
The Cemetery H culture was a Bronze Age culture in the Punjab region in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, from about 1900 BCE until about 1300 BCE. It is regarded as a regional form of the late phase of the Harappan civilisation, but also as the manifestation of a first wave of Indo-Aryan migrations, predating the migrations of the proto-Rig Vedic people.

The Vardar or Axios is the longest river in North Macedonia and a major river in Greece, where it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is 388 km (241 mi) long, out of which 76 km (47 mi) are in Greece, and drains an area of around 25,000 km2 (9,653 sq mi). The maximum depth of the river is 4 m (13 ft).
James Patrick Mallory is an American archaeologist and Indo-Europeanist. Mallory is an emeritus professor at Queen's University, Belfast; a member of the Royal Irish Academy, and the former editor of the Journal of Indo-European Studies and Emania: Bulletin of the Navan Research Group (Belfast).
Douglas Quentin Adams is an American linguist, professor of English at the University of Idaho and an Indo-European comparativist. He studied at the University of Chicago, earning PhD in 1972. Adams is an expert on Tocharian and a contributor on this subject to the Encyclopædia Britannica.

The Globular Amphora culture (GAC, German: Kugelamphoren-Kultur ; c. 3400–2800 BC, is an archaeological culture in Central Europe. Marija Gimbutas assumed an Indo-European origin, though this is contradicted by newer genetic studies that show a connection to the earlier wave of Early European Farmers rather than to Western Steppe Herders from the Ukrainian and south-western Russian steppes.

Novotitarovskaya culture, was a Bronze Age archaeological culture which flourished in the North Caucasus ca. 3300–2700 BC.
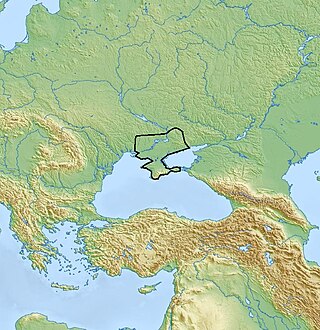
Kemi Oba culture, ca. 3700—2200 BC, an archaeological culture at the northwest face of the Sea of Azov, the lower Bug and Dnieper Rivers and the Crimea. The Kemi Oba culture is contemporaneous and partly overlapping with the Catacomb culture.
The king and the god is the title of a short dialogue composed in the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European language. It is loosely based on the "King Harishchandra" episode of Aitareya Brahmana (7.14). S. K. Sen asked a number of Indo-Europeanists to reconstruct the PIE "parent" of the text.

Worship or deification of fire, or fire rituals, religious rituals centred on a fire, are known from various religions. Fire has been an important part of human culture since the Lower Paleolithic. Religious or animist notions connected to fire are assumed to reach back to such early prehuman times.

Proto-Iranian or Proto-Iranic is the reconstructed proto-language of the Iranian languages branch of Indo-European language family and thus the ancestor of the Iranian languages such as Persian, Pashto, Sogdian, Zazaki, Ossetian, Mazandarani, Kurdish, Talysh and others. Its speakers, the hypothetical Proto-Iranians, are assumed to have lived in the 2nd millennium BC and are usually connected with the Andronovo archaeological horizon.

Proto-Armenian is the earlier, unattested stage of the Armenian language which has been reconstructed by linguists. As Armenian is the only known language of its branch of the Indo-European languages, the comparative method cannot be used to reconstruct its earlier stages. Instead, a combination of internal and external reconstruction, by reconstructions of Proto-Indo-European and other branches, has allowed linguists to piece together the earlier history of Armenian.

Horse sacrifice is the ritual killing and offering of a horse, usually as part of a religious or cultural ritual. Horse sacrifices were common throughout Eurasia with the domestication of the horse and continuing up until the spread of Abrahamic religions, or in some places like Mongolia, of Buddhism. The practice is rarely observed in some cultures even today.
Sobiesław, Soběslav or Sebeslav is a very old Slavic given name, mostly common among the West Slavs. Because of folk etymology, it is popularly supposed to derive from sobie and sław ; however, it is actually derived from a Proto-Indo-European name meaning "wise-famous", cognate with Sophocles. The feminine form is Sobiesława/Soběslava/Собѧслава.

Latvian pottery or Latvian ceramics is one of the country's oldest art forms, dating back to the Neolithic. The best-known subset of Latvian pottery is Latgalian pottery. The eastern region of Latgale is the most prolific producer of wares.

The North European hypothesis was a linguistic and archaeological theory that tried to explain the spread of the Indo-European languages in Europe and parts of Asia by locating the original homeland (Urheimat) in southern Scandinavia or in the North German Plain. This hypothesis, advanced by Karl Penka, Hermann Hirt, Gustaf Kossinna and others, had some success in the late 19th century and the early 20th century, and was endorsed by Nazism, but is today considered outdated by the majority of the academics, who tend to favor the Kurgan hypothesis.

The Mikhaylovka culture, Lower Mykhaylivka culture is a Copper Age archaeological culture which flourished on the Pontic steppe from 3600 BC to 3000 BC.

The Vakhsh culture is a Bronze Age culture which took place around 2500-1650 BC, as shown by radiocarbon dates, and flourished along the lower Vakhsh River in southern Tajikistan, earlier thought to be from ca. 1700 BC to 1500 BC.
The Dieva Dēli are heavenly beings depicted as the sons of the sky-god Dievs in Latvian mythology.














