Related Research Articles
The Adamawa languages are a putative family of 80–90 languages scattered across the Adamawa Plateau in central Africa, in Nigeria, Cameroon, Central African Republic, and Chad, spoken altogether by only one and a half million people. Joseph Greenberg classified them as one branch of the Adamawa–Ubangi family of Niger–Congo languages. They are among the least studied languages in Africa, and include many endangered languages; by far the largest is Mumuye, with 400,000 speakers. A couple of unclassified languages—notably Laal and Jalaa—are found along the fringes of the Adamawa area.

There are over 525 native languages spoken in Nigeria. The official language of Nigeria is English, the language of former colonial British Nigeria. As reported in 2003, Nigerian English and Nigerian Pidgin were spoken as a second language by 100 million people in Nigeria. Communication in the English language is much more popular in the country's urban communities than it is in the rural areas, due to globalization.
Ga is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken by about 500,000 people in the Gombi Local Government Area in Adamawa state of Nigeria. Many speakers live across the length and breath of Nigeria. It has three dialects, Ga'anda, Gabun and Boga; Blench (2006) classifies Gabun is a separate language. Its speakers are generally not monolingual in Ga'anda, instead, they use Hausa, Lala, Hona, Kilba, Fulfulde, and Bura. Ga'anda has a rich cultural heritage, its natives are very hospitable people. 70% of its population are Christians, 20% Muslims and 10% Traditionalists.
The Savannas languages, also known as Gur–Adamawa or Adamawa–Gur, is a branch of the Niger–Congo languages that includes Greenberg's Gur and Adamawa–Ubangui families.
Longuda (Nʋngʋra) is a Niger–Congo language of Nigeria. Joseph Greenberg counted it as a distinct branch, G10, of his Adamawa family. Boyd (1989) assigned it a branch within Waja–Jen. When Blench (2008) broke up Adamawa, Longuda was made a branch of the Bambukic languages.
The Tula–Waja, or Tula–Wiyaa languages are a branch of the provisional Savanna languages, closest to Kam (Nyingwom), spoken in northeastern Nigeria. They are spoken primarily in southeastern Gombe State and other neighbouring states.
The Leko languages are a small group of languages spoken in northern Cameroon and eastern Nigeria. They were labeled "G2" in Joseph Greenberg's Adamawa language-family proposal. The Duru languages are frequently classified with the Leko languages, although their relationship remains to be demonstrated.
The Mumuye–Yendang languages are a proposed group of Savanna languages spoken in eastern Nigeria. They were labeled "G5" in Joseph Greenberg's Adamawa language-family proposal.
The Mumuye languages are a group of Adamawa languages spoken in Taraba State, eastern Nigeria.
The Duru languages are a group of Savanna languages spoken in northern Cameroon and eastern Nigeria. They were labeled "G4" in Joseph Greenberg's Adamawa language-family proposal.

The Jukunoid languages are a branch of the Benue-Congo languages spoken by the Jukun and related peoples of Nigeria and Cameroon. They are distributed mostly throughout Taraba State, Nigeria and surrounding regions.
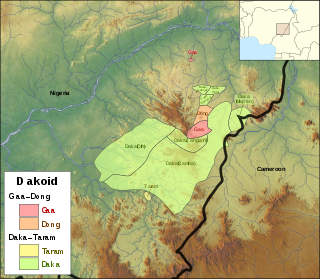
The Dakoid languages are a branch of the Northern Bantoid languages spoken in Taraba and Adamawa states of eastern Nigeria.
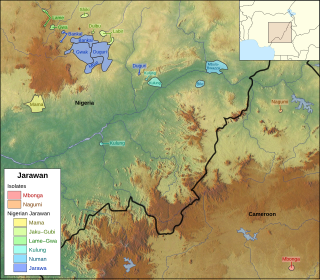
Jarawan is a group of Bantu languages spoken mostly in Bauchi State, Nigeria, with some also scattered in Taraba State and Adamawa State in the same country. Two related languages formerly spoken in Cameroon are now extinct but are believed to belong to the group.
Kwah (Kwa), also known as Baa (Bàː), is a Niger–Congo language of uncertain affiliation; the more it has been studied, the more divergent it appears. Joseph Greenberg counted it as one of the Bambukic languages of the Adamawa family. Boyd (1989) assigned it its own branch within Waja–Jen. Kleinewillinghöfer (1996) removed it from Waja–Jen as an independent branch of Adamawa. When Blench (2008) broke up Adamawa, Kwah became a provisional independent branch of his larger Savannas family.
Mboi is an Adamawa language of Nigeria. Its name is that of one of its dialects, the other two being Banga and Handa. These are rather divergent, Blench (2004) considers them to be distinct languages.
Bali is a Niger–Congo language spoken by 100,000 people in Demsa, Adamawa, Nigeria.
Kpasam is an Adamawa language of Demsa LGA, Adamawa State, Nigeria.
Kugama, also known as Wam (Wã̀m) or Gengle, is an Adamawa language of Nigeria. It is spoken in Mayo-Belwa and Fufore Local Government Areas of Adamawa State. It is classified within the Yendang group of the Adamawa language family.
The Bena–Mboi (Ɓəna–Mboi) a.k.a.Yungur languages form a branch of the Adamawa family. They are spoken in central Adamawa State, eastern Nigeria, just to the east of Lafia LGA.
The Bikwin–Jen or simply the Jen languages form a branch of the Adamawa family. They are spoken in and around Karim Lamido LGA in Taraba State, and in other nearby states of eastern Nigeria.
References
- ↑ Blench, Roger. 2009. The Maya (Yendang) languages.
- ↑ Blench, Roger (2019). An Atlas of Nigerian Languages (4th ed.). Cambridge: Kay Williamson Educational Foundation.
- Roger Blench, 2004. List of Adamawa languages (ms)
![]() This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 3.0 license.
This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 3.0 license.