption of alcoholic beverages as a recreational drug and social lubricant. Although alcoholic beverages and social attitudes toward drinking vary around the world, nearly every civilization has independently discovered the processes of brewing beer, fermenting wine and distilling spirits.

Shotgunning is a means of consuming a beverage, especially beer, very quickly by punching a hole in the side of the can, near the bottom, placing the mouth over the hole, and pulling the tab to open the top. The beverage quickly drains, and is quickly consumed.

Korean cuisine has a wide variety of traditional alcoholic drinks, known as sul (술). Many of these drinks end with the Sino-Korean word -ju, and some end with the native Korean word -sul. The Sino-Korean -ju is not used as an independent noun.

Purposeful production of alcoholic drinks is common and often reflects cultural and religious peculiarities as much as geographical and sociological conditions.
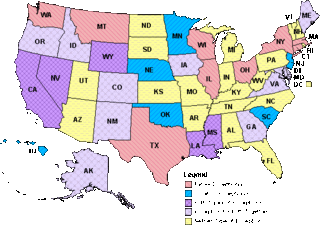
Although the minimum legal age to purchase alcohol is 21 in all U.S. states and most territories, the legal details for consumption vary greatly. Although some states completely ban alcohol usage for people under 18, the majority have exceptions that permit consumption.

Anju is a Korean term for food consumed with alcohol. It consists of a variety of foods, including both main dishes and side dishes. Consuming food with alcohol is a widespread practice in Korea, especially when the alcoholic beverage soju is involved.
An alcoholic beverage is a drink that contains ethanol, a type of alcohol and is produced by fermentation of grains, fruits, or other sources of sugar. The consumption of alcoholic drinks, often referred to as "drinking", plays an important social role in many cultures. Alcoholic drinks are typically divided into three classes—beers, wines, and spirits—and typically their alcohol content is between 3% and 50%.

Binge drinking, or heavy episodic drinking, is drinking alcoholic beverages with an intention of becoming intoxicated by heavy consumption of alcohol over a short period of time, but definitions vary considerably.

Alcohol is commonly consumed and available at pubs and liquor stores in Australia – all of which are private enterprises. Spirits can be purchased at liquor stores and pubs, whereas most grocery stores do not sell them, although they may have separate liquor stores on their premises. Alcohol consumption is higher, according to WHO studies, than in most European countries and several Central Asian and African countries, although consumption is just as high in Australia as in North America. After tobacco, alcohol is the second leading preventable cause of death and hospitalisation in Australia.
Binge drinking is the practice of consuming excessive amounts of alcohol in a short period of time. Due to the idiosyncrasies of the human body, the exact amount of alcohol that would constitute binge drinking differs among individuals. The definitions of binge drinking are also nuanced across cultures and population subgroups. For example, many studies use gender-specific measures of binge drinking. The epidemiology of binge drinking likewise differs across cultures and population subgroups.
The legal drinking age varies from country to country. In the United States, the legal drinking age is currently 21. To curb excessive alcohol consumption by younger people, instead of raising the drinking age, other countries have raised the prices of alcohol beverages and encouraged the general public to drink less. Setting a legal drinking age of 21 is designed to discourage reckless alcohol consumption by youth, limiting consumption to those who are more mature, who can be expected to make reasonable and wise decisions when it comes to drinking.

Poktanju translated literally as "bomb liquor" or "bomb shot", is a cocktail that is made by mixing soju or whiskey and beer. A poktanju consists of a shot glass of soju or whiskey dropped into a pint of beer; it is drunk quickly. It is considered to be a ritual drinking activity among office workers, friends, and colleagues. Other possible names for poktanju are boilermaker, bomb shot, bomb drink, somaek, or maekju.

North Korea has at least ten major breweries and many microbreweries that supply a wide range of beer products. The top brand is the light lager Taedonggang by the state-owned Taedonggang Brewing Company.

North Korean cuisine is the traditional culinary practices and dishes of North Korea. Its foundations are laid by the agricultural and nomadic traditions in southern Manchuria and the Korean Peninsula. Some dishes are shared by the two Koreas; however, availability and quality of Northern cuisine is much more significantly affected by sociopolitical class divides.

Many students attending colleges, universities, and other higher education institutions consume alcoholic beverages. The laws and social culture around this practice vary by country and institution type, and within an institution, some students may drink heavily whereas others may not drink at all. In the United States, drinking tends to be particularly associated with fraternities.

Alcohol in the United Kingdom is legal to buy, sell and consume. Consumption rates within the country are high among the average of OECD nations however average among European countries but consistently ranks highest on binge drinking culture. An estimated 29 million people in the United Kingdom drank alcohol in 2017.

Street Alcohol Fighter, often abbreviated as SAF is a South Korean variety web show hosted by South Korean singer-songwriter and presenter Kim Hee-chul. The program aired every Thursday at 8 pm KST on YouTube. The primary notion is that celebrities are interviewed by Kim while consuming alcoholic beverages.






















