Related Research Articles
The Adamawa languages are a putative family of 80–90 languages scattered across the Adamawa Plateau in Central Africa, in northern Cameroon, north-western Central African Republic, southern Chad, and eastern Nigeria, spoken altogether by only one and a half million people. Joseph Greenberg classified them as one branch of the Adamawa–Ubangi family of Niger–Congo languages. They are among the least studied languages in Africa, and include many endangered languages; by far the largest is Mumuye, with 400,000 speakers. A couple of unclassified languages—notably Laal and Jalaa—are found along the fringes of the Adamawa area.

Bata (Gbwata) is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Nigeria in Adamawa State in the Numan, Song, Fufore and Jimeta gire Yola maiha Demsa lamorde LGAs, and in Cameroon in North Province along the border with Nigeria. Dialects are Demsa, Garoua, Jirai, Kobotachi, Malabu, Ndeewe, Ribaw, Wadi, and Zumu (Jimo). It is often considered the same language as Bacama.
Nzanyi is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Nigeria in Adamawa State in Maiha LGA, and along the border in Cameroon. Dialects are Dede, Hoode, Lovi, Magara, Maiha, Mutidi, Nggwoli, Paka, and Rogede.
The Nimbari language, which is no longer spoken, was a member of the Leko–Nimbari group of Savanna languages. It was spoken in northern Cameroon. Ethnologue lists Badjire, Gorimbari, and Padjara-Djabi villages as Nimbari locations in Bénoué and Mayo-Louti divisions.
The Duru languages are a group of Savanna languages spoken in northern Cameroon and eastern Nigeria. They were labeled "G4" in Joseph Greenberg's Adamawa language-family proposal.
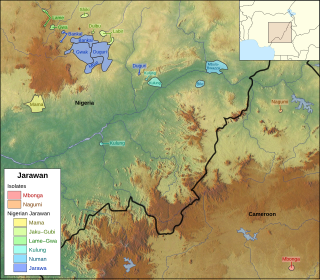
Jarawan is a group of languages spoken mostly in Bauchi State, Nigeria, with some also scattered in Plateau State, Taraba State, and Adamawa State in the same country. Two related languages formerly spoken in Cameroon are now extinct but are believed to have belonged to the group. This connection between Nigerian and Cameroonian Jarawan is attributed to Thomas (1925). Whether Jarawan languages are best classified alongside other Bantu languages or among non-Bantu Bantoid languages is a matter of ongoing debate. A number of descriptions and classifications in the early 20th century suggest that they be may historically related to Bantu languages but not necessarily Bantu themselves. Other perspectives based on lexicostatistic modeling and other phylogenetic techniques for language comparison argue instead that Jarawan languages are properly classified alongside Zone A Bantu languages (A31-A40-A60). For classifications based on these more recent studies, see for example Blench (2006), Piron (1997), and Grollemund (2012).
The Gwèri or Vere language Were also known as Kobo or Mom Jango, is a member of the Duru branch of Savanna languages. It is spoken across the northern Nigerian–Cameroonian border.
Chamba Leko is one of two languages spoken by the Chamba people, the other being Chamba Daka. It is a member of the Leko branch of Savanna languages, and is spoken across the northern Nigerian–Cameroonian border.
Oblo is a poorly attested, unclassified, and possibly extinct language of northern Cameroon. It is, or was, spoken in a tiny area including Gobtikéré, Ouro Bé, and Ouro Badjouma, in Pitoa, Bénoué Department.
The Koma language is a language cluster belonging to the Duru branch of Savannas languages of Cameroon. Blench (2004) includes three varieties separated in Ethnologue, Koma Ndera, Gɨmne, and Gɨmnɨme; within Koma Ndera, speakers of the marginal dialects, Gomnome and Ndera, can scarcely understand one another, though both understand the central dialect, Gomme.
Mundang is an Mbum language of southern Chad and northern Cameroon.
Pana is an Mbum language of the Central African Republic. A few thousand speak it in southern Chad and northern Cameroon. A dialect in Cameroon, Man, may be a separate language. Blench (2004) leaves Pondo and Gonge in CAR unclassified within the Mbum languages.
Doyayo is a language of the Duru branch of Adamawa languages spoken in Cameroon.
Kutin is a member of the Duru branch of Savanna languages. Most Nigerian speakers moved to Cameroon when the Gashaka-Gumti National Park was established.
The Dii language is a dialect cluster in the Duru branch of Savanna languages. Yag Dii is the ethnonym.
Kolbila is an Adamawa language of Cameroon and Nigeria.
Longto, or Voko (Woko), is a member of the Duru branch of Savanna languages that is spoken in Poli Subdivision of Faro Department, Cameroon.
Karang language is an Mbum language of Cameroon and Chad.
Mono is a moribund Mbum language spoken by older adults in northern Cameroon.
Kali is a presumably moribund Mbum language of northern Cameroon or the Central African Republic.
References
- ↑ Duli at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Gey". Glottolog 3.0 . Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Strümpell, F. 1922/23. 'Wörterverzeichnis der Heidensprachen des Mandaragebirges', Zeitschrift für Eingeborenensprachen 13: 47-75, 109-149.
- ↑ Boyd, Raymond. 1989. Adamawa-Ubangi. - in: Bendor-Samuel, John. (ed.) The Niger-Congo languages. Lanham - New York - London: Summer Institute of Linguistics; 178-215.
- ↑ Kleinewillinghöfer, Ulrich. 2015. Duli – Gewe (Gueve, Gey). Adamawa Languages Project.
- 1 2 Binam Bikoi, Charles, ed. (2012). Atlas linguistique du Cameroun (ALCAM)[Linguistic Atlas of Cameroon]. Atlas linguistique de l'Afrique centrale (ALAC) (in French). Vol. 1: Inventaire des langues. Yaoundé: CERDOTOLA. ISBN 9789956796069.
- Roger Blench, 2004. List of Adamawa languages (ms)